React Native坑之(设置请求的连接超时时间)
前言:好不容易rn算是入门了,可能是由于前面ios限制热更新的影响,导致大领导一句话:“防止后期可能存在的风险,所有rn项目不做啦!!“这尼玛就尴尬了~不过没关系,继续做我的原生android,当然,话虽如此,但是不代表我就此止步rn了,学习的脚步还是不能断哦,多一门技术还是没有什么坏处的。
好啦~废话不多说了,下面看看最近搞rn遇到的一点小烦恼~~~
因为项目中需要调一个接口,然后这个接口呢是有时间限制的,但是用rn原生的fetch去发送网络请求我压根就找不到有什么设置timeout的方法啊,这就尴尬了~~~~(难道rn连timeout这个东西都没有么?)带着疑问撸了一把源码,果然没有!!
我们在rn中用fetch发送一个请求可能是这样的:
async start(successCallBack, failCallBack) {
try {
let url = AppConst.BASE_URL + this.requestUrl();
let response = await fetch(url, {
headers: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.headers,
method: this.method,
body: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.body,
timeout:10
});
let responseJson = await response.json();
if(this.isShowing){
this.dismissLoadingView();
}
if (responseJson&&!this.isCancled) {
this.handleResponse(responseJson, successCallBack);
} else {
if (failCallBack&&!this.isCancled)failCallBack('请求失败');
}
} catch (erro) {
console.log('catch-->'+erro);
if(!this.isCancled)this.showSnackBar('网络异常'+erro);
if (failCallBack&&!this.isCancled)failCallBack('网络异常');
if(this.isShowing){
this.dismissLoadingView();
}
}
}注意:这里的 timeout:10是我修改过后使用的,这个工具类的源码我待会会给出的。。
我们是直接调用fetch方法,然后传递两个参数,一个是url,一个是请求一些配置参数:
let response = await fetch(url, {
headers: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.headers,
method: this.method,
body: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.body,
timeout:10
});然后我们点fetch方法进去看看它到底长啥样(它的位置在):
/xxx/node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Network/fetch.js/**
* Copyright (c) 2015-present, Facebook, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
* of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
*
* @providesModule fetch
* @nolint
*
*/
'use strict';
import 'whatwg-fetch';
module.exports = {fetch, Headers, Request, Response};
好啦~~我们继续往下看看whatwg-fetch.js(它的代码太多,我就直接看重点fetch方法):
self.fetch = function(input, init) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
var request = new Request(input, init)
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.onload = function() {
var options = {
status: xhr.status,
statusText: xhr.statusText,
headers: parseHeaders(xhr.getAllResponseHeaders() || '')
}
options.url = 'responseURL' in xhr ? xhr.responseURL : options.headers.get('X-Request-URL')
var body = 'response' in xhr ? xhr.response : xhr.responseText
resolve(new Response(body, options))
}
xhr.onerror = function() {
reject(new TypeError('Network request failed'))
}
xhr.ontimeout = function() {
reject(new TypeError('Network request failed'))
}
xhr.open(request.method, request.url, true)
if (request.credentials === 'include') {
xhr.withCredentials = true
}
if ('responseType' in xhr && support.blob) {
xhr.responseType = 'blob'
}
request.headers.forEach(function(value, name) {
xhr.setRequestHeader(name, value)
})
if(init!=null&&init.timeout!=null){
xhr.timeout=init.timeout;
}
xhr.send(typeof request._bodyInit === 'undefined' ? null : request._bodyInit)
})
}self.fetch = function(input, init) 这里有两个参数,一个是input(对应我们传递的url)一个是init,对应我们传递的对象:
let response = await fetch(url, {
headers: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.headers,
method: this.method,
body: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.body,
timeout:10
});然后把我们传递的这两个参数封装进了一个叫Request的类中,最后通过XMLHttpRequest类的send方法把Request发送了出去:
xhr.send(typeof request._bodyInit === 'undefined' ? null : request._bodyInit)
我们点进这个XMLHttpRequest看看它是咋send的,文件对应路径(/xxx/node_modules/react-native/Libraries/Network/XMLHttpRequest.js):
send(data: any): void {
.....
RCTNetworking.sendRequest(
this._method,
this._trackingName,
this._url,
this._headers,
data,
nativeResponseType,
incrementalEvents,
this.timeout,
this.__didCreateRequest.bind(this),
);
}终于看到了有用点的方法了:
RCTNetworking.sendRequest看RCTNetworking这个类名字就知道,它是一个原生跟rn交互的一个类, RCTNetworking.sendRequest里面调的就是原生的方法:
我这里就以android为例了,我们找到这个一个原生类:
/xxxx/node_modules/react-native/ReactAndroid/src/main/java/com/facebook/react/modules/network/NetworkingModule.java @Override
public String getName() {
return "RCTNetworking";
}
@Override
public void onCatalystInstanceDestroy() {
mShuttingDown = true;
cancelAllRequests();
mCookieHandler.destroy();
mCookieJarContainer.removeCookieJar();
}
@ReactMethod
/**
* @param timeout value of 0 results in no timeout
*/
public void sendRequest(
final ExecutorToken executorToken,
String method,
String url,
final int requestId,
ReadableArray headers,
ReadableMap data,
final String responseType,
final boolean useIncrementalUpdates,
int timeout) {
Request.Builder requestBuilder = new Request.Builder().url(url);
if (requestId != 0) {
requestBuilder.tag(requestId);
}
final RCTDeviceEventEmitter eventEmitter = getEventEmitter(executorToken);
OkHttpClient.Builder clientBuilder = mClient.newBuilder();
if (timeout != mClient.connectTimeoutMillis()) {
clientBuilder.readTimeout(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}好啦~~作为一个学android的童鞋,看到sendRequest这个方法的时候,是不是觉得很熟悉了呢? 是的!! 它就是使用了okhttp网络请求框架!
