创建数据项目
为了给后续的项目开发提供一个层次分明的代码结构,这里我们在解决方案下新建一个数据项目WebAPIData。
选择控制台应用程序,如图:
在WebAPIData项目下新建三个文件夹Entities、Mappers、Migrations,将会分别存放数据实体类、数据映射配置以及数据迁移配置;删除自动生成的Program.cs类。
下面我们介绍如何运用Entity Framework生成数据表。
在Entities文件夹下新建实体类Student.cs,我们需求的字段的姓名、学号、班级、电话,代码如下:
public class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string StuID { get; set; }
public string Class { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
}
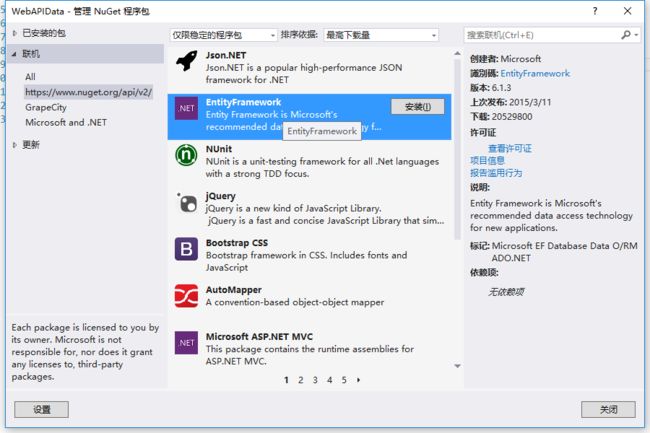
在Mappers文件夹中新建StudentMapper,cs类,我们将在该类中配置数据表的字段约束。在此,我们需要引用到Entity Framework组件,如下图:
引用完成后,我们可以看到
Entity Framework和
Entity Framework.SqlServer包含到引用中。
StudentMapper,cs类中的代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration;
using WebAPIData.Entities;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace WebAPIData.Mappers
{
class StudentMapper:EntityTypeConfiguration
{
public StudentMapper()
{
this.ToTable("Student");
this.HasKey(c => c.ID); //主键
this.Property(c => c.ID).HasDatabaseGeneratedOption(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity); //主键自增长
this.Property(c => c.ID).IsRequired();
this.Property(c => c.Name).IsRequired(); //字段非空
this.Property(c => c.Name).HasMaxLength(10); //设定字段最大长度
this.Property(c => c.StuID).IsRequired();
this.Property(c => c.StuID).HasMaxLength(20);
this.Property(c => c.Class).IsOptional(); //字段可以为空
this.Property(c => c.Phone).IsRequired();
this.Property(c => c.Phone).HasMaxLength(20);
}
}
}
Code First存在利用数据属性DataAnnotation和Fluent API两种配置数据库映射的方式。DataAnnotation配置方式是将与数据库映射相关的配置标签加到定义实体和值对象的类和类中的属性上,Fluent API是通过在继承DbContext类中定义数据库配置的方式的。
在这里我们采用Fluent API的方式,因为我们后续的开发会涉及到主外键配置以及一对一、多对一、一对多、多对都的映射关系,采用Fluent API方式可以保证我们结构清晰。DataAnnotation配置数据库映射的例子如下,在此我们不再赘述。
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
在WebAPIData下新建WebAPIContest.cs类,进行相应的配置,作为数据的上下文类,代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using WebAPIData.Entities;
using WebAPIData.Mappers;
using System.Data.Entity;
using WenAPIData.Migrations;
namespace WebAPIData
{
/*
* 1.把我们定义的POCO类作为DBSet的属性对外公开,这意味着每一个POCO类都将被转化为数据库中的表
2.重写OnModelCreating方法将我们为POCO类自定义的映射规则添加到DbModelBuilder配置中
*
*/
public class WebAPIContext:DbContext
{
public WebAPIContext()
: base("WebAPIConnection")
{
Configuration.ProxyCreationEnabled = false;
Configuration.LazyLoadingEnabled = false; //延时加载
Database.SetInitializer(new MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion());
