Openstack-nova
Openstack
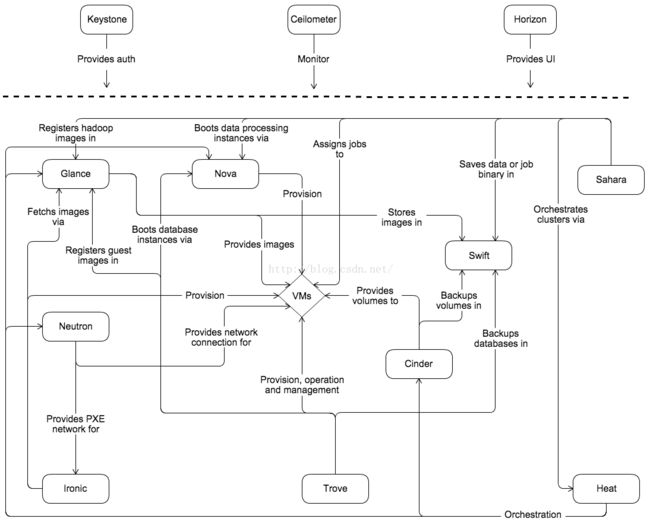
1.1 提供的服务
| Service | Project name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dashboard | Horizon | Provides a web-based self-service portal to interact with underlying OpenStack services, such as launching an instance, assigning IP addresses and configuring access controls. |
| Compute | Nova | Manages the lifecycle of compute instances in an OpenStack environment. Responsibilities include spawning, scheduling and decommissioning of virtual machines on demand. |
| Networking | Neutron | Enables Network-Connectivity-as-a-Service for other OpenStack services, such as OpenStack Compute. Provides an API for users to define networks and the attachments into them. Has a pluggable architecture that supports many popular networking vendors and technologies. |
| Object Storage | Swift | Stores and retrieves arbitrary unstructured data objects via a RESTful, HTTP based API. It is highly fault tolerant with its data replication and scale-out architecture. Its implementation is not like a file server with mountable directories. In this case, it writes objects and files to multiple drives, ensuring the data is replicated across a server cluster. |
| Block Storage | Cinder | Provides persistent block storage to running instances. Its pluggable driver architecture facilitates the creation and management of block storage devices. |
| Identity service | Keystone | Provides an authentication and authorization service for other OpenStack services. Provides a catalog of endpoints for all OpenStack services. |
| Image service | Glance | Stores and retrieves virtual machine disk images. OpenStack Compute makes use of this during instance provisioning. |
| Telemetry | Ceilometer | Monitors and meters the OpenStack cloud for billing, benchmarking, scalability, and statistical purposes. |
| Orchestration | Heat | Orchestrates multiple composite cloud applications by using either the native HOT template format or the AWS CloudFormation template format, through both an OpenStack-native REST API and a CloudFormation-compatible Query API. |
| Database service | Trove | Provides scalable and reliable Cloud Database-as-a-Service functionality for both relational and non-relational database engines. |
| Data processing service | Sahara | Provides capabilities to provision and scale Hadoop clusters in OpenStack by specifying parameters like Hadoop version, cluster topology and nodes hardware details. |
1.2 Openstack version:
1.3
1.4 openstack 架构图
http://docs.openstack.org/openstack-ops/content/figures/2/figures/osog_0001.png
二、Nova
是OpenStack云中的计算组织控制器。OpenStack云中实例(instances)生命周期的所有活动都由Nova处理。这样使得Nova成为一个负责管理计算资源、网络、认证、所需可扩展性的平台。但是,Nova自身并没有提供任何虚拟化能力,相反它使用libvirt API来与被支持的Hypervisors交互。Nova通过一个与Amazon Web Services(AWS)EC2 API兼容的web services API来对外提供服务。
2.1 提供的服务:
http://docs.openstack.org/admin-guide-cloud/common/get_started_compute.html
Use OpenStack Compute to host and manage cloud computing systems. OpenStack Compute is a major part of an Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) system. The main modules are implemented in Python.
OpenStack Compute interacts with OpenStack Identity for authentication; OpenStack Image service for disk and server images; and OpenStack dashboard for the user and administrative interface. Image access is limited by projects, and by users; quotas are limited per project (the number of instances, for example). OpenStack Compute can scale horizontally on standard hardware, and download images to launch instances.
OpenStack Compute consists of the following areas and their components:
- nova-api service
- Accepts and responds to end user compute API calls. The service supports the OpenStack Compute API , the Amazon EC2 API , and a special Admin API for privileged users to perform administrative actions. It enforces some policies and initiates most orchestration activities, such as running an instance.
- nova-api-metadata service
- Accepts metadata requests from instances. The nova-api-metadata service is generally used when you run in multi-host mode with nova-network installations. For details, see Metadata service in the OpenStack Cloud Administrator Guide.
