程序每一次操作数据库,都需要创建一个会话,我们用openSession()方法来创建。
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
这里的sqlSessionFactory用到的是默认实现类,在openSessionFromDataSource()方法中创建。
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 创建事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 根据事务工厂和默认的执行器类型,创建执行器 >>
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
这里面包含一个Executor用来执行SQL。Executor又要指定事务类型和执行器的类型。
我们先从Configuration里拿到Environment,environment里面包含事务工厂。
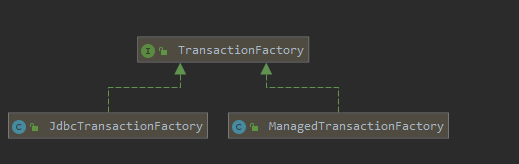
1、创建Transaction
这里会从Environment对象中取出一个TransactionFactory,它是解析 标签的时候创建的。
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 创建事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
事务工厂可以配置为JDBC或者MANAGED。
| 属性 | 工厂类 | 事务 |
|---|---|---|
| JDBC | JdbcTransactionFactory | JdbcTransaction |
| MANAGED | ManagedTransactionFactory | ManagedTransaction |
-
JDBC
会使用Connection对象commit()、rollback()、close()管理事务。
-
MANAGED
会把事务交给容器来管理。比如JBOSS,Weblogin。本地程序不会调用,不会产生事务。
如果是Spring+Mybatis,则不需要配置。我们直接在applicationContext.xml里面配置数据源和事务管理器,覆盖Mybatis的配置。
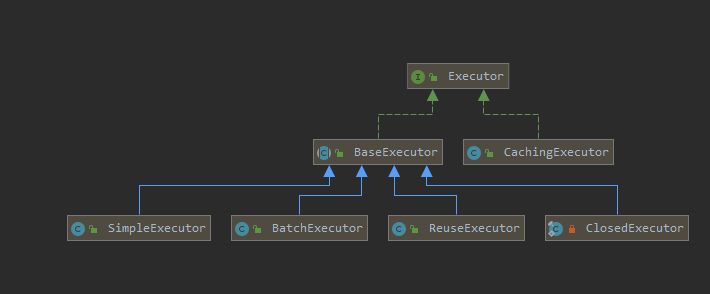
2、创建Executor
使用newExecutor方法创建:
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
-
创建执行器
Executor的基本类型有三种:SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH, 默认是SIMPLE (settingsElement()读取默认值)。
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { // 默认 SimpleExecutor executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); }他们都继承了抽象类BaseExecutor。抽象类实现了Executor接口。
这里调用是让抽象类BaseExecutor实现Executor接口,然后让具体实现类继承抽象类的实现形式是模板方法的体现。
模板方法定义一个算法的骨架,并允许子类为一个或多个步骤提供实现。模板方法使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法的某些步骤。
抽象方法是在子类中实现的,BaseExecutor最终会调用到具体的子类。
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
-
缓存装饰
如果cacheEnabled=true,会对装饰器模式对executor进行装饰。
// 二级缓存开关,settings 中的 cacheEnabled 默认是 true if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } -
插件代理
装饰完毕后,会执行:
// 植入插件的逻辑,至此,四大对象已经全部拦截完毕 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); -
返回SqlSession实现类
最终返回DefaultSqlSession,它的属性包括Configuration、Executor对象。
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
总结
创建会话的过程,我们获得了一个DefaultSqlSession,里面包含了一个Executor,Executor是SQL的实际执行对象。
创建会话
image