并发编程(六):AQS之读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock
一,AQS源码博文:并发编程:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
二,ReentrantReadWriteLock读写锁介绍
1,读写锁介绍
ReentrantReadWriteLock 虽然与 ReentrantLock 没有直接关系,但是在功能上算是对 ReentrantLock 的扩展。在 ReentrantLock 重入独占锁的功能上,添加了共享锁的扩展,分别对应 ReentrantReadWriteLock 的写锁(WriteLock)和读锁(ReadLock)。ReentrantReadWriteLock 内部定义 Sync 类继承自 AQS 对加锁方式进行扩展,在读锁写锁获取以及读写锁交叉获取提供了自身机制,以此保证线程同步。ReentrantReadWriteLock 在加锁过程中,对 Integer 的32位进行分割,以高16位表示共享锁,以低16位表示独占锁。在进行加锁时,通过左移右移以及与运算判断当前加锁状态及重入状态,并进线程进行调度。
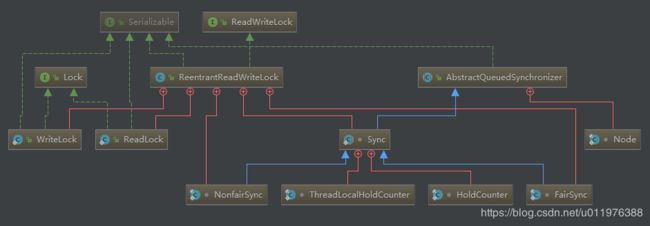
2,类图
* ReentrantReadWriteLock 实现自 ReadWriteLock 接口,并在内部定义了锁实现了相关内部类。
* Sync,FairSync,NonfairSync 三个内部类是对 AQS 的层次扩展,用来扩展加锁的一系列逻辑处理
* WriteLock,ReadLock 两个内部类实现自 Lock 接口,并通过 ReentrantReadWriteLock 创建后对外提供,在应用层进行不同的加锁处理
3,常用API
// 创建读写锁, 通过参数指定公平锁/非公平锁
public ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public ReentrantReadWriteLock(boolean fair);
// 创建读锁
public ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock()
// 创建写锁
public ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock();
// 尝试加锁
public boolean tryLock();
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
// 加锁
public void lock();
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException;
// 释放锁
public void unlock();
* 在上述API中,关于锁操作的一些API,都存在读锁和写锁的区别;其中,在读锁和写锁的处理中,又存在公平锁和非公平锁的区分;
* 后续源码分析中,读锁和写锁会分别分析,但是公平锁和分公平锁只对非公平锁进行分析,公平锁参考重入锁
4,ReentrantReadWriteLock 加锁分析
4.1,整体锁状态存储
* ReentrantReadWriteLock 在锁状态存储中,对 Integer 32位进行拆分,使用高16位存储共享锁,使用低16位存储独占锁。所以无论是共享锁的共享次数还是独占锁的重入次数,最高为((1 << 16) - 1)。
// 1 << 16就是1在二进制情况下右移16位结果为
10000 0000 0000 0000 = 2^16 = 65536
// (1 << 16) - 1也是在二进制下进行减操作
1111 1111 1111 1111 = 2^16 - 1 = 65535* ReentrantReadWriteLock 在独占锁加锁时,是对低16位进行加1,在获取独占锁的重入次数时,也是对低16位进行与运算以获取结果加锁具体看代码框
// 独占锁state递增
compareAndSetState(c, c + 1)
// 独占锁获取重入次数
// EXCLUSIVE_MASK:常量,最终结果为 (1111 1111 1111 1111),也就是对应 Integer 的低16位
// 用c和 EXCLUSIVE_MASK 进行与运算,也就是用c的低16位和 EXCLUSIVE_MASK 进行与运算,
// 与运算同1为1,其余为0,所以获取到的结果就是c的低16位表示的数字,然后再默认转换10进制,即为重入数量
static int exclusiveCount(int c) {
return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK;
}
static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
// 比如,此时共享为3次,重入为0次,则c的二进制表示为
0000 0000 0000 0011 0000 0000 0000 0000
// EXCLUSIVE_MASK的二进制表示为
0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111
// 运算结果
0000 0000 0000 0011 0000 0000 0000 0000
& 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111
-------------------------------------------
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 = 0
// 所以此时获取到的独占锁数量为0
// 假设可以获取成功,则对独占锁递增,通过CAS,用c + 1代替 c,此时,c的二进制表示为:
0000 0000 0000 0011 0000 0000 0000 0001
// 这时候继续计算,获取独占锁的次数,运算如下
0000 0000 0000 0011 0000 0000 0000 0001
& 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111
-------------------------------------------
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 = 1* 同样,ReentrantReadWriteLock 在对共享锁加锁时,是对高16位进行加锁,在获取共享锁次数时,先对 state 无符号右移16位,然后直接获取结果,具体过程如代码框
// 加锁成功后,c递增,按照重入逻辑,递增应该为1
// 而此时递增了(1 << SHARED_SHIFT),也就是二进制下 1 0000 0000 0000 0000
// 除去低16位,也就是刚好在高16位上递增1
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)
static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
// 共享锁获取锁重入次数
// 直接将state无符号右移16位,表示的就是共享锁的重入次数
// 而右移去掉的16位,也就刚好是独占锁表示的低16位
static int sharedCount(int c) {
return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT;
}
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
// 继续举例,比如此时共享次数3,独占次数为3,则state的二进制表示为
