四种读写文件的方式:系统调用(open/read/write),C语言(fopen,fgets, fputs),C++(ifstream, ofstream getline,)泛型算法
第一种方法是系统调用
(1)open系统调用
原型:
#include
#include
#include
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
作用:
用flag 的方式打开路径名为path 的文件
参数:
第一个参数是路径名,第二个参数是打开文件的方式(O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, O_RDWR)
(2)read 系统调用
原型:
#include
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
作用:
把文件描述符所描述的文件里面的内容读到buf 里面,指定读count 个字节
小插曲:
字节和字符的区别
(a)"字节":字节是一种计量单位,表示数据量的多少,是计算机用来存储容量的一种计量单位
(b)"字符":计算机使用的文字和符号
(c)区别:
ASCII 码中,一个英文字母占一个字节的空间,一个中文汉字占两个字节的空间
UTF_8 编码中,一个英文字母等于一个字节,一个中文字母等于三个字节
UNicode编码中,一个英文等于两个字节,一个中文等于两个字节,英文标点占一个字节,中文标点占两个字节
UTF-16 编码中,一个英文字母或者一个汉字都需要两个字节
UTF-32编码中,世界上任何字符的存储都需要4个字节
(3)write 系统调用
原型:
#include
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
作用:
把buffer 中count 字节的数据写到fd 文件描述符所指的文件中
测试:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
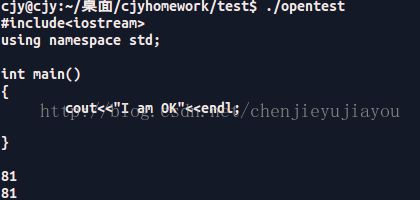
int fd1 = open("/home/cjy/test.cpp", O_RDONLY);
int fd2 = open("/home/cjy/test1.cpp", O_WRONLY);
char buf[10240];
size_t nread = read(fd1, buf, 10240);
size_t nwrite = write(fd2, buf, nread);
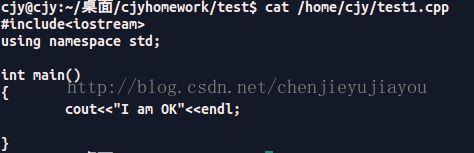
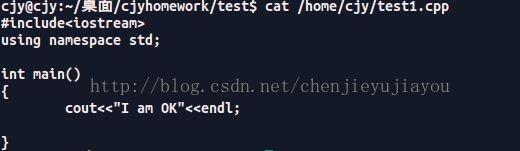
cout< 我们再来看一下test1.cpp 里面的内容
OK,验证成功
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
第二种方法是C语言文件的操作(fopen/fgets/fputs)
(1)fopen函数
原型:
#include
FILE *fopen(const char *path, const char *mode);
作用:以mode 的方式打开路径名为path 的文件
(2)fgets函数
原型:
char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream);
功能:从stream 所指的文件中读取大于1小于size 的字节数,把它们存储到s 中,读取到EOF标志或者读取到新的一行的时候,读取结束,‘\0’被存储在最后
(3)fputs函数
原型:
int fputs(const char *s, FILE *stream);
功能:把s所指的缓冲区的内容读取到stream 所指的文件中,直到遇到‘\0’就结束
成功返回一个非负的数字,失败则返回EOF
代码验证:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
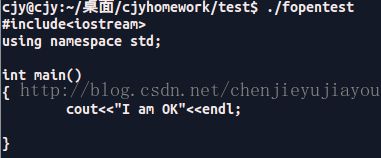
FILE *fp1 = fopen("/home/cjy/test.cpp", "r");
FILE *fp2 = fopen("/home/cjy/test1.cpp", "w");
char s[10240];
while(fgets(s,10240, fp1))
{
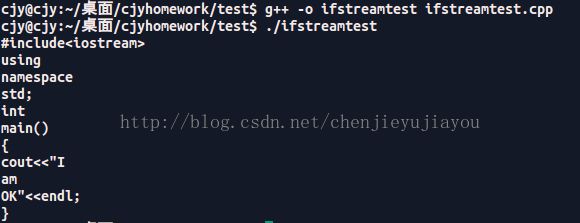
cout< 结果:
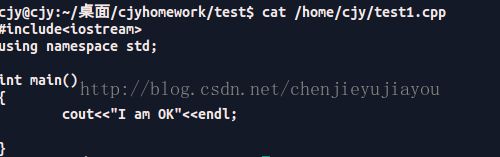
对比test1.cpp 的内容
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
第三种方法是:C++里面的ifstream
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream fin("/home/cjy/test.cpp");
ofstream fout("/home/cjy/test1.cpp");
string s;
while(getline(fin, s))
{
fout< ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
第四中方法是泛型算法
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream fin("/home/cjy/test.cpp");
vectorcontent;
istream_iteratorbegin(fin);
istream_iteratorend;
copy(begin, end, back_inserter(content));
copy(content.begin(), content.end(), ostream_iterator(cout, "\n"));
return 0;
} 也可以用继承和重载的方法:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class myline:public string{};
istream& operator>>(istream &is, myline &line)
{
getline(is, line);
return is;
}
int main()
{
ifstream fin("/home/cjy/test.cpp");
istream_iteratorbegin(fin);
istream_iteratorend;
vector content;
copy(begin, end, back_inserter(content));
copy(content.begin(), content.end(), ostream_iterator(cout, "\n"));
return 0;
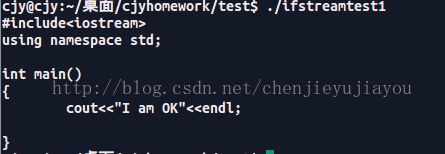
} 结果验证: