spring学习笔记三:spring整合jdbc、spring中aop事务操作
文章目录
- 1. spring学习笔记三:spring整合jdbc、spring中aop事务操作
- 1.1. spring整合jdbc
- 1.2. spring整合jdbc的步骤
- 1.3. spring提供的事务管理
- 1.3.1. 事务特性
- 1.3.2. 事务并发产生的问题
- 1.3.3. 解决事务并发问题的方法
- 1.3.4. spring中事务操作对象
- 1.3.5. spring管理事务的属性
- 1.4. spring管理事务方式
- 1.4.1. xml配置方式(aop思想)
- 1.4.2. 注解配置方式
- 1.5. spring的aop思想图
1. spring学习笔记三:spring整合jdbc、spring中aop事务操作
1.1. spring整合jdbc
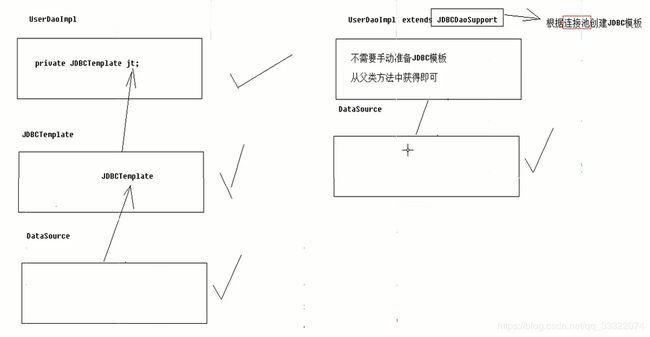
- spring提供了很多模板用于整合Dao层来操作数据库
- 对于整合jdbc,spring封装jdbc技术,并提供了一个使用jdbc技术的操作数据库的对象。JDBCTemplate–>jdbc模板对象。使用方法和DBUtils中的QueryRunner相似。
- 准备连接池,创建连接池对象,并通过连接池对象设置连接参数
- 创建Spring提供的JDBC模板,并将连接池内容放到模板里。
- 书写sql,执行sql。
//0 准备连接池
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql:///hibernate_32");
dataSource.setUser("root");
dataSource.setPassword("1234");
//1 创建JDBC模板对象
JdbcTemplate jt = new JdbcTemplate();
jt.setDataSource(dataSource);
//2 书写sql,并执行
String sql = "insert into t_user values(null,'rose') ";
jt.update(sql);
上面的方法有些地方可以抽取出来,比如准备连接池部分和配置连接参数部分。spring提供了这些内容的配置方法。可以在applicationContext.xml中配置。
1.2. spring整合jdbc的步骤
-
导包
- 4个spring核心包+2个日志包
- spring-test测试包+aop包
- c3p0第三方包+jdbc驱动第三方包
- spring-jdbc封装的包+spring-tx封装的事务包
-
建立数据库
-
书写Dao
- Dao类要继承JdbcDaoSupport类,因为如果不继承我们还需要创建JdbcTemplate类。
public class UserDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements UserDao {
@Override
public void save(User u) {
String sql = "insert into t_user values(null,?) ";
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, u.getName());
}
@Override
public void delete(Integer id) {
String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ? ";
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql,id);
}
@Override
public void update(User u) {
String sql = "update t_user set name = ? where id=? ";
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, u.getName(),u.getId());
}
- 查询单个对象,里面使用了匿名内部类的方式,第一个参数是sql,第二个参数是内部类,用于返回查询的结果,第三个是查询条件。我的理解是内部类先封装了所有的
@Override
public User getById(Integer id) {
String sql = "select * from t_user where id = ? ";
return super.getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(sql,new RowMapper<User>(){
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int arg1) throws SQLException {
User u = new User();
u.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
u.setName(rs.getString("name"));
return u;
}}, id);
}
- 查询list集合
@Override
public List<User> getAll() {
String sql = "select * from t_user ";
List<User> list = super.getJdbcTemplate().query(sql, new RowMapper<User>(){
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int arg1) throws SQLException {
User u = new User();
u.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
u.setName(rs.getString("name"));
return u;
}});
return list;
}
- 配置applicationContext.xml
- 对于数据库的连接,一般要从外部文件db.properties中获取,这样的好处就是解耦合。
- db.properties:尽量在书写时前面要加上前缀,这样防止与spring内部配置重名。
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///hibernate_32
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=1234
