Linux C/C++编程之(十四)文件操作相关函数
文章目录
- 一、概述
- 二、相关函数
- 1. stat
- 2. access
- 3. chmod
- 4. truncate
- 5. link
- 6. symlink
- 7. readlink
- 8. unlink
- 9. chown
- 10. rename
一、概述
二、相关函数
1. stat
- 作用:获得文件信息,也可以获取文件大小。
- 头文件:

- 参数说明:
- path 文件名
- buf 传出参数,定义结构体 struct stat sb; &sb
- 返回值
- 失败:返回 -1,设置 errno
- 成功:返回 0
注意: stat 碰到链接,会追溯到源文件,穿透!!!lstat 并不会穿透。
stat结构体:

linux 命令 stat 执行结果:

注意三个时间的区别:
time_t st_atime;/* time of last access */ 文件被读,比如cat,open读等
time_t st_mtime;/* time of last modification */ 文件内容发生改变
time_t st_ctime;/* time of last status change */文件属性发生变化,比如大小,权限,硬连接数等
需求:使用stat实现实现 ls -l 的功能?
![]()
在实现的过程中需要获取用户名及组名,因此先看两个函数:
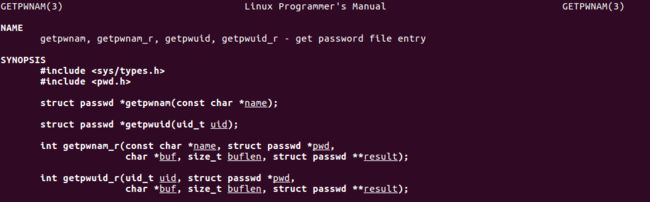
1)getpwuid
返回值
- 失败:返回NULL
- 成功:返回 struct passwd * 结构体指针
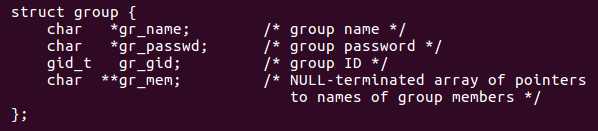
2)getgrgid
参数说明:
- gid用户组的gid
返回值
- 失败:返回NULL
- 成功:返回 struct group * 结构体指针
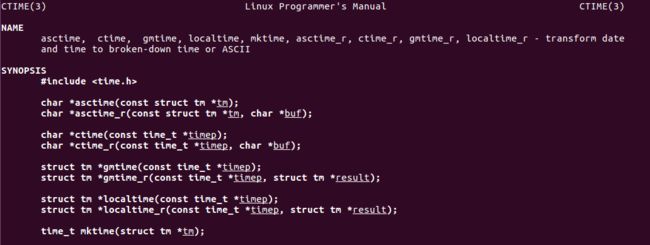
参数说明:
- timep:一个时间相关的结构体
返回值
- 失败:返回NULL
- 成功:返回 struct tm * 结构体指针
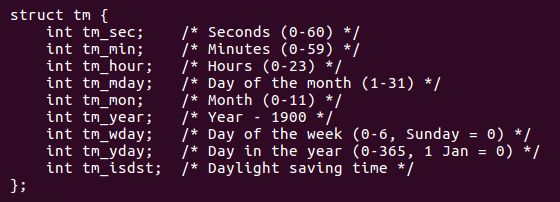
传入参数 timep 对应stat函数得到的结构体的秒数(time_t类型)。
#include2. access
返回值
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno
- 成功:如果有权限或者文件存在,对应返回0
#include3. chmod
4. truncate
参数说明:
- path文件名
- length长度,长度如果大于原文件,直接拓展,如果小于原文件,截断为length长度。
返回值
- 成功:返回0
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno
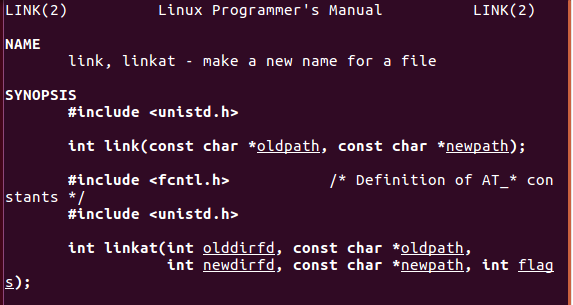
5. link
参数说明:
- oldpath原文件
- newpath硬连接文件
返回值
- 成功:返回0
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno
6. symlink
参数解释:
- oldpath原文件
- newpath创建软连接文件
返回值
- 成功:返回0
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno
7. readlink
参数解释:
- path链接名
- buf缓冲区
- bufsiz缓冲区大小
返回值
- 成功:返回buf填充的大小
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno
8. unlink
函数参数:
- pathname 链接名,文件也可以
返回值
- 成功:返回0
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno
#include9. chown
函数参数:
- path文件名
- owner用户ID,/etc/passwd
- owner组ID,/etc/group
返回值
- 成功:返回0
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno
10. rename
参数说明:
- oldpath文件名
- newpath文件新名
返回值
- 成功:返回0
- 失败:返回-1,设置errno