//为数据库配置初始化和迁移策略,如果模型的属性被改变(添加了新的属性),就把数据库迁移到最新版本。
}
public IDbSet Students { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new StudentMapper());
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}
}
在Migrations文件夹下新建Configuration.cs文件,在此将进行数据库的迁移配置,可以在Entity Framework使用Code First Migration来用测试数据建立数据库。代码如下:
namespace WenAPIData.Migrations
{
using WebAPIData.Entities;
using System;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Migrations;
using System.Linq;
internal sealed class Configuration : DbMigrationsConfiguration
{
public Configuration()
{
/**
* 在构造函数中,我们设置AutomaticMigrationsEnabled 属性为true,
* 那么就意味着EF会为我们自动迁移数据库而不考虑版本问题。
* 同时我们把AutomaticMigrationDataLossAllowed属性也设为true但这样做在开发环境中是很危险的,
* 因为如果这个属性设为false时,一旦数据库在自动迁移时发生数据丢失,那么就会抛出一个异常。
*
* */
AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = true;
this.AutomaticMigrationDataLossAllowed = true;
}
protected override void Seed(WebAPIData.WebAPIContext context)
{
//可以在此部分添加数据实例
}
}
}
到现在,我们数据实体已经配置完毕,下面我们在WebAPIDemo项目中,创建Web API控制器。首先,我们需要在WebAPIDemo加入对WebAPIData项目的引用。
应用完成后先编译下项目,我们将开始调用
WebAPIData中的类。
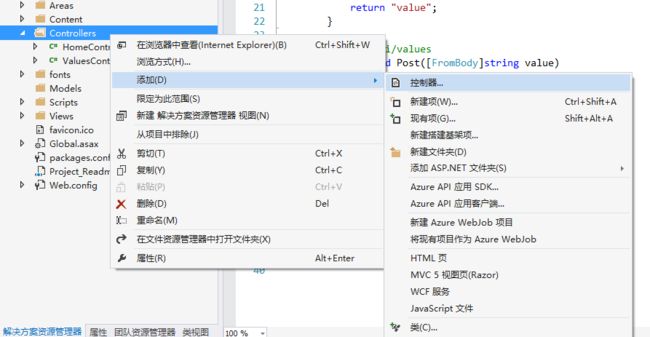
下面将添加支持CRUD(create, read, update 和 delete)的Web API 控制器。这些控制器使用Entity Framework来同数据库层交流,如图:
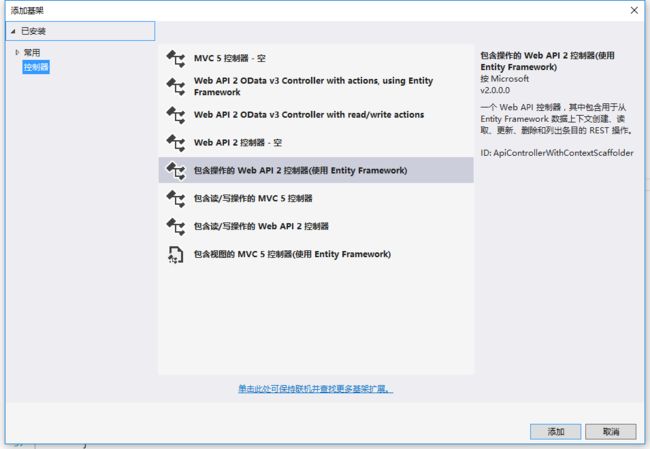
选择包含操作的Web API 2控制器(使用Entity Framework),如图:
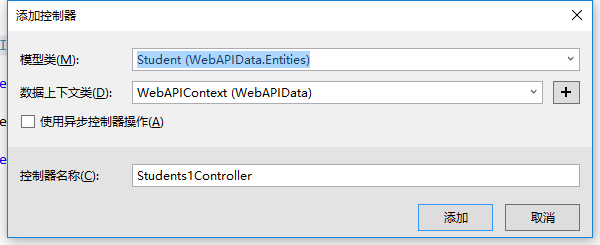
在在Add Controller对话框中,执行以下操作:
1.在模型类下拉框中,选择Student类(如果你没有在下拉框中看到它,请确保已经编译了这个项目)
2.数据库上下文类选择WebAPIContext类
单击添加,控制器类就生成了,包含基本的GET、POST、PUT、DELETE方法,代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Web.Http;
using System.Web.Http.Description;
using WebAPIData;
using WebAPIData.Entities;
namespace WebAPIDemo.Controllers
{
public class StudentsController : ApiController
{
private WebAPIContext db = new WebAPIContext();
// GET: api/Students
public IQueryable GetStudents()
{
return db.Students;
}
// GET: api/Students/5
[ResponseType(typeof(Student))]
public IHttpActionResult GetStudent(int id)
{
Student student = db.Students.Find(id);
if (student == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(student);
}
// PUT: api/Students/5
[ResponseType(typeof(void))]
public IHttpActionResult PutStudent(int id, Student student)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
if (id != student.ID)
{
return BadRequest();
}
db.Entry(student).State = EntityState.Modified;
