TensorFlow-一种改进的inception-v3迁移学习(图文)
本文是关于如何用谷歌提供的训练好的Inception-v3进行水果图片分类,涉及以下几个内容:
- 下载inception-v3(谷歌训练好的模型)
- 图片数据的下载
- 图片数据的清洗
- 将模型用于图片分类
-------------------------------------------------------------------
详解:
【创建文件】
|--baidu_search.py #通过百度爬取图片
|--ulibs.py #用于存放数据清洗等功能函数
|--inception-v3.py # 模型训练函数
|--data/ #存放数据
|--model/ #存放已训练好的模型
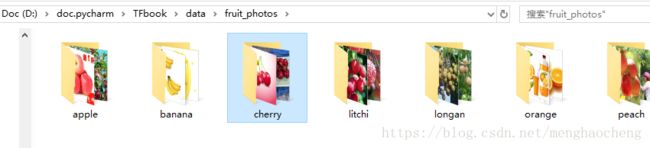
|--fruit_photos/ #存放爬取的图片
|--tmp/ #存放临时文件
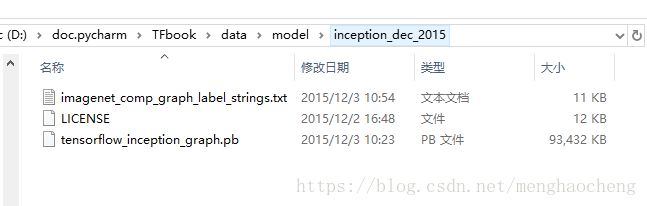
【下载inception-v3】
https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/models/inception_dec_2015.zip
解压后放在./data/model/目录下
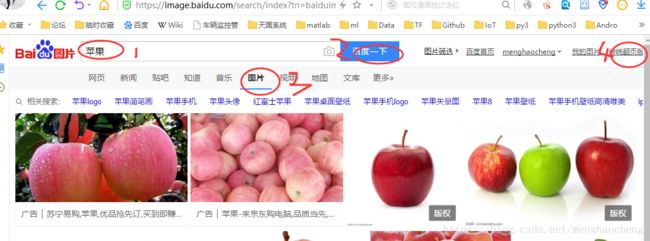
【下载水果图片】:通过关键字从百度爬取
baidu_search.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Tue Feb 27 11:10:45 2018 @author: mc.meng """ import re, os import requests from urllib.request import urlretrieve def download1(url, filename, filepath): full_name = os.path.join(filepath, filename) if os.path.exists(full_name): print("【消息】文件已经存在:", full_name) try: pic = requests.get(url, timeout=5) except: print('【错误】当前图片无法下载') return try: with open(filepath + "/" + filename, 'wb') as wf: wf.write(pic.content) except : print("【错误】写入失败") def download2(url, filename, filepath): full_name = os.path.join(filepath, filename) if os.path.exists(full_name): print("【消息】文件已经存在:", full_name) try: urlretrieve(url, full_name) except: print('【错误】当前图片无法下载') def search(word="美女", local_path="./data/down/", page=None, keep_original_name=True): local_path += word os.makedirs(local_path, exist_ok=True) url = 'http://image.baidu.com/search/flip?tn=baiduimage&ie=utf-8&word={word}&pn={pn}&gsm={gsm:x}&ct=&ic=0&lm=-1&width=0&height=0'.format(word=word, pn=20 * page, gsm=40 + 20 * page) print("HHHC:0====>page=%d,url=\"%s\"" % (page,url)) html = requests.get(url).text pic_url = re.findall('"objURL":"(.*?)",', html, re.S) i = 0 for url in pic_url: print(url) i = i + 1 filename = os.path.split(url)[1].split('?')[0] filename_split = filename.split('.') if len(filename_split) != 2: print("【错误】文件名异常:" + filename) continue #print("HHHA:0====>", filename_split[1]) if filename_split[1] != 'jpg' and filename_split[1] != 'JPG' \ and filename_split[1] != 'png' and filename_split[1] != 'PNG': print("【错误】类型异常:" + filename) continue if not keep_original_name: filename = filename.split('.')[0].strip() + "-" + str(page) + "-" + str(i) + "." + filename.split('.')[1].strip() download1(url, filename, local_path) return def search_50_page(word, local_path="./data/down/"): for i in range(1, 50): search(word, local_path, i) def search_50_page_test(): search_50_page("美女") def search_list_test(): obj_list = ["苹果", "香蕉", "桔子", "桃子", "樱桃", "龙眼", "荔枝"] #obj_list = ["苹果", "香蕉", "桔子", "橙子", "桃子", "樱桃", "龙眼", "荔枝", "雪梨", "草莓", "葡萄", "猕猴桃", "菠萝", "番石榴", "青梅"] #obj_list = ["菊花", "蒲公英", "玫瑰", "向日葵", "郁金香"] for obj in obj_list: search_50_page(obj, "./data/fruit_photos/") if __name__ == '__main__': search_list_test()
(PS:源码暗藏福利,但是我不说^V^)
等效于按下图步骤把百度图片切换到”传统翻页版“,然后手动把前面50页都下载下来了
如果你尝试过手动下载,你就会发现图片中有很多是相同的——文件名和URL都一样。此爬虫在文件保存的时候用原始文件名保存,并在在保存新文件前先判断文件是否存在,这就避免了重复的文件。
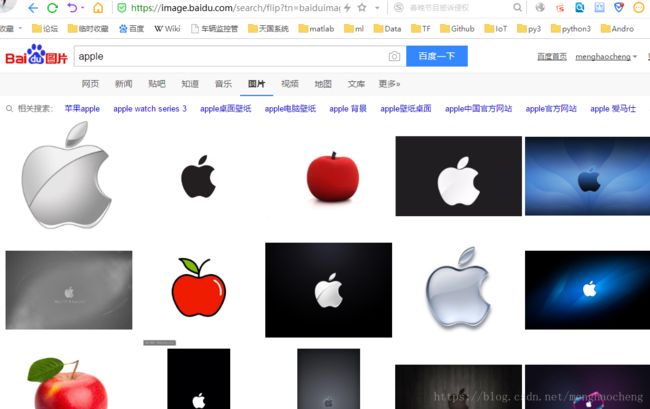
如果把“苹果”换成“apple"你将看到:
这显然不是我们想要的效果——我们今天需要的是水果图片,因此我们先用中文关键字爬取,完了之后再手动把文件夹名改成英文的:
【图片统一转成jpg】
从百度爬取的图片文件有png、jpg、gpeg等格式,为了方便处理,先把它们统一成jpg
(创建ulibs.py用于存放我们的清洗函数):
