跟踪分析Linux内核5.0系统调用select处理过程
学号:282
原创作品转载请注明出处 + https://github.com/mengning/linuxkernel/
操作系统的主要功能是为管理硬件资源和为应用程序开发人员提供良好的环境来使应用程序具有更好的兼容性,为了达到这个目的,内核提供一系列具备预定功能的多内核函数,通过一组称为系统调用(system call)的接口呈现给用户。系统调用把应用程序的请求传给内核,调用相应的的内核函数完成所需的处理,将处理结果返回给应用程序。
一、实验目的
基于Linux5.0.1内核和孟宁老师的MenuOS,追踪系统调用的过程。
二、实验步骤
环境搭建
编译5.0.1内核
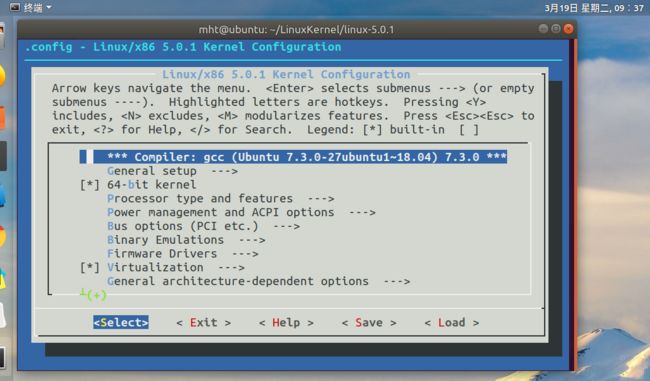
# 解压 mkdir ~/LinuxKernel tar -xv -f ~/Download/linux-5.0.1.tar.xz -C ~/LinuxKernel# 配置编译 cd ~/LinuxKernel/linux-5.0.1 make menuconfig # 基于文本选单的配置界面通过方向键,选择
kernel hacking-->Compile-time checks and compiler options-->compile the kernel with debug info
Save保存后退出。
# 编译 make # 推荐使用 make -j4多线程编译提高速度出现错误,按照提示安装需要的库即刻。漫长等待后
制作根文件系统
cd ~/LinuxKernel/ mkdir rootfs # 将MenuOS下载下来 git clone https://github.com/mengning/menu.git cd menu # 编译MenuOS gcc -pthread -o init linktable.c menu.c test.c -m32 -static cd ../rootfs cp ../menu/init ./ # 压制根文件系统 find . | cpio -o -Hnewc |gzip -9 > ../rootfs.img启动MenuOS
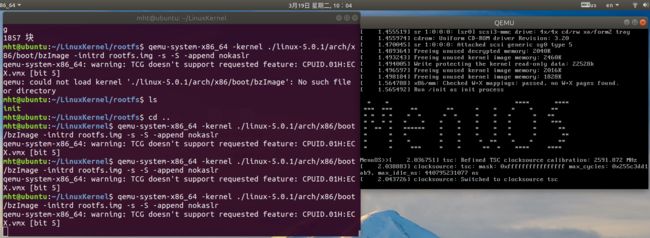
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ./linux-5.0.1/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.img -s -S -append nokaslr
选择系统调用函数
查询系统调用表,确定分析的系统调用
cat /usr/include/asm/unistd_32.h确定82号系统调用,select
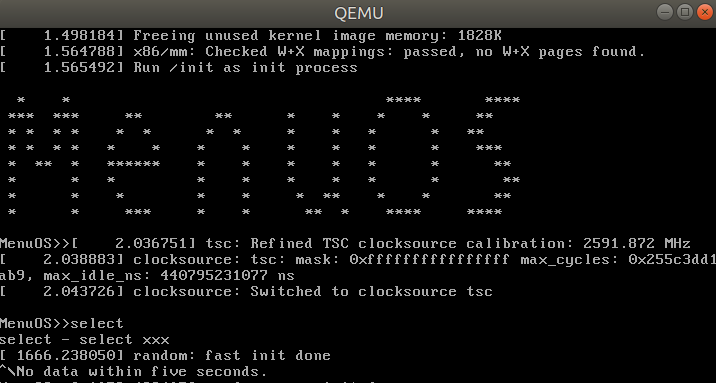
在MenuOS的test.c中插入 select系统调用的代码
/* 通过select系统调用,监听文件描述符上的可读、可写和异常等事件 */ int Select(int argc, char *argv[]){ fd_set rfds; struct timeval tv; int retval; /* Watch stdin (fd 0) to see when it has input. */ FD_ZERO(&rfds); FD_SET(0, &rfds); /* Wait up to five seconds. */ tv.tv_sec = 5; tv.tv_usec = 0; retval = select(1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv); /* Don’t rely on the value of tv now! */ if (retval == -1) perror("select()"); else if (retval) printf("Data is available now.