Alexnet网络模型在cifar-10数据集上的实现(基于tensorflow-gpu)
最近根据github和tensoflow源代码中的关于Alexnet的一些代码,完成了一个在cifar-10训练集上进行训练和测试的Alexnet模型(算是半抄半改吧,哈哈!!)。实现在测试集上的accuracy=74%左右。最近没空,我就简单写写。
一,先总结我最近学习卷积神经网络的的大致过程
1.先看周志华的《机器学习》这本教材,我是把第五章神经网络看完结束,剩下的以后有空再看。最好要把里面公式尤(其第五章)能推导一遍,实在不会的可以先放在哪里,以后数学方面再补然后再看。
2.接下来我看了斯坦福李菲菲的课程,这里给个链接:http://cs231n.stanford.edu/syllabus.html,youtube上的,可以看,把里面的PPT下载下来对着视频看,可能有听不懂,但是也不要跳着看,越跳越不懂就越烦。这里务必要把CNN(卷积神经网络)搞清楚,尤其把卷积过程和池化过程搞清楚,不清楚的可以在网上搜,有很多博客写的都很好,但是也有一些博客有些地方错的要留意,
3.看论文《Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition》,这也算是CNN的鼻祖了,论文有点长,不需要看完,我就看了其中的一小部分,就是介绍这个网络的。但是要清楚的知道Lenet每一层是怎样卷积的,然后怎样池化的,有多少卷积核,多少参数等。总之弄懂这个就行了。
4.然后尝试实现一个简单的CNN模型用于mnists手写数字识别数据集,我用的是tennsorflow +python。可以参考官网教程,给个链接:http://www.tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/tutorials/mnist_pros.html 这个教程很好,tensoflow初学者可以直接从头开始看这个中文教程,循序渐进。
5.实现一点东西后就要可以进一步看paper了,我是把Alexnet,VGG,ResNet这几篇经典论文看了一遍,等对每一个模型比较清楚的时候就可以尝试实现其中的一部分啦。。
过程先简单的说一下,以前本想对AlexNet每一个模型都专门写一个文章说一下,但是时间有限,而且需要图片等说明才好理解。有人也再学习这方面的可以留言以后一起交流一下
二、AlexNet实现
1.先构建AlexNet模型
#coding=utf-8
import math
import tensorflow as tf
def print_activations(t):
print(t.op.name,'',t.get_shape().as_list) #get_shape获取一个TensorShape对象,然后通过as_list方法返回每一个维度数
def model():
_IMAGE_SIZE=32
_IMAGE_CHANNELS=3
_RESHAPE_SIZE=3*3*128
_NUM_CLASSES=10
parameters=[]
with tf.name_scope('data'):
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,_IMAGE_SIZE*_IMAGE_SIZE*_IMAGE_CHANNELS],name='images')
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,_NUM_CLASSES],name='Output')
images=tf.reshape(x,[-1,_IMAGE_SIZE,_IMAGE_SIZE,_IMAGE_CHANNELS],name='images')
print(images)
#conv1
#这里name_scope实际上是为了解决共享变量的问题,在name_scope下进行tf.Variable(name)
#如果name重名,会自动检测命名冲突进行处理
with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
kernel=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5,5,3,64],dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
#变量解释 [a,b,c,d]分别表示,1表示是否跳过一些样本,比如a=1时,就是从1,2,3...训
#跳过一些,a=2时就选择1,3,5...,b表示高方向滑动,c表示宽方向滑动,d表示通道滑动
#same表示当卷积核超出边界时会进行0填充
conv=tf.nn.conv2d(images,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[64],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='bias')
bias=tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv1=tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope) #这里返回的是一个tensor(一个张量类),但是这里的name=scope是什么意思?