- nova-compute service
-
A worker daemon that creates and terminates virtual machine instances through hypervisor APIs. For example:
- XenAPI for XenServer/XCP
- libvirt for KVM or QEMU
- VMwareAPI for VMware
Processing is fairly complex. Basically, the daemon accepts actions from the queue and performs a series of system commands such as launching a KVM instance and updating its state in the database.
-
Compute Worker处理管理实例生命周期。他们通过Message Queue接收实例生命周期管理的请求,并承担操作工作。在一个典型生产环境的云部署中有一些compute workers。一个实例部署在哪个可用的compute worker上取决于调度算法。
- nova-scheduler service
- Takes a virtual machine instance request from the queue and determines on which compute server host it runs.
-
调度器Scheduler把nova-API调用映射为OpenStack组件。调度器作为一个称为nova-schedule守护进程运行,通过恰当的调度算法从可用资源池获得一个计算服务。Scheduler会根据诸如负载、内存、可用域的物理距离、CPU构架等作出调度决定。nova scheduler实现了一个可插入式的结构。
当前nova-scheduler实现了一些基本的调度算法:
随机算法:计算主机在所有可用域内随机选择
可用域算法:跟随机算法相仿,但是计算主机在指定的可用域内随机选择。
简单算法:这种方法选择负载最小的主机运行实例。负载信息可通过负载均衡器获得。 - nova-conductor module
- Mediates interactions between the nova-compute service and the database. It eliminates direct accesses to the cloud database made by the nova-compute service. The nova-conductor module scales horizontally. However, do not deploy it on nodes where the nova-compute service runs. For more information, see Configuration Reference Guide.
- nova-cert module
- A server daemon that serves the Nova Cert service for X509 certificates. Used to generate certificates for euca-bundle-image. Only needed for the EC2 API.
- nova-network worker daemon
- Similar to the nova-compute service, accepts networking tasks from the queue and manipulates the network. Performs tasks such as setting up bridging interfaces or changing IPtables rules.
- nova-consoleauth daemon
- Authorizes tokens for users that console proxies provide. See nova-novncproxy and nova-xvpvncproxy. This service must be running for console proxies to work. You can run proxies of either type against a single nova-consoleauth service in a cluster configuration. For information, see About nova-consoleauth.
- nova-novncproxy daemon
- Provides a proxy for accessing running instances through a VNC connection. Supports browser-based novnc clients.
- nova-spicehtml5proxy daemon
- Provides a proxy for accessing running instances through a SPICE connection. Supports browser-based HTML5 client.
- nova-xvpvncproxy daemon
- Provides a proxy for accessing running instances through a VNC connection. Supports an OpenStack-specific Java client.
- nova-cert daemon
- x509 certificates.
- euca2ools client
- A set of command-line interpreter commands for managing cloud resources. Although it is not an OpenStack module, you can configure nova-api to support this EC2 interface. For more information, see the Eucalyptus 3.4 Documentation.
- nova client
- Enables users to submit commands as a tenant administrator or end user.
- The queue
- A central hub for passing messages between daemons. Usually implemented with RabbitMQ, but can be implemented with an AMQP message queue, such as Apache Qpid or Zero MQ.
-
OpenStack
节点之间通过消息队列使用
AMQP
(
Advanced Message Queue Protocol
)完成通信。
