Java的ConcurrentHashMap 底层了解
最近有人问Java8 中ConcurrentHashMap 底层实现,这里简单列下。
大家都知道 Java8 对 HashMap 、ConcurrentHashMap 进行了改进,前者非线程安全,后者线程安全。
HashMap
Java7
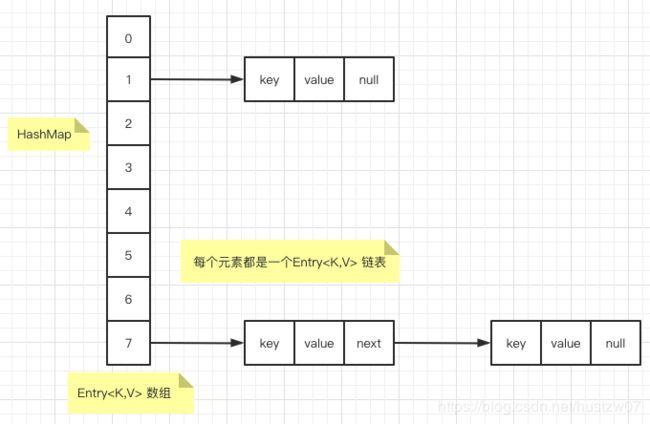
在Java 7 中,采用哈希表结构:即 数组 + 链表
先看源码
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* An empty table instance to share when the table is not inflated.
*/
static final Entry[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
/**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
*/
transient Entry[] table = (Entry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* @serial
*/
// If table == EMPTY_TABLE then this is the initial capacity at which the
// table will be created when inflated.
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor; 这里是对容量、加载因子、大小、容量等属性的定义,其中 transient Entry
而向 HashMap 添加元素时,则是对链表的遍历。(查找、删除类似)
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
Java8
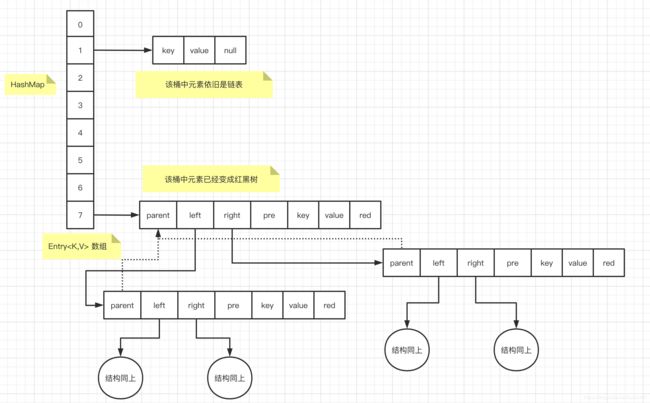
在Java 8 中,采用哈希表 + 红黑树
在元素少的时候,跟Java 7 一样,当元素个数达到8 时,开始调整成红黑树
元素少时,使用普通结点类 Node
/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node implements Map.Entry {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
} Node 里 只有 next 指向下一个元素。
当继续增加元素超过阈值时,调整。同时使用新的节点类型:
/**
* Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn
* extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or
* linked node.
*/
static final class TreeNode extends LinkedHashMap.Entry {
TreeNode parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
/**
* Returns root of tree containing this node.
*/
final TreeNode root() {
for (TreeNode r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null)
return r;
r = p;
}
}
} 有左右节点,也就是树。那什么时候调整的呢?看添加元素代码:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)// 初始化
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // 桶中第一个元素
else {
Node e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) // 在红黑树中查找
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {// 在链表中查找
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash); // 此时开始将将链表改成树使用
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
} 注意:这里将链表 为 红黑树时,是对同一个桶的元素来的。结构类似如下:
这里简单把节点属性标注下。
ConcurrentHashMap
Java7
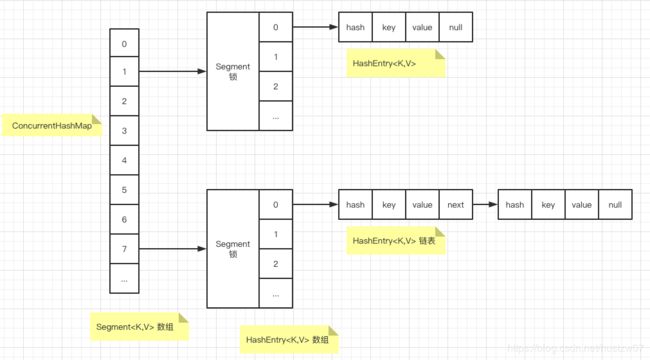
在Java 7 中,采用分段的哈希表
简单来说,有点类似两层哈希表:
源码如下:
/**
* Mask value for indexing into segments. The upper bits of a
* key's hash code are used to choose the segment.
*/
final int segmentMask;
/**
* Shift value for indexing within segments.
