最短路径之弗洛伊德算法
本文将讲解图中最短路径的求解算法之弗洛伊德算法。
在我的上一篇博客http://blog.csdn.net/yz930618/article/details/77941011中,讲解了求解最短路径的一种算法迪杰斯特拉算法。迪杰斯特拉算法是求某个顶点到其余顶点的最短路径,而本文所要讲的弗洛伊德算法则是所有顶点到所有顶点的最短路径,弗洛伊德算法十分精妙,仅通过少量代码就能实现该功能。
弗洛伊德算法原理
由于是求所有顶点到所有顶点的最短路径,所以所存储的P和D都是二维数组,其中,D表示顶点到顶点的最短路径权值之和的矩阵,P表示对应顶点的最小路径的前驱矩阵。
首先,进行初始化操作:
- D矩阵初始化为图的邻接矩阵
- P矩阵的每一行都相同,每行的值均为从0按列增加
弗洛伊德算法有三层循环:
- 第一层循环:依次将每个顶点作为中转顶点,记为Vk;
- 第二层和第三层循环:遍历所有顶点的连线情况。设Vs代表起始顶点,Ve代表结束顶点。循环内所做的操作为:判断D[Vs][Ve]与D[Vs][Vk]+D[Vk][Ve]的大小,令D[Vs][Ve]=min{D[Vs][Ve], D[Vs][Vk]+D[Vk][Ve]},并且将P矩阵对应的P[Vs][Ve]和P[Ve][Vs]修改为当前中转顶点的下标k。通俗来说,如果D[Vs][Ve] > D[Vs][Vk]+D[Vk][Ve],则说明顶点Vs直接到顶点Ve的距离大于先从Vs到Vk,然后再从Vk到Ve的矩阵。所以,两者取距离较短的那个。
弗洛伊德算法实现
下面是利用Java实现的弗洛伊德算法。
/**
* 弗洛伊德算法求最短路径
*/
public class Floyd {
int[][] arc; // 邻接矩阵
int MAXVEX; // 顶点个数
int INFINITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 权值最大值
int[][] pathMatrix; // 用于存储最短路径下标的数组
int[][] shortPathTable; // 用于存储到各点最短路径的权值和
public Floyd(int index){
MAXVEX = index;
createArc(); // 生成邻接矩阵
createPathMatrix(); // 生成pathMatrix
createShortPathTable();// 生成shortPathTable
}
// 生成pathMatrix
private void createPathMatrix() {
pathMatrix = new int[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
for(int v = 0;v < MAXVEX;v++){
for(int w = 0;w < MAXVEX;w++){
pathMatrix[v][w] = w;
}
}
}
// 生成shortPathTable
private void createShortPathTable() {
shortPathTable = new int[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
for(int v = 0;v < MAXVEX;v++){
for(int w = 0;w < MAXVEX;w++){
shortPathTable[v][w] = arc[v][w];
}
}
}
// 生成邻接矩阵
private void createArc() {
arc = new int[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
this.arc[0] = new int[]{ 0, 1, 5,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY};
