三、Map(JDK1.7HashMap扩容问题)
参考文献:
JAVA HASHMAP的死循环
老生常谈,HashMap的死循环
public V put(K key, V value) {
//初始化
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//存放key=null的元素
if (key == null){
return putForNullKey(value);
}
//获取hash值
int hash = hash(key);
//根据hash & length-1 得到将要存放的位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//遍历该位置的链表,看是否有相同的key存在
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//有相同key存在,替换旧的value值
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
//添加元素
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
hash()——5次异或,4次位运算
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
添加元素,检查是否需要扩容
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//检查是否达到扩容的阈值,进行扩容
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//扩容,参数为原来数组长度的2倍
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//不扩容直接添加
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
添加新元素(未扩容)
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//将当前位置的节点赋值给e
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
//然后当前位置用新的节点(要插入的节点)代替,新节点的next就是原节点e
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
扩容
//扩容:newCapacity,原来长度的2倍
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
//新的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//将元数组中的元素转移到新的数组中
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
转移原数组
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
//遍历原数组table,用e指向每次遍历到的桶的头结点
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
//当遍历到的e不为null的时候,此位置的所有元素(桶)全部移动到新数组
while(null != e) {
//next指向当前元素e的下一个节点(链表)
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
//新的下标
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
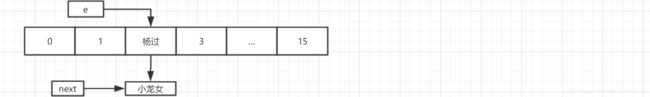
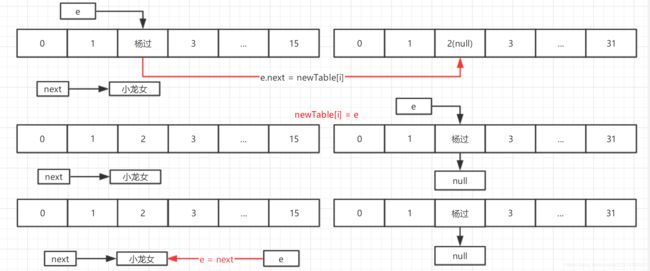
单线程下扩容过程,假设扩容后下标index=2
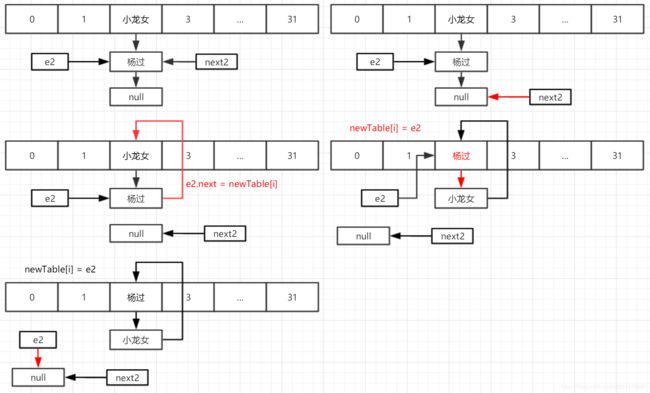
多线程下扩容过程,假设扩容后下标index=2
假设线程二扩容运行到Entry这行代码时阻塞,线程一完成扩容
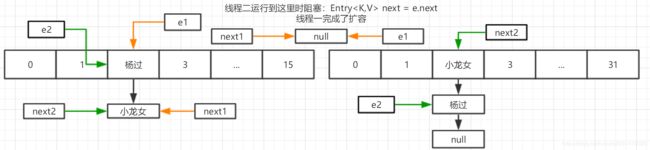
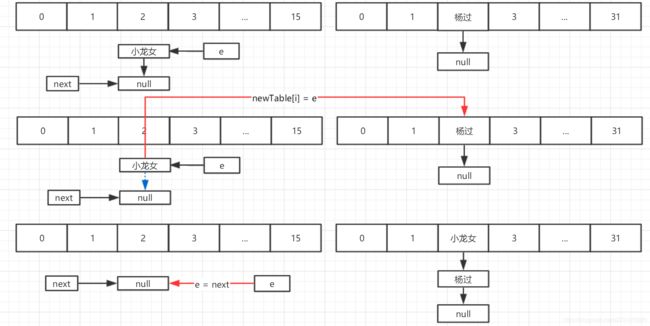
线程二继续运行第一次循环
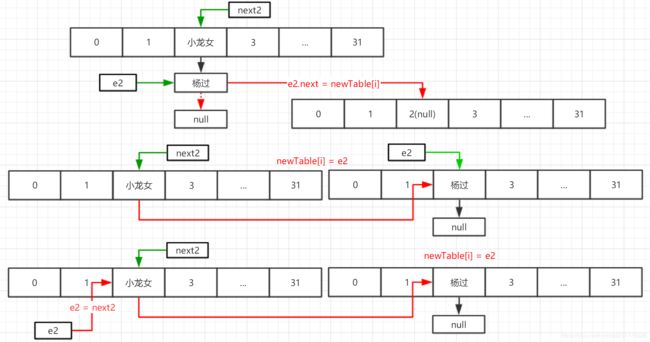
第二次循环
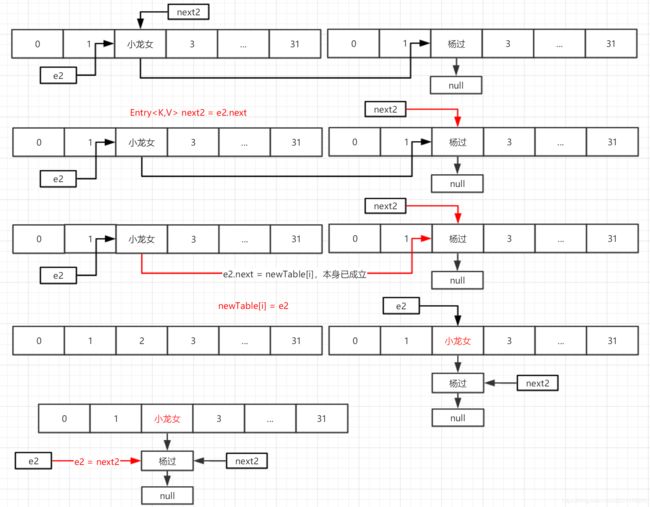
第三次循环(左右看)