Nova
通过异步调用请求响应,使用回调函数在收到响应时触发。因为使用了异步通信,不会有用户长时间卡在等待状态。这是有效的,因为许多
API
调用预期的行为都非常耗时,例如加载一个实例,或者上传一个镜像。
- SQL database
-
Stores most build-time and run-time states for a cloud infrastructure, including:
- Available instance types
- Instances in use
- Available networks
- Projects
Theoretically, OpenStack Compute can support any database that SQL-Alchemy supports. Common databases are SQLite3 for test and development work, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
实例生命周期管理
管理计算资源
网络和认证管理
REST 风格的 API
异步的一致性通信
Hypervisor 透明:支持 Xen,XenServer/XCP, KVM, UML, VMware vSphere and Hyper-V
三、Nova结构
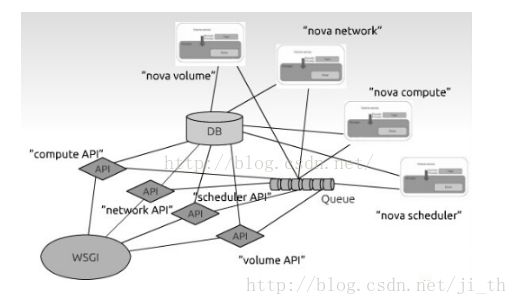
nova是云主机控制器。它包含了很多组件,API服务器(nova-api),计算服务器(nova-compute),网络控制器(nova-network),调度器(nova-schedule),消息队列以及DashBoard。
3.1OpenStack Compute逻辑框架
总的来说,nova的各个组件是以数据库和队列为中心进行通信的,下面对其中的几个组件做一个简单的介绍:
Queue,也就是消息队列,它就像是网络上的一个hub,nova各个组件之间的通信几乎都是靠它进行的,当前的Queue是用RabbitMQ实现的,它和database一起为各个守护进程之间传递消息。
database存储云基础架构中的绝大多数状态。这包括了可用的实例类型,在用的实例,可用的网络和项目。当前广泛使用的数据库是sqlite3(仅适合测试和开发工作)、MySQL和PostgreSQL。
nova-compute负责决定创造虚拟机和撤销虚拟机,通过运行一系列系统命令(例如发起一个KVM实例,)并把这些状态更新到nova-database中去,其过程相当复杂,但是基本原理很简单。
nova-schedule负责从queue里取得虚拟机请求并决定把虚拟机分配到哪个服务器上去。schedule的算法可以自己定义,目前有Simple (最少加载主机),chancd(随机主机分配) ,zone(可用区域内的随机节点)等算法。
nova-api守护进程是OpenStack Compute的中心。它为所有API查询提供一个入口, 并且同时支持OpenStack API 和 Amazon EC2 API。
Glance:该项目独立于Openstack Compute,起到镜像的作用。在该项目中,主要包括三个部分: glance-api, glance-registry and 镜像存储。Glance-api接受API调用,glance-registry存储和检索镜像的元数据。镜像存储Image blobs。存储可以选择不同的存储方案,比如用Swift实现存储。
2.2 运行架构
nova-api对外统一提供标准化接口,各子模块,如计算资源,存储资源和网络资源子模块通过相应的API接口服务对外提供服务。
这里的WSGI就是nova-api。API接口操作DB实现资源数据模型的维护。通过消息中间件,通知相应的守护进程如nova-compute等实现服务接口。API与守护进程共享DB数据库,但守护进程侧重维护状态信息,网络资源状态等。守护进程之间不能直接调用,需要通过API调用,如nova-compute为虚拟机分配网络,需要调用network-api,而不是直接调用nova-network,这样有易于解耦合。
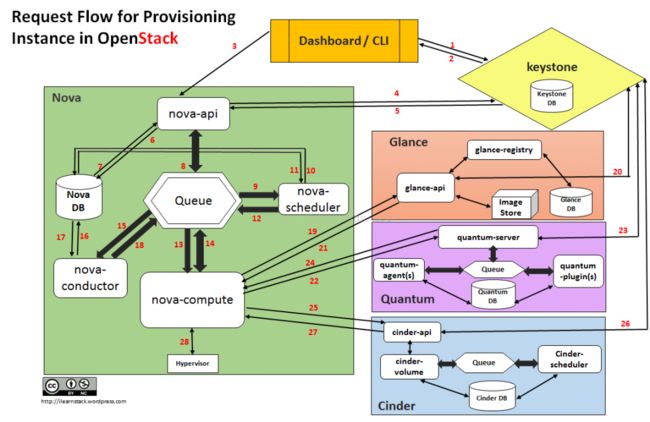
下面以创建虚拟机为例,分析Nova的不同关键子模块之间的调用关系。因为启动一个新的instance涉及到很多openstacknova里面的组件共同协作。
1、通过调用nova-api创建虚拟机接口,nova-api对参数进行解析以及初步合法性校验,调用compute-api创建虚拟机VM接口,compute-api根据虚拟机参数(CPU,内存,磁盘,网络,安全组等)信息,访问数据库创建数据模型虚拟机实例记录(创建1个虚拟机实例)
2、接下来需要调用具体的物理机实现虚拟机部署,在这里就会涉及调度模块novascheduler,compute-api通过RPC的方式将创建虚拟机的基础信息封装成消息发送至消息中间件指定消息队列“scheduler”。
3.nova-scheduler订阅了消息队列“scheduler”的内容,接受到创建虚拟机的消息后,进行过滤,根据请求的虚拟资源,即flavor的信息。scheduler会找到一个可用的主机,如果没有找到就设置虚拟机的状态设置成ERROR选择一台物理主机部署,如果有主机,如物理主机A。nova-scheduler将虚拟机基本信息,所属物理主机信息发送至消息中间件指定消息队列“compute.物理机A”
4.物理机A上nova-compute守护进程订阅消息队列“compute.物理机A”,接到消息后,根据虚拟机基本信息开始创建虚拟机
5.nova-compute调用network-api分配网络ip
6.nova-network接收到消息就,从fixedIP表(数据库)里拿出一个可用IP,nova-network根据私网资源池,结合DHCP,实现IP分配和IP地址绑定
7.nova-compute通过调用volume-api实现存储划分,最后调用底层虚拟化Hypervisor技术,部署虚拟机。
四、Nova命令行
4.1 用户管理
用户管理
创建管理员用户
用法: nova-manage user admin name [access] [secret]
其中access 和secret可选,没有的话系统会自动生成一个。
创建普通用户
用法:nova-manage user create name [access] [secret]
access和secret可选
删除一个存在的用户
用法: nova-manage user delete username
显示一个用户的accesskey和secretkey
用法:nova-manage user exports username
显示所有用户
用法:nova-manage user list
修改用户的secretkey,accesskey,和管理员标志
用法:nova-manage user modify name access secret is_admin
is_admin:是否改为管理员 ,取值 'T' 或者'F'
任何参数留空(表示为'')就会忽略掉这个参数的修改