def png_to_jpg(path): """convert images into jpg format under the path""" print("【消息】将图片转换成jpg", path) for root, sub_dir, files in os.walk(path): print("【消息】进入目录:%s" % root) if root == path or not files: continue for file in files: if file.split('.')[1] != 'jpg': print("【消息】不是jpg:", file) old_file = os.path.join(root, file) img = cv2.imread(old_file) new_file = os.path.join(root, file.split('.')[0] + ".jpg") print("转换成:", new_file) cv2.imwrite(new_file, img) os.remove(old_file) print("【消息】转换完毕") def png_to_jpg_test(): png_to_jpg("./data/fruit_photos/")
【手动删除无法预览及明显错误的图片】:
【统一命名】:
从百度爬取的图片的文件名不统一,很多“%”,长度也参差不齐,为了美观起见我们也把文件名处理一下:
类型+编号:
def rename_files(path): """rename files under path""" for root, sub_dir, files in os.walk(path): if root == path or not files: continue print("will rename files under[%s]" % root) count = 1 for file in files: os.rename(os.path.join(root, file), os.path.join(root, os.path.basename(root) + "-" + str(count) + ".jpg")) count += 1 def rename_files_test(): rename_files("./data/fruit_photos/")
效果:
【将inception-v3用于水果分类】
重头戏终于开始了,先上完整代码,然后看效果,然后再详解代码:
''' data: http://download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz model: https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/models/inception_dec_2015.zip inception-v4: http://download.tensorflow.org/models/inception_v4_2016_09_09.tar.gz ''' import glob import os.path import random import cv2 import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE = 2048 BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME = 'pool_3/_reshape:0' JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME = 'DecodeJpeg/contents:0' MODEL_DIR = './data/model/inception_dec_2015' MODEL_FILE = 'tensorflow_inception_graph.pb' THIS_MODEL_DIR = "./data/model/inception/" THIS_MODEL_FILE = "inception.pb" CACHE_DIR = './data/tmp/bottleneck/inception' #INPUT_DATA = './data/flower_photos' INPUT_DATA = './data/fruit_photos' INPUT_DATA = './data/animal_photos' VALIDATION_PERCENTAGE = 10 TEST_PERCENTAGE = 10 LEARNING_RATE = 0.01 STEPS = 1000 BATCH = 100 def create_image_lists(file_dir): training = {} validation = {} testing = {} if not os.path.exists(file_dir): print("Not such path:", file_dir) return None, None, None for this_dir, sub_dirs, files in os.walk(file_dir): if this_dir == file_dir or not files: continue np.random.shuffle(files) percent10 = int(len(files) * 0.1) this_dir = os.path.basename(this_dir.lower()) training[this_dir] = files[:percent10 * 8] validation[this_dir] = files[percent10 * 8:percent10 * 9] testing[this_dir] = files[percent10 * 9:] return training, validation, testing def get_or_create_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_path): path_seg = image_path.split('\\') label_name = path_seg[-2] os.makedirs(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, label_name), exist_ok=True) bottleneck_path = os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, path_seg[-2], path_seg[-1]) + ".txt" if not os.path.exists(bottleneck_path): image_data = gfile.FastGFile(image_path, 'rb').read() bottleneck_values = sess_mod['sess'].run(sess_mod['premod_bottleneck'], feed_dict={sess_mod['premod_input']: image_data}) bottleneck_values = np.squeeze(bottleneck_values) print("HHHA:0====>", image_path) print(bottleneck_values) bottleneck_string = ','.join(str(x ) for x in bottleneck_values) with open(bottleneck_path, 'w') as bottleneck_file: bottleneck_file.write(bottleneck_string) else: with open(bottleneck_path, 'r') as bottleneck_file: bottleneck_string = bottleneck_file.read() bottleneck_values = [float(x) for x in bottleneck_string.split(',')] return bottleneck_values def get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, images, label=None, index=None): label_list = list(images.keys()) label_list.sort() if label is None: label = label_list[random.randrange(len(label_list))] if index is None: index = random.randrange(len(images[label])) image_path = os.path.join(INPUT_DATA, label, images[label][index]) bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_path) ground_truth = np.zeros(len(label_list), dtype=np.float32) ground_truth[label_list.index(label)] = 1.0 return bottleneck, ground_truth, image_path def fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, image_lists, amount=None): bottlenecks = [] ground_truths = [] this_paths = [] if amount is None: for label in list(image_lists.keys()): for index, file in enumerate(image_lists[label]): bottleneck, ground_truth, path = get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_lists, label, index) bottlenecks.append(bottleneck) ground_truths.append(ground_truth) this_paths.append(path) else: for _ in range(amount): bottleneck, ground_truth, path = get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_lists) bottlenecks.append(bottleneck) ground_truths.append(ground_truth) this_paths.append(path) feed_dict = { sess_mod['placeholder_input']: bottlenecks, sess_mod['placeholder_labels']: ground_truths, } return feed_dict, this_paths def inference(inputs, n_classes): this_input = tf.reshape(inputs, [-1, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE], name='input_images') weights = tf.get_variable("weights", [BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE, n_classes], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.001)) biases = tf.get_variable("biases", [n_classes], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)) logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(this_input, weights), biases, "logits") return logits def loss(logits, labels): labels = tf.to_int64(labels) cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels) return tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy) def training(loss, learning_rate): tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step) return train_op def evaluation(logits, labels): with tf.name_scope('evaluation'): correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(labels, 1)) evaluation_step = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) return evaluation_step def model_save(sess, model_path, input_tensor_name, bottleneck_tensor_name): graph_def = tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def() outpput_graph_def = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, graph_def, [input_tensor_name, bottleneck_tensor_name]) with tf.gfile.GFile(model_path, "wb") as wf: wf.write(outpput_graph_def.SerializeToString()) def model_restore(model_path, input_tensor_name, bottleneck_tensor_name): with gfile.FastGFile(model_path, 'rb') as rf: graph_def = tf.GraphDef() graph_def.ParseFromString(rf.read()) in_tensor, out_tensor, = tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, return_elements=[input_tensor_name, bottleneck_tensor_name]) return in_tensor, out_tensor def run_training(epoch=STEPS): imgs_training, imgs_validation, imgs_testing = create_image_lists(INPUT_DATA) n_classes = len(imgs_training.keys()) m1_input, m1_bottleneck = model_restore(os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, MODEL_FILE), JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME) placeholder_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE], name='in_images') placeholder_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes]) logits = inference(placeholder_input, n_classes) this_loss = loss(logits, placeholder_labels) train_step = training(this_loss, LEARNING_RATE) evaluation_step = evaluation(logits, placeholder_labels) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) sess_mod = { 'sess': sess, 'premod_input': m1_input, 'premod_bottleneck': m1_bottleneck, 'placeholder_input': placeholder_input, 'placeholder_labels': placeholder_labels } for step in range(epoch): feed_dict, image_path = fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_training, BATCH) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict=feed_dict) if step % 100 == 0 or step + 1 == STEPS: feed_dict, image_path = fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_validation, BATCH) accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict=feed_dict) print("Step %d: Validation accuracy on random sampled %d examples = %.2f%%" % (step, BATCH, accuracy * 100)) accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict=fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_testing)[0]) print("Final test accuracy = %.1f%%" % (accuracy * 100)) model_save(sess, os.path.join(THIS_MODEL_DIR, THIS_MODEL_FILE), "in_images", 'logits') def predict_test(): imgs_training, imgs_validation, imgs_testing = create_image_lists(INPUT_DATA) m1_input, m1_bottleneck = model_restore(os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, MODEL_FILE), JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME) m2_input, m2_bottleneck = model_restore(os.path.join(THIS_MODEL_DIR, THIS_MODEL_FILE), "in_images:0", "logits:0") placeholder_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, len(imgs_training.keys())]) evaluation_step = evaluation(m2_bottleneck, placeholder_labels) placeholder_logits = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, len(imgs_training.keys())]) final_tensor = tf.nn.softmax(placeholder_logits) final_index = tf.argmax(final_tensor, 1) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) sess_mod = { 'sess': sess, 'premod_input': m1_input, 'premod_bottleneck': m1_bottleneck, 'placeholder_input': m2_input, 'placeholder_labels': placeholder_labels } feed_dict, image_path = fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_testing) accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict=feed_dict) print("Final test accuracy = %.1f%%" % (accuracy * 100)) while True: feed_dict, image_path = fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_testing, 1) this_logits = sess.run(m2_bottleneck, feed_dict=feed_dict) f_tensor, f_index = sess.run([final_tensor, final_index], feed_dict={placeholder_logits: this_logits}) image_path = image_path[0] f_tensor = f_tensor[0] f_index = f_index[0] print("image_path:", image_path) print("f_tensor:", f_tensor) print("f_index", f_index) label_list = list(imgs_testing.keys()) label_list.sort() f_predict = label_list[f_index] print("f_predict:", f_predict) img = cv2.imread(image_path) if img is None: print("File not found:", image_path) continue img = cv2.resize(img, (500, 500)) cv2.putText(img, os.path.basename(image_path), (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1, (255, 0, 0), 1) cv2.putText(img, f_predict, (50, 150), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 3, (255, 0, 255), 5) cv2.imshow("predict", img) key = cv2.waitKey() if key & 0xFF == ord('q'): break elif key & 0xFF == ord('d'): print("removing:", image_path) os.remove(image_path) def main(argv=None): #run_training(STEPS) predict_test() if __name__ == "__main__": tf.app.run()
