基于FPGA的AXI协议讲解(2)
基于FPGA的AXI_Full协议讲解
- 参考文献
- 项目简述
- AXI_Full读协议
- VIVADO建立AXI4_Full IP
- AXI_Full读项目
- AXI_Full读协议代码
- PS端代码
- 下板测试
- AXI_Full写项目
- AXI_Full写协议代码
- PS端代码
- 下板测试
- 总结
参考文献
[1]、V3学院
项目简述
前一篇文章我们已经进行讲解了AXI_Lite协议,该协议的突发长度是1,在工程中主要起的作用是配置寄存器。 在FPGA中最常见的就是大数据的传输,一般我们使用AXI_Full协议来进行数据的传输。这篇文章我们主要讲解使用AXI_Full协议来进行ZYNQ端的DDR3的读写,当然如果不是ZYNQ该工程同样是可以使用的,甚至不需要做什么修改。米联客的FDMA说白了就是一个AXI_Full的总线协议。Xilinx中的AXI_Full总线的数据位宽可以是64位,最大突发长度是256,每次突发最大2048个字节,由此可见该协议的数据传输速率是相当快的。
本次实验所用到的软硬件环境如下:
1、VIVADO 2019.1
2、米联客MZ7015FA开发板
本篇文章主要讲解两个项目:
1、AXI_Full读项目:PS端利用指针向指定地址写递增数据,然后PL端利用AXI_Full的读协议进行读数据,并且验证读取的数据是不是递增数,不是的话拉高相应的标志位并进行计数。
2、AXI_Full写项目:PL端利用AXI_Full的写协议进行写递增数据到ZYNQ的DDR3,然后PS端利用指针进行读取相应地址数据,并且验证是不是递增数,不是的话拉高相应的标志并进行计数。
AXI_Full读协议
我们上篇文章已经给出了AXI读协议的时序图,那个时序图在AXI_Full与AXI_Stream中最容易体现,如下:

上一篇文章我们进行讲解AXI_Lite协议的时候几乎没咋么写代码,都是使用VIVADO自带的IP封装工具进行封装,整个AXI协议封装的代码已经非常齐全,同样这次我们使用相同的方法进行操作。 经过上一篇文章可以知道AXI4协议不光只有上面的几个信号,但是我们只需要控制上面几个信号,至于其余的信号如何处理,这里我们利用VIVADO生成的AXI协议已经帮我们做了,所以不需要太过关心,因为我们是在现成的代码上更改的。
VIVADO建立AXI4_Full IP
上一篇文章我们已经讲解了利用VIVADO的IP冯传工具进行了AXI_Lite协议的封装修改完成了相应的功能,这次我们将利用同样的手段来进行AXI_Full协议的封装与修改。
1、创建IP
2、点击Next
3、点击创建一个AXI4封装的IP
4、填写IP的名字、版本、描述、目录等信息

5、进行AXI协议的选择
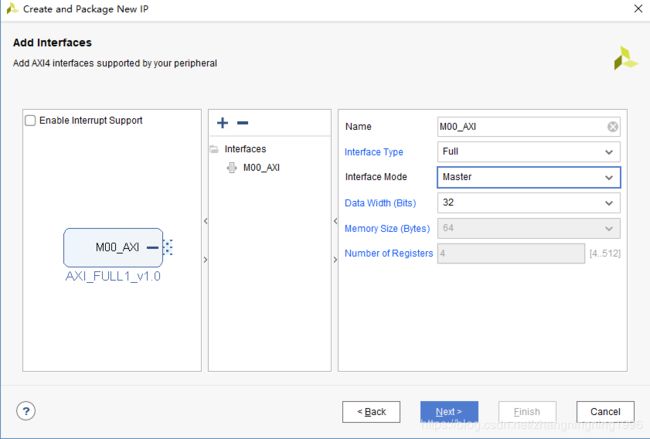
1、生成IP的名字
2、选择生成AXI4协议的类型,我们这里选择Full的类型
3、选择是主机还是从机,这里选择主机,因为PS端只有AXI4_Full协议的从机
4、数据的位宽,对于AXI_Lite协议数据位宽恒定是32个,对于AXI4协议可以是64,我们在程序中进行相应的修改成64就可
5、存储器的数目,对于AXI_Full协议的从机需要设置
6、寄存器的数目、对于AXI_Lite协议的从机需要设置

这里需要注意VIVADO给我们的历程时基于AXI4_Full测试的历程,我们进行修改的话,只需要进行如下操作:
1、如果进行读AXI操作就先把生成文件中的AXI读操作的部分全部删除掉,把写信号只保留复位端,然后自己按照自己的需求重新书写AXI的读操作。
2、生成AXI协议的端口列表都是大写的,我们内部赋值的变量一般是小写的。
AXI_Full读项目
我们上面介绍了首先要将VIVADO自动生成的AXI4协议进行修改:
1、先将AXI读操作的部分全部删除掉,删除的位置如下:

一直从读地址通道到增加用户逻辑,删除了非常多的内容。
2、将写信号只保留复位端,如下:

然后进行AXI_Full读协议的书写。
AXI_Full读协议代码
第一个项目的工程代码如下:
axi_full_v1_0模块:
`timescale 1 ns / 1 ps
module axi_full_v1_0 #
(
// Users to add parameters here
// User parameters ends
// Do not modify the parameters beyond this line
// Parameters of Axi Master Bus Interface M00_AXI
parameter C_M00_AXI_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR = 32'h01000000,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_BURST_LEN = 256,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_ID_WIDTH = 1,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH = 32,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_DATA_WIDTH = 64,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH = 0,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH = 0,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH = 0,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH = 0,
parameter integer C_M00_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH = 0
)
(
// Users to add ports here
// User ports ends
// Do not modify the ports beyond this line
// Ports of Axi Master Bus Interface M00_AXI
input wire m00_axi_init_axi_txn,
output wire m00_axi_txn_done,
output wire m00_axi_error,
input wire m00_axi_aclk,
input wire m00_axi_aresetn,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_awid,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_awaddr,
output wire [7 : 0] m00_axi_awlen,
output wire [2 : 0] m00_axi_awsize,
output wire [1 : 0] m00_axi_awburst,
output wire m00_axi_awlock,
output wire [3 : 0] m00_axi_awcache,
output wire [2 : 0] m00_axi_awprot,
output wire [3 : 0] m00_axi_awqos,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_awuser,
output wire m00_axi_awvalid,
input wire m00_axi_awready,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_wdata,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8-1 : 0] m00_axi_wstrb,
output wire m00_axi_wlast,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_wuser,
output wire m00_axi_wvalid,
input wire m00_axi_wready,
input wire [C_M00_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_bid,
input wire [1 : 0] m00_axi_bresp,
input wire [C_M00_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_buser,
input wire m00_axi_bvalid,
output wire m00_axi_bready,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_arid,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_araddr,
output wire [7 : 0] m00_axi_arlen,
output wire [2 : 0] m00_axi_arsize,
output wire [1 : 0] m00_axi_arburst,
output wire m00_axi_arlock,
output wire [3 : 0] m00_axi_arcache,
output wire [2 : 0] m00_axi_arprot,
output wire [3 : 0] m00_axi_arqos,
output wire [C_M00_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_aruser,
output wire m00_axi_arvalid,
input wire m00_axi_arready,
input wire [C_M00_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_rid,
input wire [C_M00_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_rdata,
input wire [1 : 0] m00_axi_rresp,
input wire m00_axi_rlast,
input wire [C_M00_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] m00_axi_ruser,
input wire m00_axi_rvalid,
output wire m00_axi_rready
);
// Instantiation of Axi Bus Interface M00_AXI
axi_full_v1_0_M00_AXI # (
.C_M_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR(C_M00_AXI_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR),
.C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN(C_M00_AXI_BURST_LEN),
.C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_ID_WIDTH),
.C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH),
.C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_DATA_WIDTH),
.C_M_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH),
.C_M_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH),
.C_M_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH),
.C_M_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH),
.C_M_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH(C_M00_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH)
) axi_full_v1_0_M00_AXI_inst (
.INIT_AXI_TXN(m00_axi_init_axi_txn),
.TXN_DONE(m00_axi_txn_done),
.ERROR(m00_axi_error),
.M_AXI_ACLK(m00_axi_aclk),
.M_AXI_ARESETN(m00_axi_aresetn),
.M_AXI_AWID(m00_axi_awid),
.M_AXI_AWADDR(m00_axi_awaddr),
.M_AXI_AWLEN(m00_axi_awlen),
.M_AXI_AWSIZE(m00_axi_awsize),
.M_AXI_AWBURST(m00_axi_awburst),
.M_AXI_AWLOCK(m00_axi_awlock),
.M_AXI_AWCACHE(m00_axi_awcache),
.M_AXI_AWPROT(m00_axi_awprot),
.M_AXI_AWQOS(m00_axi_awqos),
.M_AXI_AWUSER(m00_axi_awuser),
.M_AXI_AWVALID(m00_axi_awvalid),
.M_AXI_AWREADY(m00_axi_awready),
.M_AXI_WDATA(m00_axi_wdata),
.M_AXI_WSTRB(m00_axi_wstrb),
.M_AXI_WLAST(m00_axi_wlast),
.M_AXI_WUSER(m00_axi_wuser),
.M_AXI_WVALID(m00_axi_wvalid),
.M_AXI_WREADY(m00_axi_wready),