\n"); /* FD_ISSET(0, &rfds) will be true. */ else printf("No data within five seconds.\n"); return 0; } int main() { PrintMenuOS(); SetPrompt("MenuOS>>"); MenuConfig("version","MenuOS V1.0(Based on Linux 3.18.6)",NULL); MenuConfig("quit","Quit from MenuOS",Quit); MenuConfig("time","Show System Time",Time); MenuConfig("time-asm","Show System Time(asm)",TimeAsm); /* 主函数中声明 */ MenuConfig("select","select xxx",Select); ExecuteMenu(); }重新编译MenuOS,执行Select函数
cd menu gcc -pthread -o init linktable.c menu.c test.c -m32 -static cd ../rootfs cp ../menu/init ./ find . | cpio -o -Hnewc |gzip -9 > ../rootfs.img
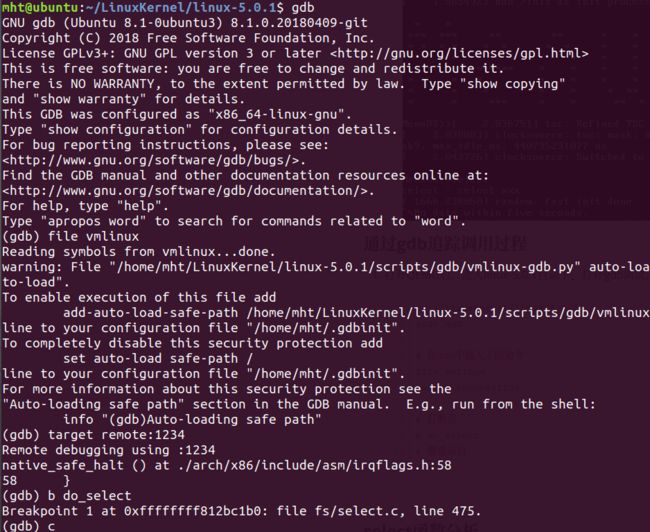
通过gdb追踪调用过程
打开QEMU后,进入linux-5.0.1目录下,打开gdb调试。
cd ~/LinuxKernel/linux-5.0.1 sudo gdb # 在gdb中输入下面命令 file vmlinux target remote:1234 # 打断点 b do_select # 继续运行 c输入ni,disass,info r三条命令,逐步跟踪系统调用
出栈操作,来恢复现场
系统调用分析
内核实现了很多的系统调用函数,函数会有自己的名称以及编号。用户要调用系统调用,首先需要使用 int 0x80 触发软中断。这个指令会在0x80代表十进制的128,所以这个指令会找终端向量表的128项,找到以后, 跳转到相应的函数(system_call)。
ENTRY(system_call)
RING0_INT_FRAME # can't unwind into user space anyway
ASM_CLAC
pushl_cfi %eax # save orig_eax
SAVE_ALL
GET_THREAD_INFO(%ebp)
# system call tracing in operation / emulation
testl $_TIF_WORK_SYSCALL_ENTRY,TI_flags(%ebp)
jnz syscall_trace_entry
cmpl $(NR_syscalls), %eax
jae syscall_badsys
# 查找系统调用表
syscall_call:
call *sys_call_table(,%eax,4)
syscall_after_call:
movl %eax,PT_EAX(%esp) # store the return value
syscall_exit:
LOCKDEP_SYS_EXIT
DISABLE_INTERRUPTS(CLBR_ANY) # make sure we don't miss an interrupt
# setting need_resched or sigpending
# between sampling and the iret
TRACE_IRQS_OFF
movl TI_flags(%ebp), %ecx
testl $_TIF_ALLWORK_MASK, %ecx # current->work
# 系统调用执行完后,进入。若没有进入,进行恢复现场工作
jne syscall_exit_work
restore_all:
TRACE_IRQS_IRET
restore_all_notrace:
