Tensorflow数据读取方式总结
1、使用placeholder读内存中的数据
最简单的一种方法是用placeholder,然后以feed_dict将数据给holder的变量,进行传递值。如下面代码所示:
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
x1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(3,2))
y1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(2,3))
z1 = tf.matmul(x1,y1)
x2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=None)
y2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=None)
z2 = x2 + y2
# using feed_dict when placehoder
with tf.Session() as sess:
z2_value = sess.run(z2,feed_dict={x2:1,y2:2})
print(z2_value)
rand_x = np.random.rand(3,2)
rand_y = np.random.rand(2,3)
z1_value,z2_value = sess.run(
[z1,z2], # run together
feed_dict={
x1:rand_x,y1:rand_y,
x2:1,y2:2
}
)
print(z1_value,z2_value)2、使用queue读硬盘中的数据
参考如下的连接,不过感觉队列读取方式较为复杂,有了Dataset API后大部分不用此方法。
十图详解tensorflow数据读取机制(附代码)
3、Dataset API
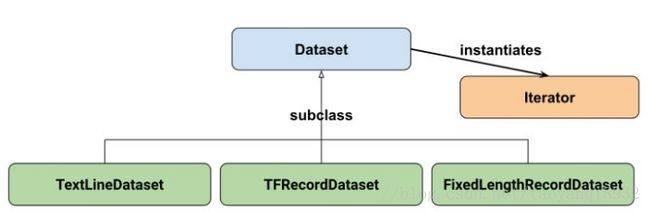
Dataset可以看作是相同类型“元素”的有序列表。在实际使用时,单个“元素”可以是向量,也可以是字符串、图片,甚至是tuple或者dict。
注意下图的继承关系
tf.data.TextLineDataset
可以直接从文件中读取数据
__init__(
filenames,
compression_type=None,
buffer_size=None
)代码示例:
with tf.Graph().as_default(),tf.Session() as sess:
# instance a dataset,np.array() => tf.constant => tensorflow
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(np.array([1,2,3,4,5]))
# we can also use tf.data.TextLineDataset because this inherit tf.data.Dataset
# dataset = tf.data.TextLineDataset.from_tensor_slices(np.array([1,2,3,4,5]))
# return a Iterator over the element of this dataset
iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
element = iterator.get_next() # every element is a number
for i in range(5):
print(sess.run(element)) # 1,2,3,4,5
##### read data from file
"""
we have a file test.csv:
1,2,0
4,5,1
7,8,2
"""
with tf.Graph().as_default(),tf.Session() as sess:
dataset = tf.data.TextLineDataset("test.csv")
iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
element = iterator.get_next() # every element is a vector
try:
while True:
print(sess.run(element))
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
print("end!")
##### more complex dataset
"""
1,2,0
4,5,1
7,8,2
the last column is label we create => batch of feature,label
"""
with tf.Graph().as_default(),tf.Session() as sess:
def to_tensor(line):
parsed_line = tf.decode_csv(line,[[0.],[0.],[0]]) # => tensor
#label = parsed_line[-1]
label = parsed_line[-1]
del parsed_line[-1]
features = parsed_line
features_names = ['feature_1','feature_2']
d = dict(zip(features_names,features)),label
return d
dataset = tf.data.TextLineDataset("test.csv").map(to_tensor).batch(2)
iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
batch_features,batch_labels = iterator.get_next()
try:
while True:
batch_fea,batch_lab = sess.run([batch_features,batch_labels])
print(batch_fea,batch_lab)
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
print("end!")
注意dataloader的使用方式
# create dataloader
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((tfx,tfy)) #reference tf_dataset_basic.py
dataset = dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=1000)
dataset = dataset.batch(32)
dataset = dataset.repeat(5)
iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator()
使用dataset具体的一个例子
x = np.random.uniform(-1,1,(1000,1))
y = np.power(x,2) + np.random.normal(0,0.1,size=x.shape)
x_train,x_test = np.split(x,[800])
y_train,y_test = np.split(y,[800])
print(
'\nx_train shape',x_train.shape,
'\ny_train shape',y_train.shape,
)
"""
plt.scatter(x_train,y_train)
plt.show()
"""
tfx = tf.placeholder(x_train.dtype,x_train.shape)
tfy = tf.placeholder(y_train.dtype,y_train.shape)
# create dataloader
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((tfx,tfy)) #reference tf_dataset_basic.py
dataset = dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=1000)
dataset = dataset.batch(32)
dataset = dataset.repeat(5)
iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator()
# built network
batch_x,batch_y = iterator.get_next() # batch_x:(32,1)
h1 = tf.layers.dense(batch_x,10,tf.nn.relu) # batch_x:(32,10)
out = tf.layers.dense(h1,1) # 32*1
loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(batch_y,out)
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
with tf.Session() as sess:
#initializable
sess.run([iterator.initializer,tf.global_variables_initializer()],
feed_dict={tfx:x_train,tfy:y_train})
for step in range(301):
try:
_,train_loss = sess.run([train,loss])
if step % 10 == 0:
test_loss = sess.run(loss,{batch_x:x_test,batch_y:y_test})
print('\nsetp:',step,
'\ntrain loss:',train_loss,
'\ntest loss:',test_loss,
)
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
print("finish!")
break
完整代码在我的github上~
参考资料
- Dataset API入门教程
- Introduction to TensorFlow Datasets and Estimators