.M_AXI_BID(m00_axi_bid),
.M_AXI_BRESP(m00_axi_bresp),
.M_AXI_BUSER(m00_axi_buser),
.M_AXI_BVALID(m00_axi_bvalid),
.M_AXI_BREADY(m00_axi_bready),
.M_AXI_ARID(m00_axi_arid),
.M_AXI_ARADDR(m00_axi_araddr),
.M_AXI_ARLEN(m00_axi_arlen),
.M_AXI_ARSIZE(m00_axi_arsize),
.M_AXI_ARBURST(m00_axi_arburst),
.M_AXI_ARLOCK(m00_axi_arlock),
.M_AXI_ARCACHE(m00_axi_arcache),
.M_AXI_ARPROT(m00_axi_arprot),
.M_AXI_ARQOS(m00_axi_arqos),
.M_AXI_ARUSER(m00_axi_aruser),
.M_AXI_ARVALID(m00_axi_arvalid),
.M_AXI_ARREADY(m00_axi_arready),
.M_AXI_RID(m00_axi_rid),
.M_AXI_RDATA(m00_axi_rdata),
.M_AXI_RRESP(m00_axi_rresp),
.M_AXI_RLAST(m00_axi_rlast),
.M_AXI_RUSER(m00_axi_ruser),
.M_AXI_RVALID(m00_axi_rvalid),
.M_AXI_RREADY(m00_axi_rready)
);
// Add user logic here
// User logic ends
endmodule
axi_full_v1_0_M00_AXI模块:
`timescale 1 ns / 1 ps
module axi_full_v1_0_M00_AXI #
(
// Users to add parameters here
// User parameters ends
// Do not modify the parameters beyond this line
// Base address of targeted slave
parameter C_M_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR = 32'h01000000,
// Burst Length. Supports 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 burst lengths
parameter integer C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN = 256,
// Thread ID Width
parameter integer C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH = 1,
// Width of Address Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH = 32,
// Width of Data Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH = 64,
// Width of User Write Address Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Read Address Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Write Data Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Read Data Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Response Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH = 0
)
(
// Users to add ports here
// User ports ends
// Do not modify the ports beyond this line
// Initiate AXI transactions
input wire INIT_AXI_TXN,
// Asserts when transaction is complete
output wire TXN_DONE,
// Asserts when ERROR is detected
output reg ERROR,
// Global Clock Signal.
input wire M_AXI_ACLK,
// Global Reset Singal. This Signal is Active Low
input wire M_AXI_ARESETN,
// Master Interface Write Address ID
output wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_AWID,
// Master Interface Write Address
output wire [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_AWADDR,
// Burst length. The burst length gives the exact number of transfers in a burst
output wire [7 : 0] M_AXI_AWLEN,
// Burst size. This signal indicates the size of each transfer in the burst
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_AWSIZE,
// Burst type. The burst type and the size information,
// determine how the address for each transfer within the burst is calculated.
output wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_AWBURST,
// Lock type. Provides additional information about the
// atomic characteristics of the transfer.
output wire M_AXI_AWLOCK,
// Memory type. This signal indicates how transactions
// are required to progress through a system.
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_AWCACHE,
// Protection type. This signal indicates the privilege
// and security level of the transaction, and whether
// the transaction is a data access or an instruction access.
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_AWPROT,
// Quality of Service, QoS identifier sent for each write transaction.
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_AWQOS,
// Optional User-defined signal in the write address channel.
output wire [C_M_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_AWUSER,
// Write address valid. This signal indicates that
// the channel is signaling valid write address and control information.
output wire M_AXI_AWVALID,
// Write address ready. This signal indicates that
// the slave is ready to accept an address and associated control signals
input wire M_AXI_AWREADY,
// Master Interface Write Data.
output wire [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_WDATA,
// Write strobes. This signal indicates which byte
// lanes hold valid data. There is one write strobe
// bit for each eight bits of the write data bus.
output wire [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8-1 : 0] M_AXI_WSTRB,
// Write last. This signal indicates the last transfer in a write burst.
output wire M_AXI_WLAST,
// Optional User-defined signal in the write data channel.
output wire [C_M_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_WUSER,
// Write valid. This signal indicates that valid write
// data and strobes are available
output wire M_AXI_WVALID,
// Write ready. This signal indicates that the slave
// can accept the write data.
input wire M_AXI_WREADY,
// Master Interface Write Response.
input wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_BID,
// Write response. This signal indicates the status of the write transaction.
input wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_BRESP,
// Optional User-defined signal in the write response channel
input wire [C_M_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_BUSER,
// Write response valid. This signal indicates that the
// channel is signaling a valid write response.
input wire M_AXI_BVALID,
// Response ready. This signal indicates that the master
// can accept a write response.
output wire M_AXI_BREADY,
// Master Interface Read Address.
output wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_ARID,
// Read address. This signal indicates the initial
// address of a read burst transaction.
output wire [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_ARADDR,
// Burst length. The burst length gives the exact number of transfers in a burst
output wire [7 : 0] M_AXI_ARLEN,
// Burst size. This signal indicates the size of each transfer in the burst
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_ARSIZE,
// Burst type. The burst type and the size information,
// determine how the address for each transfer within the burst is calculated.
output wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_ARBURST,
// Lock type. Provides additional information about the
// atomic characteristics of the transfer.
output wire M_AXI_ARLOCK,
// Memory type. This signal indicates how transactions
// are required to progress through a system.