this.arc[1] = new int[]{ 1, 0, 3, 7, 5,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY};
this.arc[2] = new int[]{ 5, 3, 0,INFINITY, 1, 7,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY};
this.arc[3] = new int[]{INFINITY, 7,INFINITY, 0, 2,INFINITY, 3,INFINITY,INFINITY};
this.arc[4] = new int[]{INFINITY, 5, 1, 2, 0, 3, 6, 9,INFINITY};
this.arc[5] = new int[]{INFINITY,INFINITY, 7,INFINITY, 3, 0, INFINITY, 5, INFINITY};
this.arc[6] = new int[]{INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY, 3, 6,INFINITY, 0, 2, 7};
this.arc[7] = new int[]{INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY, 9, 5, 2, 0, 4};
this.arc[8] = new int[]{INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY,INFINITY, 7, 4, 0};
}
// Floyd算法,求有向图的所有顶点到所有顶点的最短路径及带权长度
void ShortPath_Floyd(){
for(int k = 0;k < MAXVEX;k++){
for(int v = 0;v < MAXVEX;v++){
for(int w = 0;w < MAXVEX;w++){
if(shortPathTable[v][k] != INFINITY && shortPathTable[k][w] != INFINITY && (shortPathTable[v][w] > (shortPathTable[v][k] + shortPathTable[k][w]))){
shortPathTable[v][w] = shortPathTable[v][k] + shortPathTable[k][w];
pathMatrix[v][w] = pathMatrix[v][k];
}
}
}
}
}
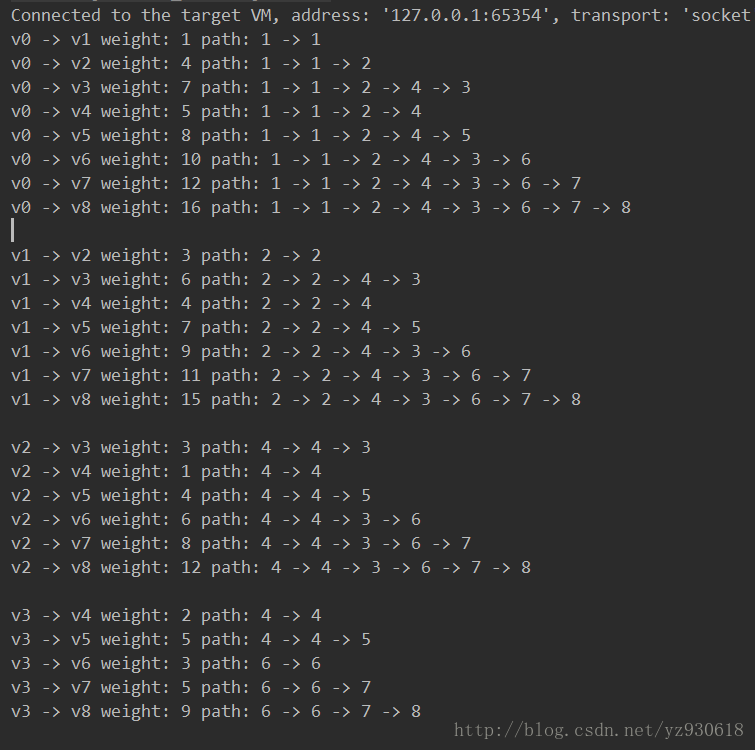
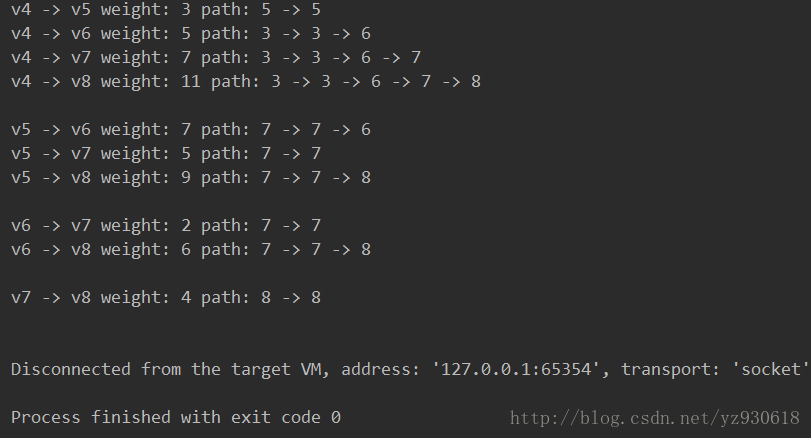
public static void main(String[] args) {
Floyd floyd = new Floyd(9);
floyd.ShortPath_Floyd();
for(int v = 0;v < 9;v++){
for(int w = v+1;w < 9;w++){
System.out.print("v"+v+" -> v"+w+" weight: "+ floyd.shortPathTable[v][w]);
int k = floyd.pathMatrix[v][w]; //获得第一个路径顶点的下标
System.out.print(" path: "+k);
while (k != w){ //如果路径顶点下标不是终点
System.out.print(" -> "+k);
k = floyd.pathMatrix[k][w]; //获得下一个路径顶点下标
}
System.out.println(" -> " + w);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}结果如下