pytorch之迁移学习(ResNet18)
pytorch之迁移学习(ResNet18)
In practice, very few people train an entire Convolutional Network from scratch (with random initialization), because it is relatively rare to have a dataset of sufficient size. Instead, it is common to pretrain a ConvNet on a very large dataset (e.g. ImageNet, which contains 1.2 million images with 1000 categories), and then use the ConvNet either as an initialization or a fixed feature extractor for the task of interest.
很少有人会用随机初始化网络去训练完整的神经网络因为训练的数据集不是足够大,而进行迁移学习,对其进行微调,上代码。下面代码参考pytorch官网的transfer learning
迁移学习的学习场景主要有两种:
Finetuning the convnet:我们使用预训练网络初始化网络,而不是随机初始化,就像在imagenet 1000数据集上训练的网络一样。 其余训练看起来像往常一样。也就是说将初始化变为了用已经训练好的网络。
ConvNet作为固定特征提取器:在这里,我们将冻结除最终完全连接层之外的所有网络的权重。 最后一个完全连接的层被替换为具有随机权重的新层,并且仅训练该层。即固定卷积层参数,调整最后面的全连接层的参数。
下面进行一个实例分析,利用ResNet18对蚂蚁和蜜蜂进行区分,此处为数据集,
首先导出需要应用的库:
from __future__ import print_function, division
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
import numpy as np
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import os
import copy
plt.ion() # interactive mode交互式模式
其次加载数据集:
将数据分为训练集验证集,resize成224x224方便ResNet网络的输入,利用dataloader对其进行叠加,对其分批次处理
data_transforms = {
'train': transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]),
'val': transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]),
}
data_dir = 'data/hymenoptera_data'
image_datasets = {x: datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, x),
data_transforms[x])
for x in ['train', 'val']}
dataloaders = {x: torch.utils.data.DataLoader(image_datasets[x], batch_size=4,
shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
for x in ['train', 'val']}
dataset_sizes = {x: len(image_datasets[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
class_names = image_datasets['train'].classes
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
三是可视化,可视化原数据集的一些照片实例如下:
def imshow(inp, title=None):
"""Imshow for Tensor."""
inp = inp.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))#从tensor变为numpy,将进行标准化的数据进行还原
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
inp = std * inp + mean
inp = np.clip(inp, 0, 1)
plt.imshow(inp)
if title is not None:
plt.title(title)
plt.pause(0.001) # pause a bit so that plots are updated
# Get a batch of training data得到一个批次的经过处理的标准化图像
inputs, classes = next(iter(dataloaders['train']))#得到标签和像素点都为tensor
# Make a grid from batch
out = torchvision.utils.make_grid(inputs)
imshow(out, title=[class_names[x] for x in classes])
def train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, num_epochs=25):
since = time.time()
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
print('Epoch {}/{}'.format(epoch, num_epochs - 1))
print('-' * 10)
# Each epoch has a training and validation phase
for phase in ['train', 'val']:
if phase == 'train':
scheduler.step()
model.train() # Set model to training mode
else:
model.eval() # Set model to evaluate mode
running_loss = 0.0
running_corrects = 0
# Iterate over data.
for inputs, labels in dataloaders[phase]:
inputs = inputs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# zero the parameter gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# forward
# track history if only in train
with torch.set_grad_enabled(phase == 'train'):
outputs = model(inputs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# backward + optimize only if in training phase
if phase == 'train':
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# statistics
running_loss += loss.item() * inputs.size(0)
running_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data)
epoch_loss = running_loss / dataset_sizes[phase]
epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / dataset_sizes[phase]
print('{} Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(
phase, epoch_loss, epoch_acc))
# deep copy the model
if phase == 'val' and epoch_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_acc
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
print()
time_elapsed = time.time() - since
print('Training complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
print('Best val Acc: {:4f}'.format(best_acc))
# load best model weights
model.load_state_dict(best_model_wts)
return model
最终可视化模型预测
def visualize_model(model, num_images=6):
was_training = model.training
model.eval()
images_so_far = 0
fig = plt.figure()
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(dataloaders['val']):
inputs = inputs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
for j in range(inputs.size()[0]):
images_so_far += 1
ax = plt.subplot(num_images//2, 2, images_so_far)
ax.axis('off')
ax.set_title('predicted: {}'.format(class_names[preds[j]]))
imshow(inputs.cpu().data[j])
if images_so_far == num_images:
model.train(mode=was_training)
return
model.train(mode=was_training)
上述为一个区分蚂蚁和蜜蜂的完整模型训练应该有的部分
其次分别应用两种迁移学习的方法对其进行训练:
1. Load a pretrained model 加载一个预训练模型reset final fully connected layer.仅仅改变最终全连接层的模型,训练时更新全部参数。
加载一个预训练模型
model_ft = models.resnet18(pretrained=True)#加载已经训练好的模型
num_ftrs = model_ft.fc.in_features
model_ft.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 2)#将全连接层做出改变类别改为两类
model_ft = model_ft.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Observe that all parameters are being optimized优化参数
optimizer_ft = optim.SGD(model_ft.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
# Decay LR by a factor of 0.1 every 7 epochs使用学习率缩减
exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer_ft, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
进行训练
调用train_model函数进行训练
model_ft = train_model(model_ft, criterion, optimizer_ft, exp_lr_scheduler,
num_epochs=25)
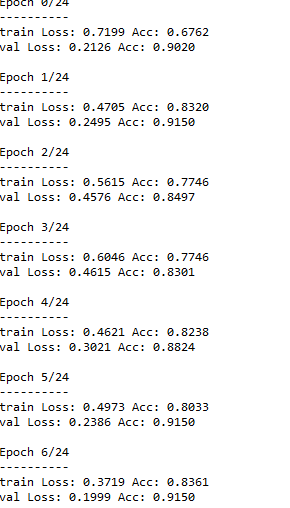
进行可视化和预测

2 第二种迁移学习训练方式
Here, we need to freeze all the network except the final layer. We need to set requires_grad == False to freeze the parameters so that the gradients are not computed in backward().固定卷积层,仅仅改变全连接层。训练时卷积层参数不变
model_conv = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
for param in model_conv.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# Parameters of newly constructed modules have requires_grad=True by default
num_ftrs = model_conv.fc.in_features
model_conv.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 2)
model_conv = model_conv.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Observe that only parameters of final layer are being optimized as
# opoosed to before.
optimizer_conv = optim.SGD(model_conv.fc.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
# Decay LR by a factor of 0.1 every 7 epochs
exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer_conv, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
训练和评估
model_conv = train_model(model_conv, criterion, optimizer_conv,
exp_lr_scheduler, num_epochs=25)
visualize_model(model_conv)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()