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_ARCACHE,
// Protection type. This signal indicates the privilege
// and security level of the transaction, and whether
// the transaction is a data access or an instruction access.
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_ARPROT,
// Quality of Service, QoS identifier sent for each read transaction
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_ARQOS,
// Optional User-defined signal in the read address channel.
output wire [C_M_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_ARUSER,
// Write address valid. This signal indicates that
// the channel is signaling valid read address and control information
output wire M_AXI_ARVALID,
// Read address ready. This signal indicates that
// the slave is ready to accept an address and associated control signals
input wire M_AXI_ARREADY,
// Read ID tag. This signal is the identification tag
// for the read data group of signals generated by the slave.
input wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_RID,
// Master Read Data
input wire [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_RDATA,
// Read response. This signal indicates the status of the read transfer
input wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_RRESP,
// Read last. This signal indicates the last transfer in a read burst
input wire M_AXI_RLAST,
// Optional User-defined signal in the read address channel.
input wire [C_M_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_RUSER,
// Read valid. This signal indicates that the channel
// is signaling the required read data.
input wire M_AXI_RVALID,
// Read ready. This signal indicates that the master can
// accept the read data and response information.
output wire M_AXI_RREADY
);
// function called clogb2 that returns an integer which has the
//value of the ceiling of the log base 2
// function called clogb2 that returns an integer which has the
// value of the ceiling of the log base 2.
function integer clogb2 (input integer bit_depth);
begin
for(clogb2=0; bit_depth>0; clogb2=clogb2+1)
bit_depth = bit_depth >> 1;
end
endfunction
// C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM is the width of the index counter for
// number of write or read transaction.
localparam integer C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM = clogb2(C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN-1);
// Burst length for transactions, in C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTHs.
// Non-2^n lengths will eventually cause bursts across 4K address boundaries.
localparam integer C_MASTER_LENGTH = 12;
// total number of burst transfers is master length divided by burst length and burst size
localparam integer C_NO_BURSTS_REQ = C_MASTER_LENGTH-clogb2((C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN*C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
// Example State machine to initialize counter, initialize write transactions,
// initialize read transactions and comparison of read data with the
// written data words.
parameter [1:0] IDLE = 2'b00, // This state initiates AXI4Lite transaction
// after the state machine changes state to INIT_WRITE
// when there is 0 to 1 transition on INIT_AXI_TXN
INIT_WRITE = 2'b01, // This state initializes write transaction,
// once writes are done, the state machine
// changes state to INIT_READ
INIT_READ = 2'b10, // This state initializes read transaction
// once reads are done, the state machine
// changes state to INIT_COMPARE
INIT_COMPARE = 2'b11; // This state issues the status of comparison
// of the written data with the read data
reg [1:0] mst_exec_state;
// AXI4LITE signals
//AXI4 internal temp signals
reg [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] axi_awaddr;
reg axi_awvalid;
reg [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] axi_wdata;
reg axi_wlast;
reg axi_wvalid;
reg axi_bready;
reg [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] axi_araddr;
reg axi_arvalid;
wire axi_rready;
//write beat count in a burst
reg [C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM : 0] write_index;
//read beat count in a burst
reg [C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM : 0] read_index;
//size of C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN length burst in bytes
wire [C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM+2 : 0] burst_size_bytes;
//The burst counters are used to track the number of burst transfers of C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN burst length needed to transfer 2^C_MASTER_LENGTH bytes of data.
reg [C_NO_BURSTS_REQ : 0] write_burst_counter;
reg [C_NO_BURSTS_REQ : 0] read_burst_counter;
reg start_single_burst_write;
reg start_single_burst_read;
reg writes_done;
reg reads_done;
reg error_reg;
reg compare_done;
reg read_mismatch;
reg burst_write_active;
reg burst_read_active;
reg [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] expected_rdata;
//Interface response error flags
wire write_resp_error;
wire read_resp_error;
wire wnext;
wire rnext;
reg init_txn_ff;
reg init_txn_ff2;
reg init_txn_edge;
wire init_txn_pulse;
// I/O Connections assignments
//I/O Connections. Write Address (AW)
assign M_AXI_AWID = 'b0;
//The AXI address is a concatenation of the target base address + active offset range
assign M_AXI_AWADDR = C_M_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR + axi_awaddr;
//Burst LENgth is number of transaction beats, minus 1
assign M_AXI_AWLEN = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN - 1;
//Size should be C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH, in 2^SIZE bytes, otherwise narrow bursts are used
assign M_AXI_AWSIZE = clogb2((C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
//INCR burst type is usually used, except for keyhole bursts
assign M_AXI_AWBURST = 2'b01;
assign M_AXI_AWLOCK = 1'b0;
//Update value to 4'b0011 if coherent accesses to be used via the Zynq ACP port. Not Allocated, Modifiable, not Bufferable. Not Bufferable since this example is meant to test memory, not intermediate cache.
assign M_AXI_AWCACHE = 4'b0010;
assign M_AXI_AWPROT = 3'h0;
assign M_AXI_AWQOS = 4'h0;
assign M_AXI_AWUSER = 'b1;
assign M_AXI_AWVALID = axi_awvalid;
//Write Data(W)
assign M_AXI_WDATA = axi_wdata;
//All bursts are complete and aligned in this example
assign M_AXI_WSTRB = {(C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8){1'b1}};
assign M_AXI_WLAST = axi_wlast;
assign M_AXI_WUSER = 'b0;
assign M_AXI_WVALID = axi_wvalid;
//Write Response (B)
assign M_AXI_BREADY = axi_bready;
//Read Address (AR)
assign M_AXI_ARID = 'b0;
assign M_AXI_ARADDR = C_M_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR + axi_araddr;
//Burst LENgth is number of transaction beats, minus 1
assign M_AXI_ARLEN = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN - 1;
//Size should be C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH, in 2^n bytes, otherwise narrow bursts are used
assign M_AXI_ARSIZE = clogb2((C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
//INCR burst type is usually used, except for keyhole bursts
assign M_AXI_ARBURST = 2'b01;
assign M_AXI_ARLOCK = 1'b0;
//Update value to 4'b0011 if coherent accesses to be used via the Zynq ACP port. Not Allocated, Modifiable, not Bufferable. Not Bufferable since this example is meant to test memory, not intermediate cache.
assign M_AXI_ARCACHE = 4'b0010;
assign M_AXI_ARPROT = 3'h0;
assign M_AXI_ARQOS = 4'h0;
assign M_AXI_ARUSER = 'b1;
assign M_AXI_ARVALID = axi_arvalid;
//Read and Read Response (R)
assign M_AXI_RREADY = axi_rready;
//Example design I/O
assign TXN_DONE = compare_done;
//Burst size in bytes
assign burst_size_bytes = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN * C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8;
assign init_txn_pulse = (!init_txn_ff2) && init_txn_ff;
//Generate a pulse to initiate AXI transaction.
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
// Initiates AXI transaction delay
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 )
begin
init_txn_ff <= 1'b0;
init_txn_ff2 <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
init_txn_ff <= INIT_AXI_TXN;
init_txn_ff2 <= init_txn_ff;
end
end
//--------------------
//Write Address Channel
//--------------------
// The purpose of the write address channel is to request the address and
// command information for the entire transaction. It is a single beat
// of information.
// The AXI4 Write address channel in this example will continue to initiate
// write commands as fast as it is allowed by the slave/interconnect.
// The address will be incremented on each accepted address transaction,
// by burst_size_byte to point to the next address.