try
{
db.SaveChanges();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException)
{
if (!StudentExists(id))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return StatusCode(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
// POST: api/Students
[ResponseType(typeof(Student))]
public IHttpActionResult PostStudent(Student student)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
db.Students.Add(student);
db.SaveChanges();
return CreatedAtRoute("DefaultApi", new { id = student.ID }, student);
}
// DELETE: api/Students/5
[ResponseType(typeof(Student))]
public IHttpActionResult DeleteStudent(int id)
{
Student student = db.Students.Find(id);
if (student == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
db.Students.Remove(student);
db.SaveChanges();
return Ok(student);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
db.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
private bool StudentExists(int id)
{
return db.Students.Count(e => e.ID == id) > 0;
}
}
}
当然了,我们在实际的项目应用中需要重写需要的CRUD方法,因为本文是简单的demo实现,所以在此不再赘述控制器中CRUD方法的编写。
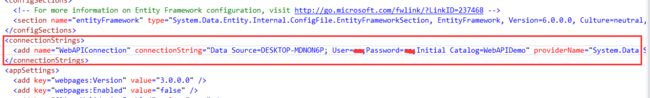
下面将初始化我们的数据库,首先需要在WebAPIDemo中的Web.config文件增加数据库的连接字符串,如图:
其中,字符串为:
上面的WebAPIDemo即为数据库名。
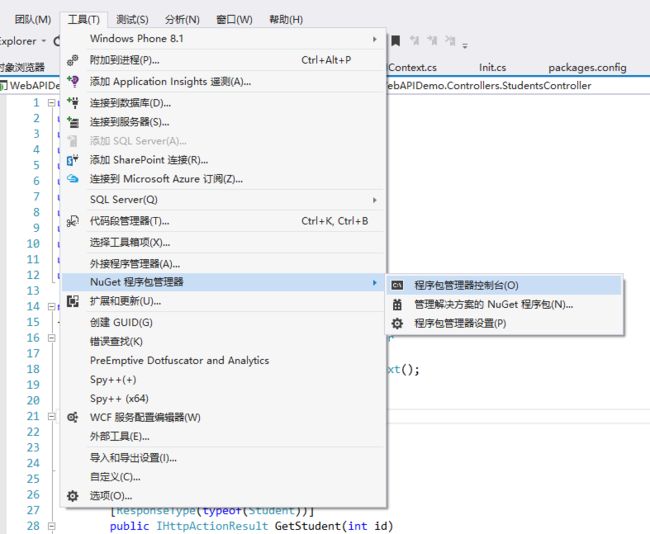
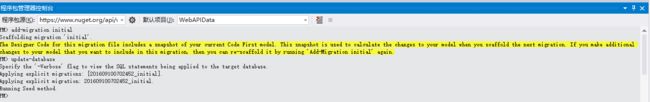
配置完成后,使用Code First Migration来用测试数据建立数据库。在工具目录下选择NuGet程序包管理器,然后选择程序包管理控制台。
在包管理控制台窗口,输入以下命令:
Add-Migration Initial
Update-Database
第一条命令生成用于创建数据库的代码,第二条命令执行那些代码。
数据库创建完成,我们打开SQL Server即可看到WebAPIDemo数据库。
我们在数据表中随意插入一些数据进行测试,如图:
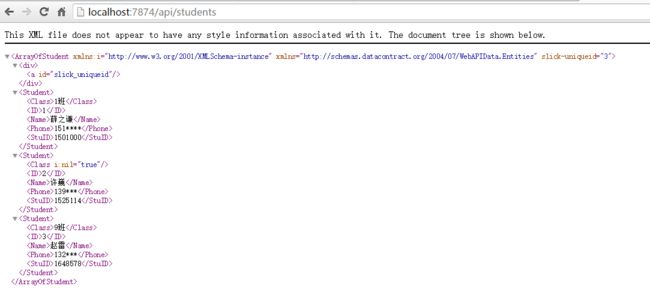
将WebAPIDemo设为启动项目,运行,我们调用Get方法进行测试,如图:
测试成功。可以看到上面调用API返回的格式是XML格式,我们将其转换为Json格式。在WebAPIDemo项目中APP_Start文件夹下的WebapiConfig.cs类中添加代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Http;
namespace WebAPIDemo
{
public static class WebApiConfig
{
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
// Web API 配置和服务
// Web API 路由
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
// New code:
var json = config.Formatters.JsonFormatter;
json.SerializerSettings.PreserveReferencesHandling =
Newtonsoft.Json.PreserveReferencesHandling.Objects; //把Json格式化器设置为防止对对象引用
config.Formatters.Remove(config.Formatters.XmlFormatter);
}
}
}
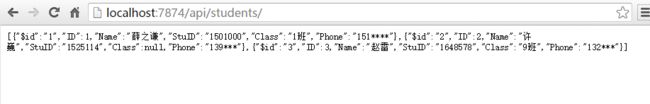
再次调用Get方法进行测试,返回Json格式如下:
至此,一个简单的从数据库获取数据封装成REST风格服务的WebAPI已经完成。
下面将简单介绍下如何使用Vue.js解析Wen API返回的数据,也会对数据的双向绑定也会做一个简单的介绍。