BFS、DFS以及Dijkstra算法 python实现
注:全文参考正月点灯笼b站up主!!
BFS:广度优先搜索,队列,先进先出;
DFS:深度优先搜索,栈, 先进后出;
Dijkstra:最短路径问题;
1、BFS和DFS
graph = {
"A" : ["B","C"],
"B" : ["A","C","D"],
"C" : ["A","B","D","E"],
"D" : ["B","C","E","F"],
"E" : ["C","D"],
"F" : ["D"]
}
def BFS(graph, s):
deque = [s]
seen = set()
seen.add(s)
while deque:
vertex = deque.pop(0)
nodes = graph[vertex]
for x in nodes:
if x not in seen:
deque.append(x)
seen.add(x)
print(vertex)
def DFS(graph, s):
stack = [s]
seen = set()
seen.add(s)
while stack:
vertex = stack.pop()
nodes = graph[vertex]
for x in nodes:
if x not in seen:
stack.append(x)
seen.add(x)
print(vertex)2、Dijkstra
import heapq
import math
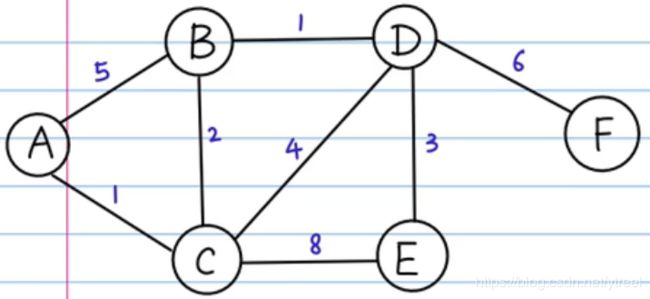
graph = {
"A" : {"B":5, "C":1},
"B" : {"A":5, "C":2, "D":1},
"C" : {"A":1, "B":2, "D":4, "E":8},
"D" : {"B":1, "C":4, "E":3 ,"F":6},
"E" : {"C":8, "D":3},
"F" : {"D":6}
}
def init_distance(graph, s):
distance = {s:0}
for x in graph.keys():
if x != s:
distance[x] = math.inf
return distance
def Dijkstra(graph, s):
pqueue = []
heapq.heappush(pqueue, (0,s))
seen = set()
parent = {s:None}
distance = init_distance(graph, s)
while pqueue:
pair = heapq.heappop(pqueue)
dist = pair[0]
vertex = pair[1]
seen.add(vertex)
nodes = graph[vertex].keys()
for x in nodes:
if x not in seen:
if dist + graph[vertex][x] < distance[x]:
heapq.heappush(pqueue, (dist + graph[vertex][x], x))
parent[x] = vertex
distance[x] = dist + graph[vertex][x]
return parent, distance
parent, distance = Dijkstra(graph, "A")
print(parent)
print(distance)