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 )
axi_awvalid <= 1'b0;
// Next address after AWREADY indicates previous address acceptance
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
axi_awaddr <= 'b0;
//--------------------
//Write Data Channel
//--------------------
//The write data will continually try to push write data across the interface.
//The amount of data accepted will depend on the AXI slave and the AXI
//Interconnect settings, such as if there are FIFOs enabled in interconnect.
//Note that there is no explicit timing relationship to the write address channel.
//The write channel has its own throttling flag, separate from the AW channel.
//Synchronization between the channels must be determined by the user.
//The simpliest but lowest performance would be to only issue one address write
//and write data burst at a time.
//In this example they are kept in sync by using the same address increment
//and burst sizes. Then the AW and W channels have their transactions measured
//with threshold counters as part of the user logic, to make sure neither
//channel gets too far ahead of each other.
//Forward movement occurs when the write channel is valid and ready
assign wnext = M_AXI_WREADY & axi_wvalid;
// WVALID logic, similar to the axi_awvalid always block above
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 )
axi_wvalid <= 1'b0;
//WLAST generation on the MSB of a counter underflow
// WVALID logic, similar to the axi_awvalid always block above
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 )
axi_wlast <= 1'b0;
/* Burst length counter. Uses extra counter register bit to indicate terminal
count to reduce decode logic */
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 || start_single_burst_write == 1'b1)
write_index <= 0;
/* Write Data Generator
Data pattern is only a simple incrementing count from 0 for each burst */
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
axi_wdata <= 'b1;
//----------------------------
//Write Response (B) Channel
//----------------------------
//The write response channel provides feedback that the write has committed
//to memory. BREADY will occur when all of the data and the write address
//has arrived and been accepted by the slave.
//The write issuance (number of outstanding write addresses) is started by
//the Address Write transfer, and is completed by a BREADY/BRESP.
//While negating BREADY will eventually throttle the AWREADY signal,
//it is best not to throttle the whole data channel this way.
//The BRESP bit [1] is used indicate any errors from the interconnect or
//slave for the entire write burst. This example will capture the error
//into the ERROR output.
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 )
axi_bready <= 1'b0;
//Flag any write response errors
assign write_resp_error = axi_bready & M_AXI_BVALID & M_AXI_BRESP[1];
//----------------------------
//Read Address Channel
//----------------------------
// Add user logic here
parameter RD_IDLE = 3'b001 ;
parameter JUDGE = 3'b010 ;
parameter READ = 3'b100 ;
reg [ 2:0] rd_state ;
reg rd_end ;
reg [31:0] test_data0 ;
reg [31:0] test_data1 ;
reg [63:0] err_cnt ;
reg err_flag ;
assign axi_rready = 1'b1;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0)
rd_state <= IDLE;
else case(rd_state)
RD_IDLE : if(init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
rd_state <= JUDGE;
else
rd_state <= rd_state;
JUDGE : rd_state <= READ;
READ : if(rd_end == 1'b1)
rd_state <= JUDGE;
else
rd_state <= rd_state;
default : rd_state <= RD_IDLE;
endcase
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
axi_araddr <= 32'd0;
else if(axi_araddr == 32'd10485760)
axi_araddr <= 32'd0;
else if(axi_arvalid == 1'b1 && M_AXI_ARREADY == 1'b1)
axi_araddr <= axi_araddr + 2048;
else
axi_araddr <= axi_araddr;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
axi_arvalid <= 1'b0;
else if(rd_state == JUDGE)
axi_arvalid <= 1'b1;
else if(M_AXI_ARREADY == 1'b1)
axi_arvalid <= 1'b0;
else
axi_arvalid <= axi_arvalid;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
rd_end <= 1'b0;
else if(M_AXI_RLAST == 1'b1)
rd_end <= 1'b1;
else
rd_end <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
test_data0 <= 64'd0;
else if(axi_araddr == 0 && M_AXI_RLAST == 1'b1)
test_data0 <= 64'd0;
else if(rd_state == READ && M_AXI_RVALID == 1'b1 && axi_rready == 1'b1)
test_data0 <= test_data0 + 2;
else
test_data0 <= test_data0;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
test_data1 <= 64'd1;
else if(axi_araddr == 0 && M_AXI_RLAST == 1'b1)
test_data1 <= 64'd1;
else if(rd_state == READ && M_AXI_RVALID == 1'b1 && axi_rready == 1'b1)
test_data1 <= test_data1 + 2;
else
test_data1 <= test_data1;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
err_flag <= 1'b0;
else if(M_AXI_RVALID == 1'b1 && axi_rready == 1'b1 && ({test_data1,test_data0} != M_AXI_RDATA))
err_flag <= 1'b1;
else
err_flag <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
err_cnt <= 64'd0;
else if(err_flag == 1'b1)
err_cnt <= err_cnt + 1'b1;
else
err_cnt <= err_cnt;
ila_0 ila_0_inst (
.clk (M_AXI_ACLK ), // input wire clk
.probe0 (axi_araddr ), // input wire [31:0] probe0
.probe1 (axi_arvalid ), // input wire [0:0] probe1
.probe2 (M_AXI_ARREADY ), // input wire [0:0] probe2
.probe3 (M_AXI_RDATA ), // input wire [31:0] probe3
.probe4 (M_AXI_RLAST ), // input wire [0:0] probe4
.probe5 (M_AXI_RVALID ), // input wire [0:0] probe5
.probe6 (rd_state ), // input wire [2:0] probe6
.probe7 (rd_end ), // input wire [0:0] probe7
.probe8 (axi_rready ), // input wire [0:0] probe8
.probe9 ({test_data1,test_data0} ), // input wire [63:0] probe9
.probe10 (err_cnt ), // input wire [63:0] probe10
.probe11 (err_flag ) // input wire [0:0] probe11
);
// User logic ends
endmodule
我们修改的代码也都写在用户逻辑的注释中。然后进行相应的IP封装,这里不再多说同学们可以查找相应的IP封装步骤,在前一篇文章我们也就进行了相应简单的介绍。
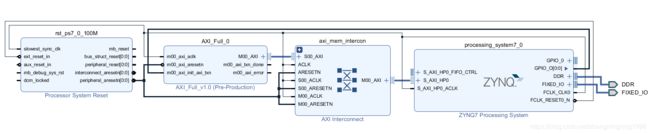
整个项目的Block Design设计如下:

详细的IP配置,我会把工程上传到群里面,需要学习的同学可以进群自取。
这里要注意一下这个信号:
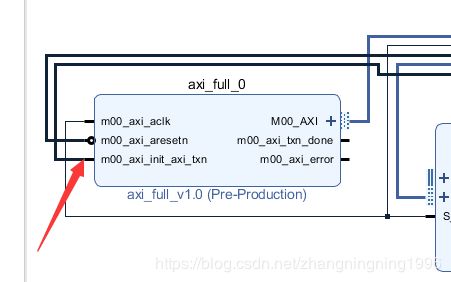
这个是AXI的复位信号,我们这里使用了PS端的一个EMIO来进行相应的控制。

PS端代码
因为是ZYNQ设计,所以会有PS端的设计,所以我们给出设计的PS端的代码:
/******************************************************************************
*
* Copyright (C) 2009 - 2014 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
* all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* Use of the Software is limited solely to applications:
* (a) running on a Xilinx device, or
* (b) that interact with a Xilinx device through a bus or interconnect.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
* XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
* WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF
* OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
* SOFTWARE.