0000 0000 0000 0011 0000 0000 0000 0011
// 无符号右移16位后,高位补0,值如下
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011 = 3
// 假设此时共享锁获取成功,state加上(1 << SHARED_SHIFT),如下
0000 0000 0000 0011 0000 0000 0000 0011
+ 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000
-------------------------------------------
0000 0000 0000 0100 0000 0000 0000 0000
// 此时继续获取数量,对state无符号右移16位,结果如下
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0100 = 4
5,功能DEMO
package com.gupao.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
/**
* @author pj_zhang
* @create 2019-10-19 12:37
**/
public class ReadAndWriteLockTest {
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantReadWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.readLock();
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.writeLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
testReadAndWriteLock();
}
public static void testWriteAndReadLock() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("开始获取锁。。。");
// 先获取写锁后获取读锁
// 读锁会顺利获取
writeLock.lock();
System.out.println("获取写锁成功。。。");
readLock.lock();
System.out.println("获取读锁成功。。。");
writeLock.unlock();
System.out.println("释放读锁成功。。。");
readLock.unlock();
System.out.println("释放写锁成功");
}, "READ_AND_WRITE").start();
}
public static void testReadAndWriteLock() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("开始获取锁。。。");
// 先获取读写再获取写锁
// 此时已经存在锁,则独占锁获取失败
readLock.lock();
System.out.println("获取读锁成功。。。");
writeLock.lock();
System.out.println("获取写锁成功。。。");
writeLock.unlock();
System.out.println("释放读锁成功。。。");
readLock.unlock();
System.out.println("释放写锁成功");
}, "READ_AND_WRITE").start();
}
/**
* 不同线程测试读写锁
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void testLockWithDiffThread() throws InterruptedException {
// 先启动一个读锁
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加读锁前执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
readLock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加读锁后执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
sleep(1000);
readLock.unlock();
}, "READ_1").start();
Thread.sleep(10);
// 再一个一个读锁,模拟读锁不阻塞
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加读锁前执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
readLock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加读锁后执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
sleep(1000);
readLock.unlock();
}, "READ_2").start();
Thread.sleep(10);
// 启动一个写锁,模拟写锁阻塞
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "_加写锁前执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
writeLock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "_加写锁后执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
sleep(1000);
writeLock.unlock();
}, "WRITE").start();
Thread.sleep(10);
// 自启动一个读锁,模拟共享锁执行时,阻塞一个写锁,之后再获取读锁,在写锁后执行
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加读锁前执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
readLock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加读锁后执行。。。, time: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
sleep(1000);
readLock.unlock();
}, "READ_3").start();
}
private static void sleep(long millSeconds) {
try {
Thread.sleep(millSeconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
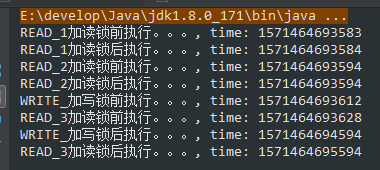
* testLockWithDiffThread() 执行结果:
1)在不同线程间,读锁间共享,不会进行锁竞争,通过CPU调度依次执行
2)写锁排斥,在尝试获取写锁时,会先判断是否存在线程持有写锁或者读写,如果存在,则添加到AQS同步队列中等待唤醒
3)写锁等待后,再启动一个读锁,此时因为写锁等待,并且已经对低16位的独占锁标识进行修改,且锁线程与当前线程不一致。则当前读锁线程获取锁失败,依次进入AQS队列等待
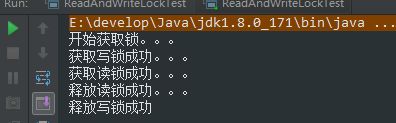
* testReadAndWriteLock 执行结果