例如:nova-manage user modify test1 '' secret '' 表示修改test1的密码为secret
废除一个用户证书
用法:nova-manage user revoke userid
project 管理
添加一个用户到一个project
用法:nova-manage project add project_id user_id
创建一个project
用法:nova-manage project create name project_manager [description]
nama : project id
project_manager :一个user id,作为project 管理者
[description] :可选,描述信息
删掉一个存在的project
用法:nova-manage project delete projectname
获取一个用户和它对应的project的环境变量,返回一个novarc(默认)文件
用法:nova-manage project environment project_id user_id [filename='novarc]
project 列表
用法:nova-manage project list
修改一个project
用法:nova-manage project modify name project_manager [description]
修改该project的project管理员为新的user,使新的用户拥有projectmanager角色
显示一个project的相关信息
nova-manage project quota project_id [key] [value]
例如:root@ubuntu10:~# nova-manage project quota testproject
metadata_items: 128
gigabytes: 1000
floating_ips: 10
instances: 10
volumes: 10
cores: 20
从一个project中移除一个user
用法:nova-manage project remove project_id user_id
删除与某个project相关的数据(如网络地址等)
用法:nova-manage project scrub project_id
把用户的userid和projectid及其相关证书,压缩到一个文件中
用法:nova-manage project zipfile project_id user_id [filename='nova.zip']
例如:nova-manage project zipfile testproject test1 creds/novatest1.zip
account 管理
功能类似于project管理,不太明白它们之间的区别
nova-manage account add 添加用户到project
nova-manage account create 创建一个新的project
nova-manage account delete 删除project
nova-manage account environment 生成一个环境变量文件
nova-manage account list 显示project
nova-manage account modify 修改一个project的管理员
nova-manage account quota 设置或者显示定额
nova-manage account remove 从一个project中删除某个用户
nova-manage account scrub 删除与一个project相关的数据,例如网络等。。
nova-manage account zipfile 把登录project的用户证书压缩到.zip
role 管理
openstack的用户角色有六种,分别是Cloud Administrator(cloudadmin 云管理员),IT Security(itsec ,it安全管理),System Administrator (sysadmin,系统管理),Network Administrator(netadmin,网络管理员),Developer(开发者),Project Manager(projectmanager, 创建工程时的默认角色,工程管理员)
给一个用户添加某个角色
用法:nova-manage role add user role [project]
若指定project,那么就是添加project上的角色
判断一个用户是否有某个角色
用法:nova-manage role has user role [project]
判断user是否具有role角色,如果指定了project,那么只有当user拥有全局角 色和project角色时,才返回真,对于判断角色projectmanager,必须指定project.
删除一个用户的角色
用法:nova-manage role remove user role [project]
若指定project,那么就是删除user在project上的这个角色
network 管理
创建用于分配的ip地址池,类似于虚拟机内网。
用法:nova-manage network create fixed_range=FLAG, [num_networks=FLAG],
[network_size=FLAG], [vlan_start=FLAG],
[_start=FLAG], [fixed_range_v6=FLAG]
例如:nova-manage network create 172.16.0.1/24 1 256
创建172.16.0.1/24内的1个网络,256个ip地址
其他的参数目前还没用过。
显示创建的网络
用法:nova-manage network list
删除一个网络
用法:nova-manage network delete network
fixed_range :就是上面list时显示的
例如:nova-manage network delete 172.16.0.1/24
注意:如果删除网络,并不会把数据库中的fixed_ips表的ip地址删掉,需要手动删除。
上面是固定ip的管理,下面是floating ip(浮动ip?)的管理
创建一定范围内的浮动ip,可以是一个,也可以是一组。
用法:nova-manage floating create host ip_range
例如: nova-manage floating create ubuntu10 192.168.1.20/32
删除一个浮动ip,或者一组浮动ip
用法:nova-manage floating delete ip_range
列出所有浮动ip
用法:nova-manage floating list
4.2 常用命令
openstack nova 命令有很多方便查找,这里记录一下。
absolute-limits Print a list of absolute limits for a user
actions Retrieve server actions.
add-fixed-ip Add new IP address to network.