*
* Except as contained in this notice, the name of the Xilinx shall not be used
* in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in
* this Software without prior written authorization from Xilinx.
*
******************************************************************************/
/*
* helloworld.c: simple test application
*
* This application configures UART 16550 to baud rate 9600.
* PS7 UART (Zynq) is not initialized by this application, since
* bootrom/bsp configures it to baud rate 115200
*
* ------------------------------------------------
* | UART TYPE BAUD RATE |
* ------------------------------------------------
* uartns550 9600
* uartlite Configurable only in HW design
* ps7_uart 115200 (configured by bootrom/bsp)
*/
#include 上面就是我们写的PS端的c代码,是不是第一次感觉C语言这么简单,指针这么好用。
大家注意一下这里的起始地址不能选择成0,因为要给PS端的软件一定的存储空间,C语言并不像Verilog语言一样映射成了电路。

与PS端的地址相对应,AXI_Full的读地址同样没从0地址,虽然我们写的时候是从0地址开始的,但是输出的时候加上了一个常数,如下:
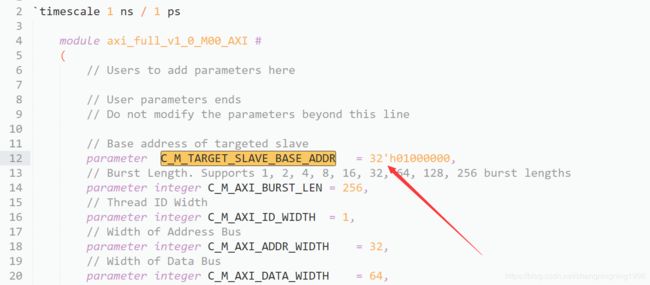

由此可以看出地址是相互对应的,只是对应ZYNQ而言需要保留软件程序的存储空间。
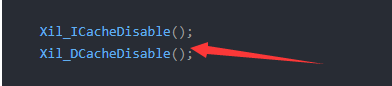
这里一定要关闭cache,否则相应的数据是错误的,因为PS端的软件会在Cacha中缓存相应的数据,如下:
下板测试
我们进行下班测试之后进行ila抓取,然后出现下面现象:
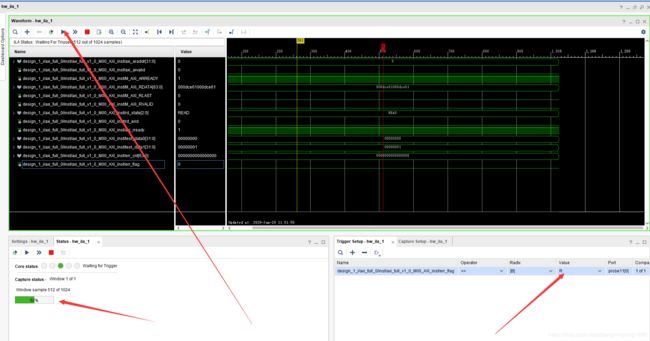

我们使用错误标志信号当作触发信号进行触发,但是没能触发从而说明了我们实验的正确性。进行立即触发发现读出数据与测试数据确实相等,从而证明了实验的正确性。
AXI_Full写项目
我们上面介绍了首先要将VIVADO自动生成的AXI4协议进行修改:
1、先将AXI写操作的部分全部删除掉,删除的位置如下:

一直从写地址通道删除到读地址通道。
2、将读信号只保留复位端,如下:
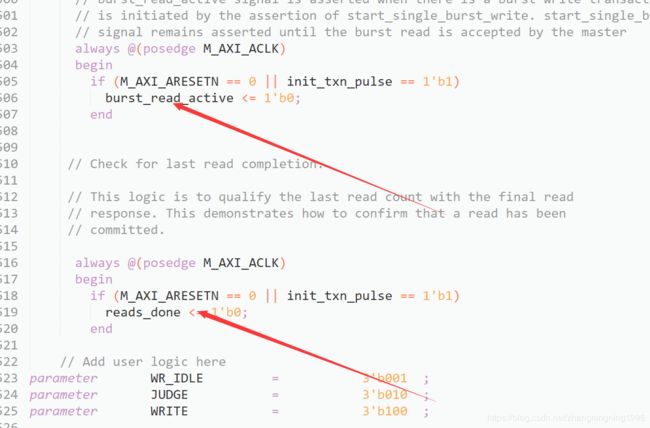
然后进行AXI_Full写协议的书写。
AXI_Full写协议代码
这里进行的额外操作与AXI_Full读协议的操作一样,额外的介绍这里将不再给出,我们直接给出相应的代码供大家学习。
design_1_wrapper模块:
//Copyright 1986-2019 Xilinx, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Tool Version: Vivado v.2019.1 (win64) Build 2552052 Fri May 24 14:49:42 MDT 2019
//Date : Sat Jun 20 19:29:57 2020
//Host : BF-201811061741 running 64-bit major release (build 9200)
//Command : generate_target design_1_wrapper.bd
//Design : design_1_wrapper
//Purpose : IP block netlist
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
`timescale 1 ps / 1 ps
module design_1_wrapper
(DDR_addr,
DDR_ba,
DDR_cas_n,
DDR_ck_n,
DDR_ck_p,
DDR_cke,
DDR_cs_n,
DDR_dm,
DDR_dq,
DDR_dqs_n,
DDR_dqs_p,
DDR_odt,
DDR_ras_n,
DDR_reset_n,
DDR_we_n,
FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn,
FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp,
FIXED_IO_mio,
FIXED_IO_ps_clk,
FIXED_IO_ps_porb,
FIXED_IO_ps_srstb);
inout [14:0]DDR_addr;
inout [2:0]DDR_ba;
inout DDR_cas_n;
inout DDR_ck_n;
inout DDR_ck_p;
inout DDR_cke;
inout DDR_cs_n;
inout [3:0]DDR_dm;
inout [31:0]DDR_dq;
inout [3:0]DDR_dqs_n;
inout [3:0]DDR_dqs_p;
inout DDR_odt;
inout DDR_ras_n;
inout DDR_reset_n;
inout DDR_we_n;
inout FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn;
inout FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp;
inout [53:0]FIXED_IO_mio;
inout FIXED_IO_ps_clk;
inout FIXED_IO_ps_porb;
inout FIXED_IO_ps_srstb;
wire [14:0]DDR_addr;
wire [2:0]DDR_ba;
wire DDR_cas_n;
wire DDR_ck_n;
wire DDR_ck_p;
wire DDR_cke;
wire DDR_cs_n;
wire [3:0]DDR_dm;
wire [31:0]DDR_dq;
wire [3:0]DDR_dqs_n;
wire [3:0]DDR_dqs_p;
wire DDR_odt;
wire DDR_ras_n;
wire DDR_reset_n;
wire DDR_we_n;
wire FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn;
wire FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp;
wire [53:0]FIXED_IO_mio;
wire FIXED_IO_ps_clk;
wire FIXED_IO_ps_porb;
wire FIXED_IO_ps_srstb;
design_1 design_1_i
(.DDR_addr(DDR_addr),
.DDR_ba(DDR_ba),
.DDR_cas_n(DDR_cas_n),
.DDR_ck_n(DDR_ck_n),
.DDR_ck_p(DDR_ck_p),
.DDR_cke(DDR_cke),
.DDR_cs_n(DDR_cs_n),
.DDR_dm(DDR_dm),
.DDR_dq(DDR_dq),
.DDR_dqs_n(DDR_dqs_n),
.DDR_dqs_p(DDR_dqs_p),
.DDR_odt(DDR_odt),
.DDR_ras_n(DDR_ras_n),
.DDR_reset_n(DDR_reset_n),
.DDR_we_n(DDR_we_n),
.FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn(FIXED_IO_ddr_vrn),
.FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp(FIXED_IO_ddr_vrp),
.FIXED_IO_mio(FIXED_IO_mio),
.FIXED_IO_ps_clk(FIXED_IO_ps_clk),
.FIXED_IO_ps_porb(FIXED_IO_ps_porb),
.FIXED_IO_ps_srstb(FIXED_IO_ps_srstb));
endmodule
AXI_Full_v1_0_M00_AXI模块:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
// *********************************************************************************
// Project Name : OSXXXX
// Author : zhangningning
// Email : [email protected]
// Website : https://blog.csdn.net/zhangningning1996
// Module Name : AXI_Full_v1_0_M00_AXI.v
// Create Time : 2020-06-20 20:04:44
// Editor : sublime text3, tab size (4)
// CopyRight(c) : All Rights Reserved
//
// *********************************************************************************
// Modification History:
// Date By Version Change Description
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// XXXX zhangningning 1.0 Original
//
// *********************************************************************************
module AXI_Full_v1_0_M00_AXI #
(
// Users to add parameters here
// User parameters ends
// Do not modify the parameters beyond this line
// Base address of targeted slave
parameter C_M_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR = 32'h01000000,
// Burst Length. Supports 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 burst lengths
parameter integer C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN = 256,
// Thread ID Width
parameter integer C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH = 1,
// Width of Address Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH = 32,
// Width of Data Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH = 64,
// Width of User Write Address Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Read Address Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Write Data Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Read Data Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH = 0,
// Width of User Response Bus
parameter integer C_M_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH = 0
)
(
// Users to add ports here
// User ports ends
// Do not modify the ports beyond this line
// Initiate AXI transactions
input wire INIT_AXI_TXN,
// Asserts when transaction is complete
output wire TXN_DONE,
// Asserts when ERROR is detected
output reg ERROR,
// Global Clock Signal.