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_ESPFIX32
movl PT_EFLAGS(%esp), %eax # mix EFLAGS, SS and CS
# Warning: PT_OLDSS(%esp) contains the wrong/random values if we
# are returning to the kernel.
# See comments in process.c:copy_thread() for details.
movb PT_OLDSS(%esp), %ah
movb PT_CS(%esp), %al
andl $(X86_EFLAGS_VM | (SEGMENT_TI_MASK << 8) | SEGMENT_RPL_MASK), %eax
cmpl $((SEGMENT_LDT << 8) | USER_RPL), %eax
CFI_REMEMBER_STATE
je ldt_ss # returning to user-space with LDT SS
#endif
restore_nocheck:
RESTORE_REGS 4 # skip orig_eax/error_code
# 效果等同与iret, 返回到用户态程序继续执行
irq_return:
INTERRUPT_RETURN
如果进入syscall_exit_work,能会进行信号处理以及进程调度
syscall_exit_work:
testl $_TIF_WORK_SYSCALL_EXIT, %ecx
jz work_pending
TRACE_IRQS_ON
ENABLE_INTERRUPTS(CLBR_ANY) # could let syscall_trace_leave() call
# schedule() instead
movl %esp, %eax
call syscall_trace_leave
jmp resume_userspace
END(syscall_exit_work)
syscall_exit_work以后, 有语句work_pending, 可能会跳转进入work_pending
work_pending:
testb $_TIF_NEED_RESCHED, %cl
jz work_notifysig
work_resched:
call schedule
LOCKDEP_SYS_EXIT
DISABLE_INTERRUPTS(CLBR_ANY) # make sure we don't miss an interrupt
# setting need_resched or sigpending
# between sampling and the iret
TRACE_IRQS_OFF
movl TI_flags(%ebp), %ecx
andl $_TIF_WORK_MASK, %ecx # is there any work to be done other
# than syscall tracing?
# .....
END(work_pending)
流程图
三、总结
- 指令流执行到系统调用函数时,系统调用函数通过int 0x80指令进入系统调用入口程序,并且把系统调用号放入%eax中,如果需要传递参数,则把参数放入%ebx,%ecx和%edx中。
- 进入系统调用入口程序(System_call)后,它首先把相关的寄存器压入内核堆栈(以备将来恢复),这个过程称为保护现场。
- 保护现场的工作完成后,开始检查系统调用号是不是一个有效值,如果不是则退出。接下来根据系统调用号开始调用系统调用处理程序(这是一个正式执行系统调用功能的函数),从系统调用处理程序返回后,就会去检查当前进程是否处于就绪态、进程时间片是否用完,如果不在就绪态或者时间片已用完,那么就会去调用进程调度程序schedule(),转去执行其他进程。
- 如果不执行进程调度程序,那么接下来就会开始执行ret_from_sys_call,这个程序主要执行一些系统调用的后处理工作。比如它会去检查当前进程是否有需要处理的信号,如果有则去调用do_signal(),然后进行一些恢复现场的工作,返回到原先的进程指令流中。
至此整个系统调用的过程就结束了。