print_activations(conv1)
tf.summary.histogram('Convolution_layers/conv1',conv1)
tf.summary.scalar('Convolution_layers/conver1',tf.nn.zero_fraction(conv1))
#这一步时local Response Normalization技术详情可以查看论文中描述
#lrn1
with tf.name_scope('lrn1') as scope:
lrn1=tf.nn.local_response_normalization(conv1,
alpha=1e-4,
beta=0.75,
depth_radius=2,
bias=2.0)
#pool1
pool1=tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1,ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],
padding='VALID',name='pool1')
print_activations(pool1)
#conv2
with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 64, 64], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
tf.summary.histogram('Convolution_layers/conv2',conv2)
tf.summary.scalar('Convolution_layers/conver2',tf.nn.zero_fraction(conv2))
print_activations(conv2)
#lrn2
with tf.name_scope('lrn2') as scope:
lrn2 = tf.nn.local_response_normalization(conv2,alpha=1e-4,beta=0.75,
depth_radius=2, bias=2.0)
# pool2
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='VALID',name='pool2')
print_activations(pool2)
#conv3
with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
kernel =tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,64,128],dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
conv=tf.nn.conv2d(pool2,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[128],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias=tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv3=tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
print_activations(conv3)
tf.summary.histogram('Convolution_layers/conv3',conv3)
tf.summary.scalar('Convolution_layers/conver3',tf.nn.zero_fraction(conv3))
#conv4
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
kernel =tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,128,128],dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
conv=tf.nn.conv2d(conv3,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[128],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias=tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv4=tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
print_activations(conv4)
tf.summary.histogram('Convolution_layers/conv4',conv4)
tf.summary.scalar('Convolution_layers/conver4',tf.nn.zero_fraction(conv4))
#conv5
with tf.name_scope('conv5') as scope:
kernel =tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,128,128],dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
conv=tf.nn.conv2d(conv4,kernel,[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[128],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
bias=tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases)
conv5=tf.nn.relu(bias,name=scope)
print_activations(conv5)
tf.summary.histogram('Convolution_layers/conv5',conv5)
tf.summary.scalar('Convolution_layers/conver5',tf.nn.zero_fraction(conv5))
#pool5
pool5=tf.nn.max_pool(conv5,ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],
padding='VALID',name='pool5')
print_activations(pool5)
#fully_connected1
with tf.name_scope('fully_connected1') as scope:
reshape=tf.reshape(pool5,[-1,_RESHAPE_SIZE])
dim=reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weights =tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([dim,384],dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
print_activations(weights)
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[384],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
local3=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape,weights)+biases,name=scope)
print_activations(local3)
tf.summary.histogram('Fully connected layers/fc1',local3)
tf.summary.scalar('Fully connected layers/fc1',tf.nn.zero_fraction(local3))
#fully_connected2
with tf.name_scope('fully_connected') as scope:
weights =tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([384,192],dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
print_activations(weights)
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[192],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
local4=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3,weights)+biases,name=scope)
print_activations(local4)
tf.summary.histogram('Fully connected layers/fc2',local4)
tf.summary.scalar('Fully connected layers/fc4',tf.nn.zero_fraction(local4))
#output
with tf.name_scope('output') as scope:
weights =tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([192,_NUM_CLASSES],dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1),name='weights')
print_activations(weights)
biases=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[_NUM_CLASSES],dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True,name='biases')
softmax_linear=tf.add(tf.matmul(local4,weights),biases,name=scope)
tf.summary.histogram('Fully connected layers/output',softmax_linear)
global_step=tf.Variable(initial_value=0,name='global_step',trainable=False)
y_pred_cls=tf.argmax(softmax_linear,axis=1)
return x,y,softmax_linear,global_step,y_pred_cls
2.提取数据,用到的是cifar-10,代码里有自动下载
import pickle
import numpy as np
import os
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
import tarfile
import zipfile
import sys
def get_data_set(name="train", cifar=10):
x = None
y = None
l = None
maybe_download_and_extract()
folder_name = "cifar_10" if cifar == 10 else "cifar_100"
f = open('./data_set/'+folder_name+'/batches.meta', 'rb')
datadict = pickle.load(f, encoding='latin1')
f.close()
l = datadict['label_names']