input wire M_AXI_ACLK,
// Global Reset Singal. This Signal is Active Low
input wire M_AXI_ARESETN,
// Master Interface Write Address ID
output wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_AWID,
// Master Interface Write Address
output wire [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_AWADDR,
// Burst length. The burst length gives the exact number of transfers in a burst
output wire [7 : 0] M_AXI_AWLEN,
// Burst size. This signal indicates the size of each transfer in the burst
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_AWSIZE,
// Burst type. The burst type and the size information,
// determine how the address for each transfer within the burst is calculated.
output wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_AWBURST,
// Lock type. Provides additional information about the
// atomic characteristics of the transfer.
output wire M_AXI_AWLOCK,
// Memory type. This signal indicates how transactions
// are required to progress through a system.
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_AWCACHE,
// Protection type. This signal indicates the privilege
// and security level of the transaction, and whether
// the transaction is a data access or an instruction access.
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_AWPROT,
// Quality of Service, QoS identifier sent for each write transaction.
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_AWQOS,
// Optional User-defined signal in the write address channel.
output wire [C_M_AXI_AWUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_AWUSER,
// Write address valid. This signal indicates that
// the channel is signaling valid write address and control information.
output wire M_AXI_AWVALID,
// Write address ready. This signal indicates that
// the slave is ready to accept an address and associated control signals
input wire M_AXI_AWREADY,
// Master Interface Write Data.
output wire [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_WDATA,
// Write strobes. This signal indicates which byte
// lanes hold valid data. There is one write strobe
// bit for each eight bits of the write data bus.
output wire [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8-1 : 0] M_AXI_WSTRB,
// Write last. This signal indicates the last transfer in a write burst.
output wire M_AXI_WLAST,
// Optional User-defined signal in the write data channel.
output wire [C_M_AXI_WUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_WUSER,
// Write valid. This signal indicates that valid write
// data and strobes are available
output wire M_AXI_WVALID,
// Write ready. This signal indicates that the slave
// can accept the write data.
input wire M_AXI_WREADY,
// Master Interface Write Response.
input wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_BID,
// Write response. This signal indicates the status of the write transaction.
input wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_BRESP,
// Optional User-defined signal in the write response channel
input wire [C_M_AXI_BUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_BUSER,
// Write response valid. This signal indicates that the
// channel is signaling a valid write response.
input wire M_AXI_BVALID,
// Response ready. This signal indicates that the master
// can accept a write response.
output wire M_AXI_BREADY,
// Master Interface Read Address.
output wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_ARID,
// Read address. This signal indicates the initial
// address of a read burst transaction.
output wire [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_ARADDR,
// Burst length. The burst length gives the exact number of transfers in a burst
output wire [7 : 0] M_AXI_ARLEN,
// Burst size. This signal indicates the size of each transfer in the burst
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_ARSIZE,
// Burst type. The burst type and the size information,
// determine how the address for each transfer within the burst is calculated.
output wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_ARBURST,
// Lock type. Provides additional information about the
// atomic characteristics of the transfer.
output wire M_AXI_ARLOCK,
// Memory type. This signal indicates how transactions
// are required to progress through a system.
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_ARCACHE,
// Protection type. This signal indicates the privilege
// and security level of the transaction, and whether
// the transaction is a data access or an instruction access.
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_ARPROT,
// Quality of Service, QoS identifier sent for each read transaction
output wire [3 : 0] M_AXI_ARQOS,
// Optional User-defined signal in the read address channel.
output wire [C_M_AXI_ARUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_ARUSER,
// Write address valid. This signal indicates that
// the channel is signaling valid read address and control information
output wire M_AXI_ARVALID,
// Read address ready. This signal indicates that
// the slave is ready to accept an address and associated control signals
input wire M_AXI_ARREADY,
// Read ID tag. This signal is the identification tag
// for the read data group of signals generated by the slave.
input wire [C_M_AXI_ID_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_RID,
// Master Read Data
input wire [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_RDATA,
// Read response. This signal indicates the status of the read transfer
input wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_RRESP,
// Read last. This signal indicates the last transfer in a read burst
input wire M_AXI_RLAST,
// Optional User-defined signal in the read address channel.
input wire [C_M_AXI_RUSER_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXI_RUSER,
// Read valid. This signal indicates that the channel
// is signaling the required read data.
input wire M_AXI_RVALID,
// Read ready. This signal indicates that the master can
// accept the read data and response information.
output wire M_AXI_RREADY
);
// function called clogb2 that returns an integer which has the
//value of the ceiling of the log base 2
// function called clogb2 that returns an integer which has the
// value of the ceiling of the log base 2.
function integer clogb2 (input integer bit_depth);
begin
for(clogb2=0; bit_depth>0; clogb2=clogb2+1)
bit_depth = bit_depth >> 1;
end
endfunction
// C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM is the width of the index counter for
// number of write or read transaction.
localparam integer C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM = clogb2(C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN-1);
// Burst length for transactions, in C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTHs.