add-floating-ip Add a floating IP address to a server.
add-secgroup Add a Security Group to a server.
aggregate-add-host Add the host to the specified aggregate.
aggregate-create Create a new aggregate with the specified details.
aggregate-delete Delete the aggregate by its id.
aggregate-details Show details of the specified aggregate.
aggregate-list Print a list of all aggregates.
aggregate-remove-host Remove the specified host from the specified aggregate.
aggregate-set-metadata Update the metadata associated with the aggregate.
aggregate-update Update the aggregate's name and optionally availability zone.
boot Boot a new server.
cloudpipe-create Create a cloudpipe instance for the given project
cloudpipe-list Print a list of all cloudpipe instances.
cloudpipe-update Update a cloudpipe instance
console-log Get console log output of a server.
credentials Show user credentials returned from auth
delete Immediately shut down and delete a server.
diagnostics Retrieve server diagnostics.
dns-create Create a DNS entry for domain, name and ip.
dns-create-private-domain Create the specified DNS domain.
dns-create-public-domain Create the specified DNS domain.
dns-delete Delete the specified DNS entry.
dns-delete-domain Delete the specified DNS domain.
dns-domains Print a list of available dns domains.
dns-list List current DNS entries for domain and ip or domain and name.
endpoints Discover endpoints that get returned from the authenticate services
fixed-ip-get Show information for a fixed IP
fixed-ip-reserve Reserve a fixed IP
fixed-ip-unreserve Unreserve fixed IP
flavor-create Create a new flavor
flavor-delete Delete a specific flavor
flavor-key Set or unset extra_spec for a flavor.
flavor-list Print a list of available 'flavors' (sizes of servers).
flavor-show Show details about the given flavor.
floating-ip-create Allocate a floating IP for the current tenant.
floating-ip-delete De-allocate a floating IP.
floating-ip-list List floating ips for this tenant.
floating-ip-pool-list List all floating ip pools.
get-vnc-console Get a vnc console to a server.
host-action Perform a power action on a host.
host-describe Describe a specific host
host-list List all hosts by service
host-update Update host settings.
hypervisor-list List hypervisors.
hypervisor-servers List instances belonging to specific hypervisors.
hypervisor-show Display the details of the specified hypervisor.
hypervisor-stats Get hypervisor statistics over all compute nodes.[cpu,mem]
hypervisor-uptime Display the uptime of the specified hypervisor.
image-create Create a new image by taking a snapshot of a running server.
image-delete Delete an image.
image-list Print a list of available images to boot from.
image-meta Set or Delete metadata on an image.
image-show Show details about the given image.
keypair-add Create a new key pair for use with instances
keypair-delete Delete keypair by its id
keypair-list Print a list of keypairs for a user
list List active servers.
list-extensions List available extensions
live-migration Migrates a running instance to a new machine.
lock Lock a server.
meta Set or Delete metadata on a server.
migrate Migrate a server.
network-list Print a list of available networks.
network-show Show details about the given network.
pause Pause a server.
quota-class-show List the quotas for a quota class.
quota-class-update Update the quotas for a quota class.
quota-defaults List the default quotas for a tenant.
quota-show List the quotas for a tenant.
quota-update Update the quotas for a tenant.
rate-limits Print a list of rate limits for a user
reboot Reboot a server.
rebuild Shutdown, re-image, and re-boot a server.
remove-fixed-ip Remove an IP address from a server.
remove-floating-ip Remove a floating IP address from a server.
remove-secgroup Remove a Security Group from a server.
rename Rename a server.
rescue Rescue a server.
reset-state Reset the state of an instance
resize Resize a server.
resize-confirm Confirm a previous resize.
resize-revert Revert a previous resize (and return to the previous
VM).
resume Resume a server.
root-password Change the root password for a server.
secgroup-add-group-rule
Add a source group rule to a security group.
secgroup-add-rule Add a rule to a security group.
secgroup-create Create a security group.
secgroup-delete Delete a security group.
secgroup-delete-group-rule
Delete a source group rule from a security group.
secgroup-delete-rule
Delete a rule from a security group.
secgroup-list List security groups for the current tenant.
secgroup-list-rules
List rules for a security group.
service-list List nova services
show Show details about the given server.
ssh SSH into a server.
start Start a server.
stop Stop a server.
suspend Suspend a server.
unlock Unlock a server.
unpause Unpause a server.
unrescue Unrescue a server.
usage-list List usage data for all tenants
volume-attach Attach a volume to a server.
volume-create Add a new volume.
volume-delete Remove a volume.
volume-detach Detach a volume from a server.
volume-list List all the volumes.
volume-show Show details about a volume.
volume-snapshot-create Add a new snapshot.
volume-snapshot-delete Remove a snapshot.
volume-snapshot-list List all the snapshots.
volume-snapshot-show Show details about a snapshot.