if name is "train":
for i in range(5):
f = open('./data_set/'+folder_name+'/data_batch_' + str(i + 1), 'rb')
datadict = pickle.load(f, encoding='latin1') #提取数据
f.close()
_X = datadict["data"]
_Y = datadict['labels']
#print('_X')
#print(_X)
#print(np.shape(_X))
_X = np.array(_X, dtype=float) / 255.0
#print(np.shape(_X))
_X = _X.reshape([-1, 3, 32, 32])
#print(np.shape(_X))
_X = _X.transpose([0, 2, 3, 1])#矩阵转置,里面的编号是指将原来的维度变换到当前维度
#例如,原来的2变换到当前1维度
_X = _X.reshape(-1, 32*32*3)
if x is None:
x = _X
y = _Y
else:
x = np.concatenate((x, _X), axis=0) #将x与读取的_X拼接起来
y = np.concatenate((y, _Y), axis=0)
elif name is "test":
f = open('./data_set/'+folder_name+'/test_batch', 'rb')
datadict = pickle.load(f, encoding='latin1')
f.close()
x = datadict["data"]
y = np.array(datadict['labels'])
x = np.array(x, dtype=float) / 255.0
x = x.reshape([-1, 3, 32, 32])
x = x.transpose([0, 2, 3, 1])
x = x.reshape(-1, 32*32*3)
def dense_to_one_hot(labels_dense, num_classes=10):
num_labels = labels_dense.shape[0]
index_offset = np.arange(num_labels) * num_classes
labels_one_hot = np.zeros((num_labels, num_classes))
labels_one_hot.flat[index_offset + labels_dense.ravel()] = 1
return labels_one_hot
return x, dense_to_one_hot(y), l
get_data_set(name="train")
def _print_download_progress(count, block_size, total_size):
pct_complete = float(count * block_size) / total_size
msg = "\r- Download progress: {0:.1%}".format(pct_complete)
sys.stdout.write(msg)
sys.stdout.flush()
def maybe_download_and_extract():
main_directory = "./data_set/"
cifar_10_directory = main_directory+"cifar_10/"
if not os.path.exists(main_directory):
os.makedirs(main_directory)
url = "http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz"
filename = url.split('/')[-1]
file_path = os.path.join(main_directory, filename)
zip_cifar_10 = file_path
file_path, _ = urlretrieve(url=url, filename=file_path, reporthook=_print_download_progress)
print()
print("Download finished. Extracting files.")
if file_path.endswith(".zip"):
zipfile.ZipFile(file=file_path, mode="r").extractall(main_directory)
elif file_path.endswith((".tar.gz", ".tgz")):
tarfile.open(name=file_path, mode="r:gz").extractall(main_directory)
print("Done.")
os.rename(main_directory+"./cifar-10-batches-py", cifar_10_directory)
os.remove(zip_cifar_10)
3.训练(这里batch_size大小为128,包括了每100步对测试集进行一次测试)
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from time import time
from alexnet import model
from data import get_data_set
train_x,train_y,tain_l=get_data_set("train")
test_x,test_y,test_l=get_data_set("test")
x,y,output,global_step,y_pred_cls=model()
_IMG_SIZE = 32
_NUM_CHANNELS = 3
_BATCH_SIZE = 128
_CLASS_SIZE = 10
_ITERATION = 300
_SAVE_PATH = "tensorboard/cifar-10/"
_SAVE_BOARD_PATH="tensorboard/board/"
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=output,labels=y))
optimizer=tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-3).minimize(loss,global_step=global_step)
correct_prediction=tf.equal(y_pred_cls,tf.argmax(y,axis=1))
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)
tf.summary.scalar("Accyracy/train",accuracy)
tf.summary.histogram('histogram',accuracy)
saver=tf.train.Saver()
sess=tf.Session()
merged=tf.summary.merge_all()
train_writer=tf.summary.FileWriter(_SAVE_BOARD_PATH,sess.graph)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#sess_path=saver.save(sess,_SAVE_PATH)
#try:
# print("Trying to restore last checkpoint..... ")
# last_chk_path=tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir=_SAVE_PATH) #将变量保存在此路径
# saver.restore(sess,save_path=last_chk_path)
# print("Restored checkpoint from:",last_chk_path)
#except:
# print("Failed to restore checkpoint.Initializing variables instead")
# sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
def train(num_iterations):
for i in range(num_iterations):
randidx=np.random.randint(len(train_x),size=_BATCH_SIZE) #此处返回的是小于冷(train)的离散均匀分布,总共有128个
batch_xs=train_x[randidx]
batch_ys=train_y[randidx]
start_time=time()
i_global,_=sess.run([global_step,optimizer],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
duration=time()-start_time
if(i_global%10==0)or(i==num_iterations-1):
_loss,batch_acc=sess.run([loss,accuracy],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
msg= "Glo bal Step: {0:>6}, accuracy: {1:>6.1%}, loss = {2:.2f} ({3:.1f} examples/sec, {4:.2f} sec/batch)"
print(msg.format(i_global, batch_acc, _loss, _BATCH_SIZE / duration, duration))
resultmerged=sess.run(merged,feed_dict={xs:batch_xs,ys:batch_ys})
train_writer.add_summary(resultmerged,i_global)
if (i_global%100==0)or(i==num_iterations-1):
acc=predict_test()
print('test accuracy is:')
print(acc)
saver.save(sess,save_path=_SAVE_PATH,global_step=global_step)
print("Saved checkpoint")
def predict_test(show_confusion_matrix=False):
i=0
predicted_class=np.zeros(shape=len(test_x),dtype=np.int)#返回一个新的数组,用零填充
print('test_x的长度:')
print(len(test_x))
while i4.预测,根据训练结束后的变量值测试accuracy以及生成以列表如下图
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from data import get_data_set
from alexnet import model
test_x, test_y, test_l = get_data_set("test", cifar=10)
x, y, output, global_step, y_pred_cls = model()
_IMG_SIZE = 32
_NUM_CHANNELS = 3
_BATCH_SIZE = 128
_CLASS_SIZE = 10
_SAVE_PATH = "tensorboard/cifar-10/"
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess = tf.Session()
try:
print("Trying to restore last checkpoint ...")