// Non-2^n lengths will eventually cause bursts across 4K address boundaries.
localparam integer C_MASTER_LENGTH = 12;
// total number of burst transfers is master length divided by burst length and burst size
localparam integer C_NO_BURSTS_REQ = C_MASTER_LENGTH-clogb2((C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN*C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
// Example State machine to initialize counter, initialize write transactions,
// initialize read transactions and comparison of read data with the
// written data words.
parameter [1:0] IDLE = 2'b00, // This state initiates AXI4Lite transaction
// after the state machine changes state to INIT_WRITE
// when there is 0 to 1 transition on INIT_AXI_TXN
INIT_WRITE = 2'b01, // This state initializes write transaction,
// once writes are done, the state machine
// changes state to INIT_READ
INIT_READ = 2'b10, // This state initializes read transaction
// once reads are done, the state machine
// changes state to INIT_COMPARE
INIT_COMPARE = 2'b11; // This state issues the status of comparison
// of the written data with the read data
reg [1:0] mst_exec_state;
// AXI4LITE signals
//AXI4 internal temp signals
reg [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] axi_awaddr;
reg axi_awvalid;
wire[C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] axi_wdata;
reg axi_wlast;
reg axi_wvalid;
wire axi_bready;
reg [C_M_AXI_ADDR_WIDTH-1 : 0] axi_araddr;
reg axi_arvalid;
reg axi_rready;
//write beat count in a burst
reg [C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM : 0] write_index;
//read beat count in a burst
reg [C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM : 0] read_index;
//size of C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN length burst in bytes
wire [C_TRANSACTIONS_NUM+2 : 0] burst_size_bytes;
//The burst counters are used to track the number of burst transfers of C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN burst length needed to transfer 2^C_MASTER_LENGTH bytes of data.
reg [C_NO_BURSTS_REQ : 0] write_burst_counter;
reg [C_NO_BURSTS_REQ : 0] read_burst_counter;
reg start_single_burst_write;
reg start_single_burst_read;
reg writes_done;
reg reads_done;
reg error_reg;
reg compare_done;
reg read_mismatch;
reg burst_write_active;
reg burst_read_active;
reg [C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] expected_rdata;
//Interface response error flags
wire write_resp_error;
wire read_resp_error;
wire wnext;
wire rnext;
reg init_txn_ff;
reg init_txn_ff2;
reg init_txn_edge;
wire init_txn_pulse;
// I/O Connections assignments
//I/O Connections. Write Address (AW)
assign M_AXI_AWID = 'b0;
//The AXI address is a concatenation of the target base address + active offset range
assign M_AXI_AWADDR = C_M_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR + axi_awaddr;
//Burst LENgth is number of transaction beats, minus 1
assign M_AXI_AWLEN = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN - 1;
//Size should be C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH, in 2^SIZE bytes, otherwise narrow bursts are used
assign M_AXI_AWSIZE = clogb2((C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
//INCR burst type is usually used, except for keyhole bursts
assign M_AXI_AWBURST = 2'b01;
assign M_AXI_AWLOCK = 1'b0;
//Update value to 4'b0011 if coherent accesses to be used via the Zynq ACP port. Not Allocated, Modifiable, not Bufferable. Not Bufferable since this example is meant to test memory, not intermediate cache.
assign M_AXI_AWCACHE = 4'b0010;
assign M_AXI_AWPROT = 3'h0;
assign M_AXI_AWQOS = 4'h0;
assign M_AXI_AWUSER = 'b1;
assign M_AXI_AWVALID = axi_awvalid;
//Write Data(W)
assign M_AXI_WDATA = axi_wdata;
//All bursts are complete and aligned in this example
assign M_AXI_WSTRB = {(C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8){1'b1}};
assign M_AXI_WLAST = axi_wlast;
assign M_AXI_WUSER = 'b0;
assign M_AXI_WVALID = axi_wvalid;
//Write Response (B)
assign M_AXI_BREADY = axi_bready;
//Read Address (AR)
assign M_AXI_ARID = 'b0;
assign M_AXI_ARADDR = C_M_TARGET_SLAVE_BASE_ADDR + axi_araddr;
//Burst LENgth is number of transaction beats, minus 1
assign M_AXI_ARLEN = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN - 1;
//Size should be C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH, in 2^n bytes, otherwise narrow bursts are used
assign M_AXI_ARSIZE = clogb2((C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
//INCR burst type is usually used, except for keyhole bursts
assign M_AXI_ARBURST = 2'b01;
assign M_AXI_ARLOCK = 1'b0;
//Update value to 4'b0011 if coherent accesses to be used via the Zynq ACP port. Not Allocated, Modifiable, not Bufferable. Not Bufferable since this example is meant to test memory, not intermediate cache.
assign M_AXI_ARCACHE = 4'b0010;
assign M_AXI_ARPROT = 3'h0;
assign M_AXI_ARQOS = 4'h0;
assign M_AXI_ARUSER = 'b1;
assign M_AXI_ARVALID = axi_arvalid;
//Read and Read Response (R)
assign M_AXI_RREADY = axi_rready;
//Example design I/O
assign TXN_DONE = compare_done;
//Burst size in bytes
assign burst_size_bytes = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN * C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8;
assign init_txn_pulse = (!init_txn_ff2) && init_txn_ff;
//Generate a pulse to initiate AXI transaction.
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
// Initiates AXI transaction delay
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 )
begin
init_txn_ff <= 1'b0;
init_txn_ff2 <= 1'b0;
end
else
begin
init_txn_ff <= INIT_AXI_TXN;
init_txn_ff2 <= init_txn_ff;
end
end
//--------------------
//Write Address Channel
//--------------------
//----------------------------
//Read Address Channel
//----------------------------
//The Read Address Channel (AW) provides a similar function to the
//Write Address channel- to provide the tranfer qualifiers for the burst.
//In this example, the read address increments in the same
//manner as the write address channel.
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 )
begin
axi_arvalid <= 1'b0;
end
end
// Next address after ARREADY indicates previous address acceptance
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
begin
axi_araddr <= 'b0;
end
end
//--------------------------------
//Read Data (and Response) Channel
//--------------------------------
// Forward movement occurs when the channel is valid and ready
assign rnext = M_AXI_RVALID && axi_rready;
// Burst length counter. Uses extra counter register bit to indicate
// terminal count to reduce decode logic
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 || start_single_burst_read)
begin
read_index <= 0;
end
end
/*
The Read Data channel returns the results of the read request
In this example the data checker is always able to accept
more data, so no need to throttle the RREADY signal
*/
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 )
begin
axi_rready <= 1'b0;
end
end
//Check received read data against data generator
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
begin
read_mismatch <= 1'b0;
end
end
//Flag any read response errors
assign read_resp_error = axi_rready & M_AXI_RVALID & M_AXI_RRESP[1];
//----------------------------------------
//Example design read check data generator
//-----------------------------------------
//Generate expected read data to check against actual read data
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)// || M_AXI_RLAST)
expected_rdata <= 'b1;
end
//----------------------------------
//Example design error register
//----------------------------------
//Register and hold any data mismatches, or read/write interface errors
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
begin
error_reg <= 1'b0;
end
end
//--------------------------------
//Example design throttling
//--------------------------------
// For maximum port throughput, this user example code will try to allow
// each channel to run as independently and as quickly as possible.
// However, there are times when the flow of data needs to be throtted by
// the user application. This example application requires that data is
// not read before it is written and that the write channels do not
// advance beyond an arbitrary threshold (say to prevent an
// overrun of the current read address by the write address).
// From AXI4 Specification, 13.13.1: "If a master requires ordering between
// read and write transactions, it must ensure that a response is received
// for the previous transaction before issuing the next transaction."