运行过程中如果出现错误,一般是图片文件无法打开(文件损坏、原图是gif文件等),直接将其删除就好了。
输出:
94.2%的准确率,还算不错。
【可视化预测结果】
主函数修改如下再运行:
def main(argv=None): #run_training(500) predict_test()
按q键退出,按d键删除当前文件,按其它何意键切换到下一张:
【代码详解】:
主函数开始:
def main(argv=None): run_training(STEPS) #predict_test()
可以看出,我们的模型分训练和预测两个阶段:
run_training()是将inception-3迁移到我们的水果分类,训练并将保存新模型;
predict_test()是使用新模型进行预测,并可视化展示预测结果;
【模型保存及恢复】:
model_save()、model_restore()分别是保存和恢复模型
def model_save(sess, model_path, input_tensor_name, bottelneck_tensor_name): graph_def = tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def() outpput_graph_def = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, graph_def, [input_tensor_name, bottelneck_tensor_name]) with tf.gfile.GFile(model_path, "wb") as wf: wf.write(outpput_graph_def.SerializeToString()) def model_restore(model_path, input_tensor_name, bottelneck_tensor_name): with gfile.FastGFile(model_path, 'rb') as rf: graph_def = tf.GraphDef() graph_def.ParseFromString(rf.read()) in_tensor, out_tensor, = tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, return_elements=[input_tensor_name, bottelneck_tensor_name]) return in_tensor, out_tensor
参数:
model_path:指定了模型文件所在的路径;
input_tensor_name: 模型的输入张量名称;
bottelneck_tensor_name: 模型的瓶颈张量;
sess: 保存模型时需要传入当前的会话;
model_restore()在run_training()和predict_test()中都有使用:在run_training()中是恢复inception-v3模型;而在predict_test()中不仅要恢复inception-v3模型,还要恢复我们刚刚训练好的新模型,因此调用了两次。
【四大金刚】:模型、损失、训练、评估
def inference(inputs, n_classes): this_input = tf.reshape(inputs, [-1, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE], name='input_images') weights = tf.get_variable("weights", [BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE, n_classes], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.001)) biases = tf.get_variable("biases", [n_classes], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)) logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(this_input, weights), biases, "logits") return logits def loss(logits, labels): labels = tf.to_int64(labels) cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels) return tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy) def training(loss, learning_rate): tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step) return train_op def evaluation(logits, labels): with tf.name_scope('evaluation'): correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(labels, 1)) evaluation_step = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) return evaluation_step
这四个函数都是针对我们的新模型而言:
inference: 向前传播模型;
loss: 损失的计算;
training: 通过最小化损失训练模型参数;
evaluation: 计算预测的精确度;
【瓶颈张量的计算】
def create_image_lists(file_dir): training = {} validation = {} testing = {} if not os.path.exists(file_dir): print("Not such path:", file_dir) return None, None, None for this_dir, sub_dirs, files in os.walk(file_dir): if this_dir == file_dir or not files: continue np.random.shuffle(files) percent10 = int(len(files) * 0.1) this_dir = os.path.basename(this_dir.lower()) training[this_dir] = files[:percent10 * 8] validation[this_dir] = files[percent10 * 8:percent10 * 9] testing[this_dir] = files[percent10 * 9:] return training, validation, testing def get_or_create_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_path): path_seg = image_path.split('\\') label_name = path_seg[-2] os.makedirs(os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, label_name), exist_ok=True) bottleneck_path = os.path.join(CACHE_DIR, path_seg[-2], path_seg[-1]) + ".txt" if not os.path.exists(bottleneck_path): image_data = gfile.FastGFile(image_path, 'rb').read() bottleneck_values = sess_mod['sess'].run(sess_mod['premod_bottleneck'], feed_dict={sess_mod['premod_input']: image_data}) bottleneck_values = np.squeeze(bottleneck_values) print("HHHA:0====>", image_path) print(bottleneck_values) bottleneck_string = ','.join(str(x ) for x in bottleneck_values) with open(bottleneck_path, 'w') as bottleneck_file: bottleneck_file.write(bottleneck_string) else: with open(bottleneck_path, 'r') as bottleneck_file: bottleneck_string = bottleneck_file.read() bottleneck_values = [float(x) for x in bottleneck_string.split(',')] return bottleneck_values def get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, images, label=None, index=None): label_list = list(images.keys()) label_list.sort() if label is None: label = label_list[random.randrange(len(label_list))] if index is None: index = random.randrange(len(images[label])) image_path = os.path.join(INPUT_DATA, label, images[label][index]) bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_path) ground_truth = np.zeros(len(label_list), dtype=np.float32) ground_truth[label_list.index(label)] = 1.0 return bottleneck, ground_truth, image_path
create_image_lists():
理解这个函数需要结合我们的目录结构:fruit_photos下面每种水果的图片放在一个以该水果命名的小目录中:
参数file_dir传入的将是fruit_photos所在路径。用os.walk遍历这个目录,并按1:1:8的比例把所有图片分割成训练、验证、测试三个数据集,每个数据集都是一个字典:以水果名称为键,以图片名称列表为值。
get_or_create_bottleneck():
获取或创建瓶颈向量:
用指定的模型计算指定图片的瓶颈向量。什么意思呢?具体就是获取图片A经过inception-v3这个模型之后的输出。参数sess_mod是封装了inception-v3的输入、输出、和用于计算的sess:
bottleneck_values = sess_mod['sess'].run(sess_mod['premod_bottleneck'], feed_dict={sess_mod['premod_input']: image_data})
可对比tensorflow的经典方式进行理解:sess.run(z, feed_dict={x:a, y:b})
计算瓶颈向量比较耗时,为了避免重复计算,把计算结果存放在CACHE_DIR/水果名/中,以图片名.txt命名。每次获取时先尝试从该目录中获取,如果文件不存在,则用模型进行计算并保存。
参数image_path指明了给获取哪张图片的瓶颈向量。
get_cached_bottleneck():
基于get_or_create_bottleneck()的封装,参数:
images: 图片列表,也就是create_image_list中分割出来的training, validation, testing三个数据集中的一个;
label: 水果名称,如果没有指定,则随机选择一种水果
index: 文件下标,如果没有指定,则随机选择一个下标
如:get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, training, "apple", 0)的意思是获取训练集中的苹果的下标为0的图片的瓶颈向量;
又如:get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, training)的意思是从训练集中随机获取一张图片的瓶颈向量。
【训练字典的生成】
def fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, image_lists, amount=None): bottlenecks = [] ground_truths = [] this_paths = [] if amount is None: for label in list(image_lists.keys()): for index, file in enumerate(image_lists[label]): bottleneck, ground_truth, path = get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_lists, label, index) bottlenecks.append(bottleneck) ground_truths.append(ground_truth) this_paths.append(path) else: for _ in range(amount): bottleneck, ground_truth, path = get_cached_bottleneck(sess_mod, image_lists) bottlenecks.append(bottleneck) ground_truths.append(ground_truth) this_paths.append(path) feed_dict = { sess_mod['placeholder_input']: bottlenecks, sess_mod['placeholder_labels']: ground_truths, } return feed_dict, this_paths
这个函数最终输出一个字典,用于新模型的计算。
feed_dict = {
sess_mod['placeholder_input']: bottlenecks,
sess_mod['placeholder_labels']: ground_truths,
}
bottlenecks是图片经过inception-v3的输出,它将作为新模型的输入。sess_mod['placeholder_input']是新模型的输出占位张量;sess_mod['placeholder_labels']是图片的正确标签——计算瓶颈向量的时候“顺便”生成的。
再看amount这个参数:训练的时候用BATCH,评估的时候未指定——等效于None,predict_test()的时候用1,这是为什么呢?