volume-type-create Create a new volume type.
volume-type-delete Delete a specific flavor.
volume-type-list Print a list of available 'volume types'.
x509-create-cert Create x509 cert for a user in tenant.
x509-get-root-cert Fetches the x509 root cert.
bash-completion Prints all of the commands and options to stdout
五、典型实例
为了看看nova是如何工作的,我们可以以启动一个实例为例来进行说明,因为启动一个新的instance涉及到很多openstack nova里面的组件共同协作。在一个经典部署的 OpenStack中,Nova、Swift和 Glance这三大组件需要协同交互,这里我们通过启动实例这样一个典型操作来看看它们之间的交互:
· 1.客户端利用API发出请求,要求启动一个实例。
· 2.该请求通过一系列检查 (比如配额、权限等等)后,由 Nova API服务器进行处理。
· 3. Nova API服务器通过队列将启动实例的任务交给了 Nova调度器。
· 4.调度器根据调度规则决定在哪运行实例 —即从 N个计算节点中选取符合规则的节点
· 5.调度器通过队列向指定的计算节点发出消息让其开始创建实例
· 6.计算节点通知客户端实例开始创建,现在客户端可以继续其它任务
· 7.在后台,计算节点利用 Glance API在 Glance注册表中查找所需的镜像文件
· 8-9. Glance API向计算节点返回该镜像文件的物理位置和元数据
· 10.得到了物理位置等信息,计算节点就可以 Swift Proxy请求镜像文件
· 12-13. Swift Proxy从Swift工作单元中获得映象,并将其传递给计算节点
获得了镜像文件之后,计算节点就可以利用 libvirt API 来与被支持的Hypervisors交互:
· 计算节点会在数据库中更新实例的详细信息,并调用hypervisor开始配置实例的块设备
· 计算节点向网络节点的队列发出消息以便为实例配置网络
· 一旦收到返回的网络信息,计算节点就开始最后的配置调整,并启动实例
· 创建实例完成之后,无论成功与否,结算节点都会更新数据库,并在消息队列中发出通知

接下来我们来看一下 Nova 各部件在执行启动实例时的通讯过程。
Nova 部件间的通讯
最核心的 Nova 几个服务包括:API,计算服务,调度器和网络。API 是 Nova 的 HTTP 界面,计算服务则运行在每一台主机上负责与 hypervisor 通讯(通常每台主机有一个计算服务)。网络服务管理 IP 地址池并且与交换机、路由器、防火墙等相关服务通讯。调度器则负责既有的池中选择最适合的计算节点来负责运行新的实例(同时它也负责获取卷)。Nova 本身是按分布式应用程序进行架构的,在上一篇文章中,我们已经介绍了各个部件的功能,这里我们简单回忆一下:
· API服务器(nova-api):处理用户请求并将之路由给云控制器
· 云控制器(Cloud Controller):nova-api的一个类,负责处理计算节点、网络控制器、 API 服务器和调度器之间的通讯
· 调度器:选择某一主机来运行命令
· 计算工作单元:管理计算实例:启动或终止实例、挂载或卸载卷等等…
· 网络控制器:管理网络资源:分配固定IP地址、配置 VLAN …
注意:云控制器不是 Nova 7个部件之一,它只是 API 服务器的一个内部类而已。为了方便叙述通讯过程,这里我们单独把它抽离出来。在 Nova 内部,启动实例的流程是这样的:首先 API服务器接收到来自用户的 run_instances 命令。 API服务器将该消息转发到云控制器(1)。我们知道这里需要进行验证以确保用户具有所需的权限。云控制器将消息发送给调度器(2)。调度程序将消息转换为一个随机的主机,并询问他开始一个新的实例(3)。在主机上抓起的消息(4)的计算工作。计算工人需要一个固定的IP,所以将消息发送到网络控制器(5,6,7,8)推出一个新的实例。
2、 Openstack nova :虚拟机的启动过程
Table of Contents
- 概述
- 流程
- horizon/cli
- nova-api
- nova-conductor
- nova-scheduler
- nova-compute
概述
这几天从创建虚拟机这条线缕了一下nova的代码,将虚拟机启动的流程整理在此, 更详细的代码解读将在另外的博客中逐步总结。
由于整理得比较仓促,细节处可能有误,本文会随时更新。
流程
horizon或CLI
- dashboard或者CLI获取用户的凭证,并通过REST API向keystone服务发起权限验证, keystone 验证通过之后会返回一个auth_token,后续请求都将使用该auth_token。
- dashboard或者CLI将用户输入整理一下,调用REST API向nova-api发送创建虚拟机的 请求。
nova-api
- nova-api接到创建虚拟机的请求
- 使用请求中包含的auth_token向keystone发送请求作权限验证。
- 整理请求中的参数,形成create_kwargs
- admin_password 获取request中的password
- access_ips
将request中的access_ips,ipv4或ipv6取出来了整理进create_kwargs。 - availabilityzone
获取request中的os-availability-zone,填进create_kwargs。 - block device mapping 即block device mapping v2,获取request中的block_device_mapping_v2信息, 依其形成BlockDeviceDict填进create_kwargs。