last_chk_path = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir=_SAVE_PATH)
saver.restore(sess, save_path=last_chk_path)
print("Restored checkpoint from:", last_chk_path)
except:
print("Failed to restore checkpoint. Initializing variables instead.")
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
i = 0
predicted_class = np.zeros(shape=len(test_x), dtype=np.int)
while i < len(test_x):
j = min(i + _BATCH_SIZE, len(test_x))
batch_xs = test_x[i:j, :]
batch_ys = test_y[i:j, :]
predicted_class[i:j] = sess.run(y_pred_cls, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
i = j
correct = (np.argmax(test_y, axis=1) == predicted_class)
acc = correct.mean()*100
correct_numbers = correct.sum()
print("Accuracy on Test-Set: {0:.2f}% ({1} / {2})".format(acc, correct_numbers, len(test_x)))
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true=np.argmax(test_y, axis=1), y_pred=predicted_class)
for i in range(_CLASS_SIZE):
class_name = "({}) {}".format(i, test_l[i])
print(cm[i, :], class_name)
class_numbers = [" ({0})".format(i) for i in range(_CLASS_SIZE)]
print("".join(class_numbers))
sess.close()以下是4中代码运行结果
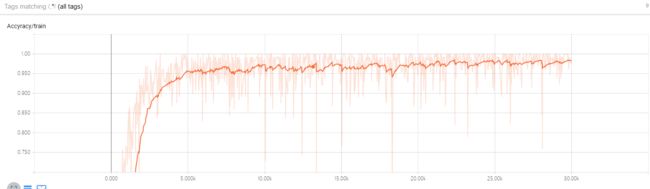
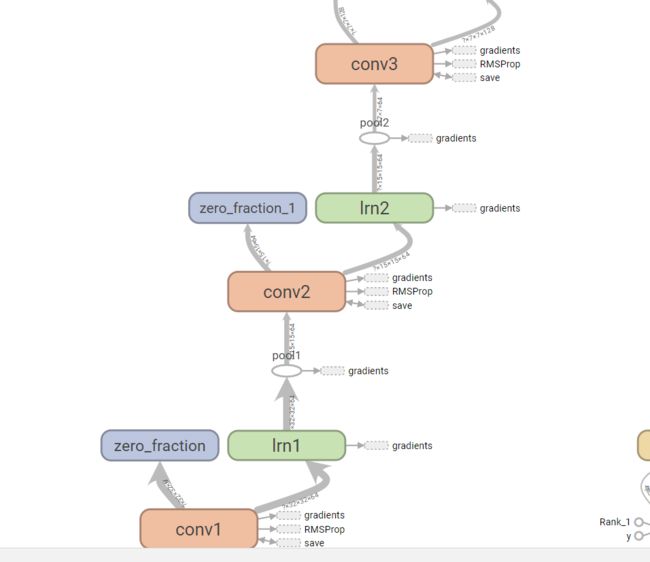
下面是在tensorboard上生成的网络结构,图比较大,截成两部分了
下面是在训练集上生成的accuracy图
时间紧迫,我就这样简单写写,以后有空再对每个文件具体说明。 暂时 有什么疑问可以在下方留言
声明:本人刚开始学深度学习,有什么说错的地方希望大家体谅
并能予以提出,我会加以改正!谢谢~
最后再贴上我github上代码的链接:https://github.com/xi-mao/alexnet-cifar-10 ,可以直接下载使用