- ac.xml中配置引用指定的外部文件
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" />
- 动态获取外部文件
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" >
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" >property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" >property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" >property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" >property>
bean>
- 配置JdbcTemplate,将其放入spring容器
- JdbcTemplate依赖dataSource,因此需要ref=“dataSource”。
- 如果java类继承了JdbcDaoSupport,就不需要再依赖jdbcTemple了,这段不配置也行。
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" >property>
bean>
- spring容器中配置UserDao
<bean name="userDao" class="cn.it.a_jdbctemplate.UserDaoImpl" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" >property>
bean>
1.3. spring提供的事务管理
1.3.1. 事务特性
- 原子性Atomicity:事务包含的sql语句要么全部成功,要么全部执行失败。
- 一致性Consistency:事务执行之前和执行之后必须处于一致性状态:例如A和B转账,两者总钱数必须一定。不能转账事务结束后,总钱数少了。
- 隔离性isolation:即:并发事务隔离,多个用户同时操作事务,不能相互干扰。
- 持久性:事务一旦提交,数据库中的改变就是永久性的。
1.3.2. 事务并发产生的问题
- 脏读:指一个事务处理过程中读取了另一个未提交的事务数据。
- 不可重复读:不可重复读是指在对于数据库中的某个数据,一个事务范围内多次查询却返回了不同的数据值,这是由于在查询间隔,被另一个事务修改并提交了。
- 幻读:幻读和不可重复读一个道理,幻读是从整体上来讲的,不可重复读是从个体上来讲的。
- 参考文章详细点击此处
1.3.3. 解决事务并发问题的方法
- 配置事务隔离级别
① Serializable (串行化):可避免脏读、不可重复读、幻读的发生。
② Repeatable read (可重复读):可避免脏读、不可重复读的发生。
③ Read committed (读已提交):可避免脏读的发生。
④ Read uncommitted (读未提交):最低级别,任何情况都无法保证
1.3.4. spring中事务操作对象
- 因为在不同平台操作事务的代码各不相同,spring提供了一个接口。PlatformTransactionManager接口。该接口常见的实现类有:dataSourceTransactionManager,HibernateTransactionManager。等
- spring中操作事务最核心的对象是TransactionManager对象。
1.3.5. spring管理事务的属性
-
事务的隔离级别
- ACID特性
-
是否只读
- true:只能读取
- false:可对数据库操作
-
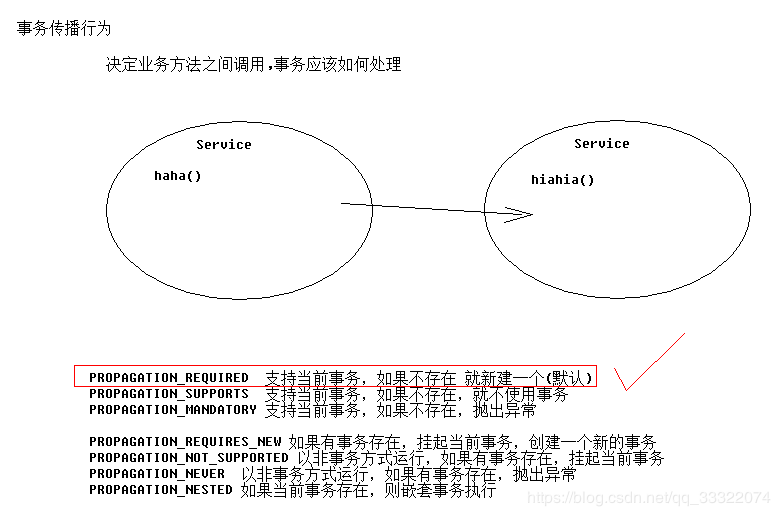
事务的传播行为。
1.4. spring管理事务方式
1.4.1. xml配置方式(aop思想)
- 导包
- aop,aspect包
- aop联盟,weaving织入包
- 导入新的约束(tx)
- bean:基本包
- Context:读取properties配置
- aop:配置aop
- tx:配置事务通知
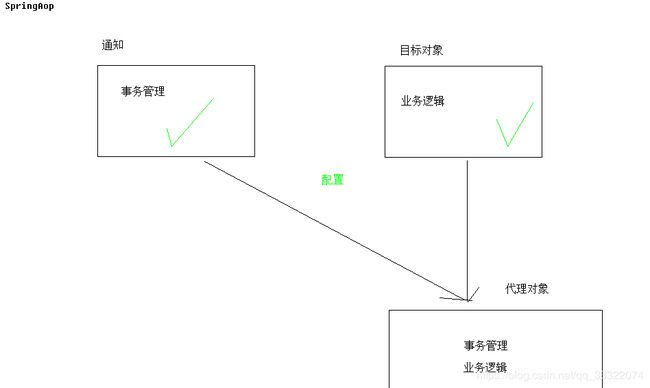
- 配置通知
- 配置事务通知
- 配置每个方法的事务属性
- propagation是配置事务传播行为的,默认required,市场基本使用这个。
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager" >
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="persist*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="modify*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="remove*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="get*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="find*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
- 配置将通知织入目标
- 配置切点
- 配置切面,即:将通知加入切点内。
<aop:config >
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="txPc"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPc" />
aop:config>
1.4.2. 注解配置方式
- 导包
- 导入新的约束
- 开启注解管理事务
<tx:annotation-driven/>
- 使用注解
@Override
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false)
public void transfer(final Integer from,final Integer to,final Double money) {
//减钱
ad.decreaseMoney(from, money);
int i = 1/0;
//加钱
ad.increaseMoney(to, money);
}
或者将@Transactional提到类上面,这样所有的方法都会开启事务,如果有些方法特殊,就在方法上面添加@Transactional()根据就近原则,就实行该注解。