- block device mapping v1 即legacy device mapping,获取request中的block_device_mapping信息,直接 填写进create_kwargs,同时在create_kwargs中将legacy_bdm置真,便于后续流程。 此项与上一项对应的处理不同版本的block device mapping数据。
- config drive
获取request中的config_drive信息填写进create_kwargs。 config_drive允许用户在一个数据盘中存放信息被cloud-init读取,cloud-init依 据这些信息在虚拟机初次启动时作一些自动化的配置。 - disk config
获取request中的api disk config,形如OS-DCF:diskConfig,处理为internal disk config,填写进create_kwargs。 - keypairs create
获取request中的key_name填写进create_kwargs。 - multiple create
获取request中的min_count,max_count,以及return reservation id。 该选项实现一个请求创建多个instance的功能,自动创建的instance的名称可以nova.conf中作定义。 这三个参数分别指定了一次创建虚拟机数目的最小值,最大值和是否要返回reservation_id。 是不是要返回reservation id由return_reservation_id决定。该值是multiple create的 虚拟机id上限的意思。 - personality
获取request中的personality,整理填写进create_kwargs中的injected_files, injected_files中的文件将被放进虚拟机中。 - scheduler_hints
获取request中的os:scheduler_hints或OS-SCH-HNT:scheduler_hints填写进create_kwargs中的 scheduler_hints。代码中说其意义是传递给scheduler的键值对。推测为nova-scheduler所需。 - security_groups
获取request中的security_groups参数,整理填写进create_kwargs。其中有一个list(set())操作, 去掉重复指定的值。 - user_data
获取request中的user_data填写进create_kwargs。 - image_uuid,requested_networks,flavor_id
- 将create_kwargs作为参数传给computeapi发起创建。
- computeapi对请求作鉴权,nova鉴权的配置文件默认在/etc/nova/policy.json,该文件里定义了nova中哪 些角色可以作哪些操作。
- 校验所有参数的合法性
- 检查multiple create下,不能指定ip或者neutron network port
- reservation id是否新建
- security_groups,min_count,max_count,block_device_mapping设定默认值
- 如果没有指定flavor,设定默认的flavor
- 获取相应image或者volume的信息,确保其支持auto_disk_config,即自动调整磁盘大小
- 处理availabilityzone信息,检查policy是否许可forced_host,forced_node
- 检查请求中所提到的各资源是否存在,是否合法
- availabilityzone是否存在
- flavor是否存在
- user_data长度是否合法,并解码
- 对于create和rebuild进行特殊检查
- metadata quota
- injected_files quota
- image的状态等信息校验
- 获取security_groups,是否存在
- 访问network api检查requested_networks合法性
- 从image信息中获取kernel和ramdisk信息
- 校验config drive.
- 获取keypair校验
- 校验root device name,即在虚拟机中磁盘的设备路径,例如/dev/vda
- numa topology
- 从flavor获取pci request info
- 通知network api配置sriov ports
- 以上处理之后构建新参数列表base_options
- 将image中的一些信息更新进base_options
- 返回base_options
- check_and_transform_bdm检查所有block device mappings的合法性,其root device有没有重合之类 对于image则基于image建立block device mapping。同一volume不可attach给两个instance。
- get_requested_instance_group检查scheduler_hints是否合法。
- provision_instance
- 将实例的vm_state设置为BUILDING,task_state设置为SCHEDULING。
- check_num_instances_quota数据库中获取quota,quota检查,计算quota,cpu,RAM,该quota对象更改后提交。
- 针对可创建的虚拟机数目循环在数据库中创建。
- 调用security_groups api处理安全组。
- 在数据库中创建相应block_device_mapping条目。
- 对于指定了instance group的实例,更新instancegroup相关quota,更新instancegroup数据库表。