原来amount是指明要随机填充的图片数量,当为空时候将填充传入的整个图片列表。predict_test()阶段由于要向用户展示图片,因此每次只填充一张。
【运行训练】
def run_training(epoch=STEPS): imgs_training, imgs_validation, imgs_testing = create_image_lists(INPUT_DATA) n_classes = len(imgs_training.keys()) m1_input, m1_bottleneck = model_restore(os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, MODEL_FILE), JPEG_DATA_TENSOR_NAME, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_NAME) placeholder_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, BOTTLENECK_TENSOR_SIZE], name='in_images') placeholder_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes]) logits = inference(placeholder_input, n_classes) this_loss = loss(logits, placeholder_labels) train_step = training(this_loss, LEARNING_RATE) evaluation_step = evaluation(logits, placeholder_labels) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) sess_mod = { 'sess': sess, 'premod_input': m1_input, 'premod_bottleneck': m1_bottleneck, 'placeholder_input': placeholder_input, 'placeholder_labels': placeholder_labels } for step in range(epoch): feed_dict, image_path = fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_training, BATCH) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict=feed_dict) if step % 100 == 0 or step + 1 == STEPS: feed_dict, image_path = fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_validation, BATCH) accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict=feed_dict) print("Step %d: Validation accuracy on random sampled %d examples = %.2f%%" % (step, BATCH, accuracy * 100)) accuracy = sess.run(evaluation_step, feed_dict=fill_feed_dict(sess_mod, imgs_testing)[0]) print("Final test accuracy = %.1f%%" % (accuracy * 100)) model_save(sess, os.path.join(THIS_MODEL_DIR, THIS_MODEL_FILE), "in_images", 'logits')
这是训练的主干过程,解释完前面的小函数之后,这个函数似乎没有太多需要解释的了,它就是把前介绍的函数调用了一遍!
sess_mod的这样封装的原因是sess、m1_input,m1_bottelneck这几个参数经过多层传递最终执行,把它们入在字典中可减少中间函数的参数数量,增加代码的可读性。
【图片展示函数片段】
while True: this_logits = sess.run(m2_bottleneck, feed_dict=feed_dict) f_tensor, f_index = sess.run([final_tensor, final_index], feed_dict={placeholder_logits: this_logits}) image_path = image_path[0] f_tensor = f_tensor[0] f_index = f_index[0] print("image_path:", image_path) print("f_tensor:", f_tensor) print("f_index", f_index) label_list = list(imgs_testing.keys()) label_list.sort() f_predict = label_list[f_index] print("f_predict:", f_predict) img = cv2.imread(image_path) if img is None: print("File not found:", image_path) continue img = cv2.resize(img, (500, 500)) cv2.putText(img, os.path.basename(image_path), (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1, (255, 0, 0), 1) cv2.putText(img, f_predict, (50, 150), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 3, (255, 0, 255), 5) cv2.imshow("predict", img) key = cv2.waitKey() if key & 0xFF == ord('q'): break elif key & 0xFF == ord('d'): print("removing:", image_path) os.remove(image_path)
用opencv,
cv2.imread(): 读取图片;
cv2.resize(): 将图片大小调整为500*500,这是因为原图的大小并非统一的,建议读者试试去掉的效果;
cv2.putText(): 在图上显示文字;
cv2.imshow(): 显示图片;
cv2.waitKey(): 等待用户输入:
如果用户输入q: 退出循环;
如果用户输入d: 删除当前图片,这在剔除错误图片时相当方便
【扩展】
将model_save()/model_restore()收入ulibs.py中,然后通过以下方式调用:
import ulibs
ulibs.model_save()
ulibs.model_restore()参考:《TensorFlow实战Google尝试学习框架》--郑泽宇 顾思宇