1)在同一线程后,尝试获取两种锁,从打印结果可以看出,线程获取读锁后,再获取写锁时阻塞,等待读锁释放
2)线程在获取读锁后,对高16进行修改,并设置锁线程为当前线程
3)线程继续获取写锁,因为高位已经被修改,所以写锁获取失败,等待读锁释放
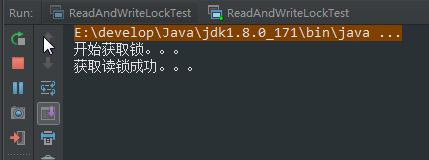
* testWriteAndReadLock 执行结果
1)在同一线程中,尝试获取两种所,从打印结果可以看出,线程获取写锁后,再获取读锁成功
2)线程获取写锁后,对低16位进行修改,并设置锁线程为当前线程
3)线程继续获取读锁,虽然判断独占线程已经存在,但是加锁线程表示当前线程,所以线程获取锁成功
三,ReentrantReadWriteLock部分源码分析
1,初始化部分
* ReentrantReadWriteLock():调用重载构造器,并传递参数表示默认非公平锁
public ReentrantReadWriteLock() {
this(false);
}* ReentrantReadWriteLock(boolean fair)
public ReentrantReadWriteLock(boolean fair) {
// 通过入参表示公平锁还是非公平锁
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
// 初始化读写锁对象
readerLock = new ReadLock(this);
writerLock = new WriteLock(this);
}* 初始化读写锁
// 初始化读锁
protected ReadLock(ReentrantReadWriteLock lock) {
sync = lock.sync;
}
// 初始化写锁
protected WriteLock(ReentrantReadWriteLock lock) {
sync = lock.sync;
}* 获取读写锁
// 获取写锁
public ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock() {
return writerLock;
}
// 获取读锁
public ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock() {
return readerLock;
}四,ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock源码分析
1,尝试加锁
* tryLock():直接通过 Sync 尝试加读锁
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryReadLock();
}* tryReadLock()
final boolean tryReadLock() {
// 获取当前线程
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 自旋尝试获取锁,可能存在线程竞争导致的CAS失败问题
for (;;) {
// 获取当前的加锁次数,注意此处次数是经过高低位处理后的次数,并不是真实次数,需要进行解析
int c = getState();
// exclusiveCount:低16位解析,获取独占锁数量,判断是否存在独占锁
// getExclusiveOwnerThread:判断当前线程是否是锁线程
// 所以如果存在独占锁,并且锁线程不是当前线程,则尝试失败
// 否则当前步骤成功
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return false;
// 高16位解析,获取共享锁数量
int r = sharedCount(c);
// 共享锁最大值判断,
// MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
if (r == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// 按照重入逻辑,如果可以加锁,则是对state+1
// 但是共享锁是对高16位进行操作,所以应该在高16位的基础上加1,
// SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
// r为0,表示当前并没有共享锁进入,则初始化当前线程为头线程
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
// 当前线程重入,则对重入此时递增
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
// 此处表示获取共享锁的线程不是当前锁线程
// 存在新线程尝试获取共享锁,则cachedHoldCounter必定为null
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
// readHolds集成自ThreadLocal,为每一个新线程分配一个HoldCounter
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
// 可能存在其他途径创建线程的HoldCounter,这样在readHolds中可能不存在(个人理解)
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
// 初始化完成后,对count递增,表示线程加锁及重入
rh.count++;
}
return true;
}
}
}* readHolds.get():此处涉及 ThreadLocal 的初始化部分
// ThreadLocalHoldCounter继承自ThreadLocal
// 泛型表示ThreadLocal为每一个线程分配一个 HoldCounter 对象
// 当前类重写了父类的initialValue()方法,并初始化了一个HoldCounter对象
// 表示 ThreadLocalHoldCounter 默认为每一个线程分配一个已经初始化好的对象
// 每一次get时,如果获取不到线程已经存储的信息,则直接返回一个新对象
static final class ThreadLocalHoldCounter extends ThreadLocal {
public HoldCounter initialValue() {
return new HoldCounter();
}
} 2,加锁
* lock()
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
}* tryAcquireShared(int unused)
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 存在写锁,并且不是当前线程获取,则获取锁失败
// 此处不排除存在写锁,如果存在写锁则写锁为当前线程持有
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// readerShouldBlock():判断是否存在下一个节点,且下一个节点不是共享节点
int r = sharedCount(c);
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
r < MAX_COUNT &&
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
// 下面为加锁处理
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
// 继续尝试获取共享锁
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}* fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current)