- 将虚拟机创建事件通过rpc广播出去,便于ceilometer等记录。
- 记载虚拟机状态变化record_action_start,创建InstanceActions表
- 将虚拟机创建命令通过rpc发送给nova-conductor。
- 命令发送成功,nova-api的流程即已走完,此时界面按钮或者CLI将返回。
nova-conductor
- nova-conductor从消息队列中拾起创建虚拟机请求
- 从数据库中读取相关资源的信息,整理请求参数为json格式。
- 信息整合之后,通过scheduler client向scheduler发送rpc请求,让scheduler选择合适的nova-compute节点。
- scheduler选好nova-compute节点之后,通过消息队列返回结果。
- conductor通过compute rpc api发送给相应nova-compute节点。
nova-scheduler
- nova-scheduler从消息队列中拾起节点选择的请求
- 发起rpc广播schedule事件开始
- scheduler有一系列Filter,在不同层面定义过滤策略。将所有节点通过这些策略进行过滤。
- 为过滤之后的节点列表依据一定的策略作排序。
- 从排序后的节点列表中自前向后选择一定数目的节点,所取节点数目取决于scheduler的配置项scheduler_host_subset_size。
- 在最后选择出的节点列表中,随机选择节点。
- 发起rpc广播schedule事件结束。
nova-compute
- nova-compute从消息队列中拾起虚拟机创建请求
- 为实例加锁,并新建线程进行创建虚拟机操作,以便释放rpc的workder线程。
- 每个compute节点有最大并行创建数限制,该限制由eventlet.semaphore实现。
- 设置虚拟机task_state由SCHEDULING变为None,vm_state变为BUILDING。
- 发起rpc广播虚拟机create事件开始。
- 锁定虚拟机创建所需的资源。
- 为虚拟机创建准备虚拟网络和虚拟磁盘等资源。
- 创建虚拟网络
- 将vm_state设置为BUILDING,task_state设置为NETWORKING。
- 获取macs和dhcp配置信息。
- 通过network_api发送请求为虚拟机创建虚拟网络。
- 创建虚拟磁盘
- 将vm_state设置为BUILDING,task_state变为BLOCK_DEVICE_MAPPING。
- 虚拟机的磁盘设备有这几类:卷,快照,镜像和以及待创建的空盘。
- 对于卷,挂载到compute节点。
- 对于快照,调用cinder依据快照创建新卷,挂载到compute节点。
- 对于镜像,调用cinder依据镜像创建新卷,挂载到compute节点。
- 对于所需特定大小的空卷,通知cinder依大小创建并挂载到compute节点。
- 创建虚拟网络
- 虚拟机所需资源准备就绪以后,设置vm_state为BUILDING,设置task_state为SPAWNING。
- 准备虚拟机配置路径,组装xml。
- 调用特定hypervisor的driver(libvirt,xenapi,hyperv,vmware)来创建虚拟机。
- 发起rpc广播虚拟机create事件结束。
- 将虚拟机power state设置为1,将vm state设置为active,将task_state置为None。
- 如果虚拟机创建失败,允许retry的情况下会通过重发给scheduler进行reschedule操作,重发创建过程。
六、源码和开发
七、Nova 生产环境的配置模式
从功能上看, Nova平台中有两类节点:控制节点和计算节点,其角色由安装的服务决定,控制节点包括网络控制 Network、调度管理 Scheduler、api服务、存储卷管理、数据库管理、身份管理和镜像管理等,计算节点主要提供 nova-compute 服务。节点之间使用 AMQP作为通讯总线,只要将 AMQP消息被写入特定的消息队列中,相关的服务就可以获取该消息进行处理。由于使用了消息总线,因此服务之间是位置透明的,你可以将所有服务可以部署在同一台主机上,即 All-in-One(一般用于测试),也可以根据业务需要,将其分开部署在不同的主机上。用在生产环境 Nova平台配置一般有三种类型:最简配置:需要至少两个节点,除了 nova-compute外所有服务都部署在一台主机里,这台主机进行各种控制管理,即控制节点。 图1-1OpenStack双节点架构
标准配置:控制节点的服务可以分开在多个节点,标准的生产环境推荐使用至少 4 台主机来进一步细化职责。控制器、网络、卷和计算职责分别由一台主机担任。
图1-2 OpenStack 多节点架构
高级配置:很多情况下(比如为了高可用性),需要把各种管理服务分别部署在不同主机,(比如分别提供数据库集群服务、消息队列、镜像管理、网络控制等),形成更复杂的架构:
图1-3 OpenStack 高级架构
这种配置上的弹性得益于 Nova 选用 AMQP 作为消息传递技术,更准确地说,Nova 服务使用远程过程调用(RPC)彼此进行沟通。。AMQP 代理(可以是 RabbitMQ 或 Qpid)位于任两个 Nova 服务之间,使它们以松耦合的方式进行通信。因此不单 API 服务器可以和服务进行通讯,服务之间也可以相互通讯,如计算服务和网络服务、卷服务进行通讯以获得必要的资源。每一个 Nova 服务(Compute、scheduler 等等)在初始化时会创建两个消息队列:其路由选择关键字分别为“NODE-TYPE.NODE-ID”(如:Compute.)和“NODE-TYPE”(如 Compute)。后者则接收一般性消息,而前者则只接收发给特定节点的命令,例如执行 “euca-terminate instance”, 很明显,该命令只应发送给运行该实例的某个计算节点。无论是那一种生产配置模式,都允许用户根据需添加更多的计算节点,由 N 台服务器执行计算任务。