*/
final int segmentShift;
/**
* The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table.
*/
final Segment[] segments;
// 这三个元素是展示用
transient Set keySet;
transient Set> entrySet;
transient Collection values; 这里定义一个 Segment
static final class Segment extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
// 其他
/**
* The per-segment table. Elements are accessed via
* entryAt/setEntryAt providing volatile semantics.
*/
transient volatile HashEntry[] table;
/**
* The number of elements. Accessed only either within locks
* or among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.
*/
transient int count;
/**
* The total number of mutative operations in this segment.
* Even though this may overflows 32 bits, it provides
* sufficient accuracy for stability checks in CHM isEmpty()
* and size() methods. Accessed only either within locks or
* among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.
*/
transient int modCount;
/**
* The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold.
* (The value of this field is always (int)(capacity *
* loadFactor).)
*/
transient int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table. Even though this value
* is same for all segments, it is replicated to avoid needing
* links to outer object.
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;
Segment(float lf, int threshold, HashEntry[] tab) {
this.loadFactor = lf;
this.threshold = threshold;
this.table = tab;
}
} 每次增加、删除元素时,对 Segment 加锁,然后对其下的 HashEntry
数据结构如下:
一般情况下 ConcurrentHashMap 默认 16个段。
对 ConcurrentHashMap 添加元素源码如下,先hash 找到哪个段,然后调用段的 put 方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, false); // 在段中 增加元素
} 而 Segment 的 put 方法,则是:加锁、操作、解锁。三步:
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
Java8
在Java 8 中,采用数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
跟HashMap 相比,两者类似,讲下ConcurrentHashMap,先看源码:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();// 判断key value 均不空
int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); // 对hashCode 进行哈希
int binCount = 0;
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) // 首次插入元素,初始化数据结构
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {// 应该插入的位置为 null,直接插入且不需要加锁
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node(hash, key, value, null)))// 注意:这里把 hash 当作构造Node的参数,说明是普通的链表节点
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)// 说明这个点已经被处理过了 这里是控制并发扩容的核心
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);// 当前线程也参与扩容
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {// 要放入的元素存在
if (fh >= 0) { // 链表节点:Node的构造参数中,各个子类的hash 不同
binCount = 1;
for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) { // 遍历链表
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { // 找到节点
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) { // 遍历下一个节点直到结束也没有找到,则插入
pred.next = new Node(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { // 红黑树
Node p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)// 元素个数 >= 8 时,
treeifyBin(tab, i); // 链表 => 红黑树
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
} 在 添加元素的时候才执行了 initTable 函数,而 ConcurrentHashMap 的构造函数只是设置几个参数而已。
/**
* Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
*/
private final Node[] initTable() {
Node[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node[] nt = (Node[])new Node[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
} 从代码可知,初始化时,也只是创建了一个空的 Node
回过头,看 put 函数的代码最后,可知:只有当元素个数 大于等于8 时,才会将 链表转成 红黑树
接下来看下,在红黑树中添加元素:
/**
* Finds or adds a node.
* @return null if added
*/
final TreeNode putTreeVal(int h, K k, V v) {
Class kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
for (TreeNode p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if (p == null) { // 避免空树
first = root = new TreeNode(h, k, v, null, null);
break;
}
else if ((ph = p.hash) > h) // 红黑树是根据元素的 hashCode 的 hash 构建的
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h) // 判断是在 左子树 还是 右子树 中查找
dir = 1;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk))) // 刚好是当前节点,则返回
return p;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) { // 对于 key 是“两个相同的对象” 情况,因为 == 比较的是地址
if (!searched) {
TreeNode q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null) || // 在左子树中找到
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null)) // 在右子树中找到
return q;
}
// 用这个方法来比较两个对象,目的是一定要比较出两个对象的大小!也即是一必须要确定要插入的节点是左节点,还是右节点
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);//
}
TreeNode xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { // 循环找到叶子结点
TreeNode x, f = first;
first = x = new TreeNode(h, k, v, f, xp);
if (f != null)
f.prev = x;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
if (!xp.red)
x.red = true;
else {
lockRoot();
try {
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);// 调整树
} finally {
unlockRoot();
}
}
break;
}
}
assert checkInvariants(root);
return null;
} 简单来说:
1.如果找到,则返回结点。注意:返回的是结点
2.如果没找到,则比较hash 肯定能找到一个合适位置,并插入。然后调整红黑树
这个设计几个结点类,且都是 ConcurrentHashMap 的内部类,
Node :普通结点,链表时使用。下边几个类的父类,hash 字段 为 对象的 hashCode
ForwardingNode :用于rehashing 使用。 hash 字段 为 MOVED
ReservationNode hash 字段为 RESERVED
TreeBin : hash 字段为 TREEBIN
TreeNode :hash 字段 为参数