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
// 判断是否独占锁,且不是当前线程
// 当前线程获取独占锁后,可继续获取共享锁
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// 存在下一个节点,并且下一个不是共享锁节点,则需要阻塞
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {
// firstReader表示当前线程,说明正在执行中,默认不阻塞
if (firstReader == current) {
} else {
// 此处判断当前线程是否在执行中,rh.count表示重入
// 如果在执行中,则继续可以获取执行,如果不在执行中,则获取失败
if (rh == null) {
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
}
}
if (rh.count == 0)
return -1;
}
}
// 最大值判断
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// 获取锁成功
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
}
return 1;
}
}
}* readerShouldBlock():存在下一个节点,并且下一个节点不是共享节点,返回true,否则返回false
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();
}
// 此处判断是否存在下一个节点,以及下一个节点是否为共享节点(取反)
final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {
Node h, s;
return (h = head) != null &&
(s = h.next) != null &&
!s.isShared() &&
s.thread != null;
}3,释放锁
* unlock()
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}* tryReleaseShared(int unused)
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 判断当前线程是否firstReader
// 此处条件判断,主要为了递减线程重入次数,如果可以释放,则对关键标识对象置空,帮助GC,并方便后续操作判断
if (firstReader == current) {
// 继续判断firstReaderHoldCount重入次数,如果为1,说明可以彻底释放,重置firstReader
// 不为1,递减即可
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;
else
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else {
// 当前线程不是firstReader,则从readHolds中获取,并判断count重入次数
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
int count = rh.count;
// count <=1,同样表示彻底释放,从readHolds中移除
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
--rh.count;
}
for (;;) {
// 获取共享锁的重入次数,并递减,是否为0标识
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0;
}
}五,ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock源码分析
1,尝试加锁
* tryLock( )
public boolean tryLock( ) {
return sync.tryWriteLock();
}* tryWriteLock()
final boolean tryWriteLock() {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// c不为0,表示存在独占锁或者共享锁
if (c != 0) {
// 获取独占锁重入次数
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
// w为0,说明独占锁为空,则表示存在共享锁,获取锁失败
// w不为0,并且锁线程不是当前线程,说明存在其他线程持有独占锁,获取锁失败
// 此处证明在同一线程下,获取共享锁后,不可获取独占锁
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
if (w == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
}
// CAS设置重入状态,设置成功后,添加锁线程为当前线程
if (!compareAndSetState(c, c + 1))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}2,加锁
* lock()
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}* tryAcquire(int acquires):此处尝试加锁与上一步尝试加锁基本一致,只是加了一步判断
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
if (c != 0) {
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
// writerShouldBlock:判断写锁是否需要阻塞
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}* writerShouldBlock():该方法在非公平锁中默认返回false,再公平锁实现中,进行了AQS队列存在性校验,保证顺序执行
// 非公平锁
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return false;
}
// 公平锁
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return hasQueuedPredecessors();
}
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}3,释放锁
* unlock()
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}* tryRelease(int releases)
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// 判断当前线程是否锁线程
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
// 获取释放后的独占锁重入次数
int nextc = getState() - releases;
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
// 重入次数为0,则释放成功,置空锁线程,
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(nextc);
return free;
}