// This example accomplishes this user application throttling through:
// -Reads wait for writes to fully complete
// -Address writes wait when not read + issued transaction counts pass
// a parameterized threshold
// -Writes wait when a not read + active data burst count pass
// a parameterized threshold
// write_burst_counter counter keeps track with the number of burst transaction initiated
// against the number of burst transactions the master needs to initiate
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 )
begin
write_burst_counter <= 'b0;
end
end
// read_burst_counter counter keeps track with the number of burst transaction initiated
// against the number of burst transactions the master needs to initiate
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
begin
read_burst_counter <= 'b0;
end
end
//implement master command interface state machine
always @ ( posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 1'b0 )
begin
// reset condition
// All the signals are assigned default values under reset condition
mst_exec_state <= IDLE;
start_single_burst_write <= 1'b0;
start_single_burst_read <= 1'b0;
compare_done <= 1'b0;
ERROR <= 1'b0;
end
end //MASTER_EXECUTION_PROC
// burst_write_active signal is asserted when there is a burst write transaction
// is initiated by the assertion of start_single_burst_write. burst_write_active
// signal remains asserted until the burst write is accepted by the slave
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
burst_write_active <= 1'b0;
end
// Check for last write completion.
// This logic is to qualify the last write count with the final write
// response. This demonstrates how to confirm that a write has been
// committed.
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
writes_done <= 1'b0;
end
// burst_read_active signal is asserted when there is a burst write transaction
// is initiated by the assertion of start_single_burst_write. start_single_burst_read
// signal remains asserted until the burst read is accepted by the master
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
burst_read_active <= 1'b0;
end
// Check for last read completion.
// This logic is to qualify the last read count with the final read
// response. This demonstrates how to confirm that a read has been
// committed.
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
begin
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
reads_done <= 1'b0;
end
// Add user logic here
parameter WR_IDLE = 3'b001 ;
parameter JUDGE = 3'b010 ;
parameter WRITE = 3'b100 ;
reg [ 2:0] state ;
reg wr_end ;
reg [63:0] wr_data ;
reg [ 7:0] wr_cnt ;
assign axi_wdata = wr_data;
assign axi_bready = 1'b1;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0)
state <= WR_IDLE;
else case(state)
WR_IDLE : if(init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
state <= JUDGE;
else
state <= WR_IDLE;
JUDGE : state <= WRITE;
WRITE : if(wr_end == 1'b1)
state <= JUDGE;
default : state <= WR_IDLE;
endcase
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
axi_awaddr <= 32'd0;
else if(axi_awaddr == 32'd10485760)
axi_awaddr <= 32'd0;
else if(axi_awvalid == 1'b1 && M_AXI_AWREADY == 1'b1)
axi_awaddr <= axi_awaddr + 2048;
else
axi_awaddr <= axi_awaddr;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
axi_awvalid <= 1'b0;
else if(state == JUDGE)
axi_awvalid <= 1'b1;
else if(M_AXI_AWREADY == 1'b1)
axi_awvalid <= 1'b0;
else
axi_awvalid <= axi_awvalid;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
wr_cnt <= 8'd0;
else if(axi_wvalid == 1'b1 && M_AXI_WREADY == 1'b1)
wr_cnt <= wr_cnt + 1'b1;
else
wr_cnt <= wr_cnt;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
axi_wvalid <= 1'b0;
else if(axi_awvalid == 1'b1 && M_AXI_AWREADY == 1'b1)
axi_wvalid <= 1'b1;
else if(wr_cnt == 'd255 && axi_wvalid == 1'b1 && M_AXI_WREADY == 1'b1)
axi_wvalid <= 1'b0;
else
axi_wvalid <= axi_wvalid;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
wr_data <= 64'd0;
else if(axi_awaddr == 0 && M_AXI_WLAST == 1'b1)
wr_data <= 64'd0;
else if(axi_wvalid == 1'b1 && M_AXI_WREADY == 1'b1)
wr_data <= wr_data + 1'b1;
else
wr_data <= wr_data;
always @(*)
if(wr_cnt == 'd255 && axi_wvalid == 1'b1 && M_AXI_WREADY == 1'b1)
axi_wlast <= 1'b1;
else
axi_wlast <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK)
if(M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1)
wr_end <= 1'b0;
else if(M_AXI_BVALID == 1'b1 && M_AXI_BRESP == 2'b00)
wr_end <= 1'b1;
else
wr_end <= 1'b0;
ila_0 ila_0_inst (
.clk (M_AXI_ACLK ), // input wire clk
.probe0 (axi_awaddr ), // input wire [31:0] probe0
.probe1 (axi_awvalid ), // input wire [0:0] probe1
.probe2 (M_AXI_AWREADY ), // input wire [0:0] probe2
.probe3 (axi_wdata ), // input wire [63:0] probe3
.probe4 (axi_wlast ), // input wire [0:0] probe4
.probe5 (axi_wvalid ), // input wire [0:0] probe5
.probe6 (M_AXI_WREADY ), // input wire [0:0] probe6
.probe7 (M_AXI_BRESP ), // input wire [1:0] probe7
.probe8 (M_AXI_BVALID ), // input wire [0:0] probe8
.probe9 (M_AXI_BREADY ), // input wire [0:0] probe9
.probe10 (state ), // input wire [2:0] probe10
.probe11 (wr_end ), // input wire [0:0] probe11
.probe12 (wr_data ), // input wire [63:0] probe12
.probe13 (wr_cnt ) // input wire [7:0] probe13
);
// User logic ends
endmodule
PS端代码
PS端的代码如下:
/******************************************************************************
*
* Copyright (C) 2009 - 2014 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved.
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
* all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* Use of the Software is limited solely to applications:
* (a) running on a Xilinx device, or
* (b) that interact with a Xilinx device through a bus or interconnect.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
* XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
* WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF
* OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
* SOFTWARE.
*
* Except as contained in this notice, the name of the Xilinx shall not be used
* in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealings in
* this Software without prior written authorization from Xilinx.
*
******************************************************************************/
/*
* helloworld.c: simple test application
*
* This application configures UART 16550 to baud rate 9600.
* PS7 UART (Zynq) is not initialized by this application, since
* bootrom/bsp configures it to baud rate 115200
*
* ------------------------------------------------
* | UART TYPE BAUD RATE |
* ------------------------------------------------
* uartns550 9600
* uartlite Configurable only in HW design
* ps7_uart 115200 (configured by bootrom/bsp)
*/
#include 下板测试
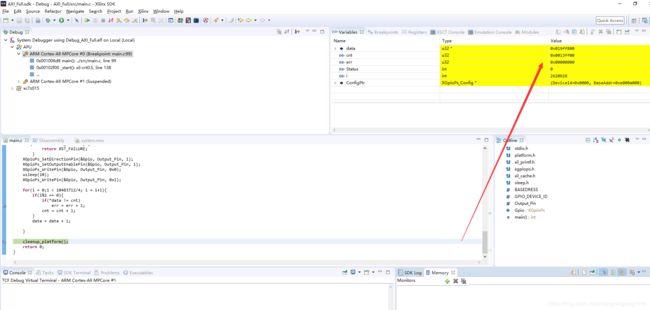
从上面的结果中可以看出,我们利用指针将DDR中的数据依次取出,从而验证了是累计数,进而说明我们实验的正确性。同时可以发现,C语言的运行速度确实远远慢于Verilog语言。
总结
创作不易,认为文章有帮助的同学们可以关注、点赞、转发支持。为行业贡献及其微小的一部分。或者对文章有什么看法或者需要更近一步交流的同学,可以加入下面的群:
![]()