数据结构 — 栈
目录
文章目录
- 目录
- 栈
- 栈的特性与结构
- 栈的操作集
- 应用示例:括号匹配问题
栈
首先需要说明本文讨论的栈(Stack)是一种数据结构,而非用户态虚拟存储器中的空间结构。作为数据结构的栈是一种特殊的线性表,其数据成员也与线性表一致。区别在于栈是后进先出的,而线性表允许在任意位置插入和删除数据元素。所以,栈也被称作后进先出的线性表,或简称后进先出表。
栈的一种应用场景就是改变数据元素序列的顺序,其思路就是:顺序的将数据元素压栈,但却根据需要让数据元素按照预期的时机出栈,从而改变它们的序列。
在软件设计中,利用栈来进行数据元素序列转换的例子很多。例如:在编译软件系统中,就需要频繁地把中缀表达式形式的算术表达式,转换成后缀表达式形式的算术表达式。又例如:任何支持递归算法的程序设计语言,都是借助栈来实现递归算法需要的后调用的过程先执行的要求的。
栈的特性与结构
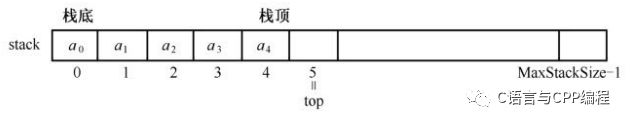
栈的核心特性之一显然就是 后进先出。而栈的结构具有栈底(含元素)、栈顶(不含元素)的概念,入栈和出栈都只能在栈顶完成。
栈的操作集
- 初始化栈(StackInitiate):设定栈长,并将栈顶置零。
- 非空否判断(StackNotEmpty):若堆栈非空,则返回 1,否则返回 0。
- 入栈(StackPush):在栈顶插入数据元素。
- 出栈(StackPop):把栈顶数据元素弹出(删除并返回)。
- 取栈顶数据元素(StackTop):取当前栈顶数据元素(返回,但不删除)。
应用示例:括号匹配问题
假设一个算术表达式中包含圆括号、方括号和花括号三种类型的括号,编写一个函数,用来判别表达式中括号是否正确配对,并设计一个测试主函数。
算法思路: 检验括号是否配对可以设置一个栈,每读入一个括号,如果是左括号,则直接进栈,如果读入的是右括号,并且与当前栈顶的左括号是同类型的,则说明括号是配对的,将栈顶的左括号出栈,否则不配对。如果输入序列已经读完,而栈中仍然有等待配对的左括号,则该括号不配对。
- stack.h
#ifndef __STACK // 避免头文件被多次导入。
#define __STACK
#include - stack.c
#include 编译 libstack 静态库:
gcc -c stack.c --std c99
ar -crv libstack.a stack.o
- main.c
#include 编译 main 程序:
gcc main.c -o main -L./ -lstack
运行:
$ ./main
INPUT >{}
Match successful.
$ ./main
INPUT >[]
Match successful.
$ ./main
INPUT >{{}
Match failed.
$ ./main
INPUT >{{}]
Not symbol match.
$ ./main
INPUT >(())
Match successful.