我们好像有点偏离了我们的主题了,哈哈~~,好了,重点来了~~我们看到最后okhttp的一行代码:
if (timeout != mClient.connectTimeoutMillis()) {
clientBuilder.readTimeout(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}这个就是我们今天要找的东西,这个timeout是谁传给okhttp的呢?是rn传递过去的,我们又一步一步往上找了:
RCTNetworking.sendRequest(
this._method,
this._trackingName,
this._url,
this._headers,
data,
nativeResponseType,
incrementalEvents,
this.timeout,
this.__didCreateRequest.bind(this),
);
}好了,我们看到了传递的timeout为this.timeout,那么this是谁了,正是我们前面说过的XMLHttpRequest对象,我们赶紧找找这个this.timeout在哪赋值的:
readyState: number = UNSENT;
responseHeaders: ?Object;
status: number = 0;
timeout: number = 0;
responseURL: ?string;除了默认给了个0以外找不到其它赋值的地方了~~~~(怪不得我去网上找都找不到给rn设置超时的方法,原来如此啊!)是的,我们似乎已经找不到了思路了,就是给XMLHttpRequest对象的timeout属性设置一个值就可以了,那问题来了,我们怎么给XMLHttpRequest的timeout属性设置值呢???
我们找不到在哪new的XMLHttpRequest对象就在哪赋值,我们回到最初的fetch方法:
/xxxx/node_modules/whatwg-fetch/fetch.jsself.fetch = function(input, init) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
var request = new Request(input, init)
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.onload = function() {
var options = {
status: xhr.status,
statusText: xhr.statusText,
headers: parseHeaders(xhr.getAllResponseHeaders() || '')
}
options.url = 'responseURL' in xhr ? xhr.responseURL : options.headers.get('X-Request-URL')
var body = 'response' in xhr ? xhr.response : xhr.responseText
resolve(new Response(body, options))
}
xhr.onerror = function() {
reject(new TypeError('Network request failed'))
}
xhr.ontimeout = function() {
reject(new TypeError('Network request failed'))
}
xhr.open(request.method, request.url, true)
if (request.credentials === 'include') {
xhr.withCredentials = true
}
if ('responseType' in xhr && support.blob) {
xhr.responseType = 'blob'
}
request.headers.forEach(function(value, name) {
xhr.setRequestHeader(name, value)
})
//我们只需要加上下面这段代码即可
if(init!=null&&init.timeout!=null){
xhr.timeout=init.timeout;
}
xhr.send(typeof request._bodyInit === 'undefined' ? null : request._bodyInit)
})
}我们加上一段给xhr对象的timeout属性赋值的代码:
//我们只需要加上下面这段代码即可
if(init!=null&&init.timeout!=null){
xhr.timeout=init.timeout;
}然后在我们调用的时候,我们就可以开心的传递我们的timeout参数了:
let response = await fetch(url, {
headers: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.headers,
method: this.method,
body: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.body,
timeout:10000
});注意啦!!!这个timeout的单位是以毫秒为单位的。。。。
好啦!!!搞定了~~我们需要重启一下我们的npm,然后运行项目~
我们来测试一下:
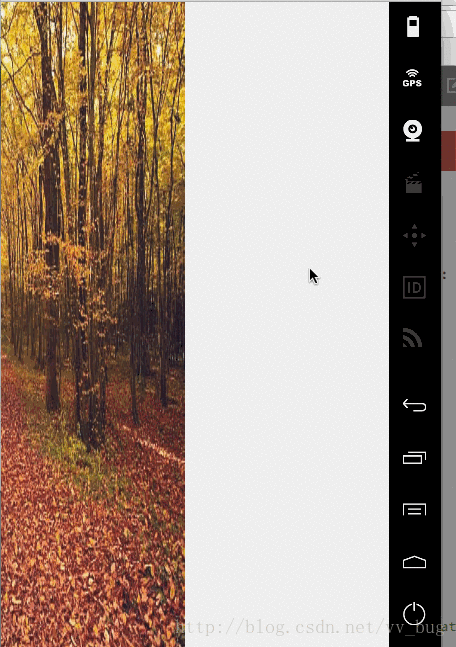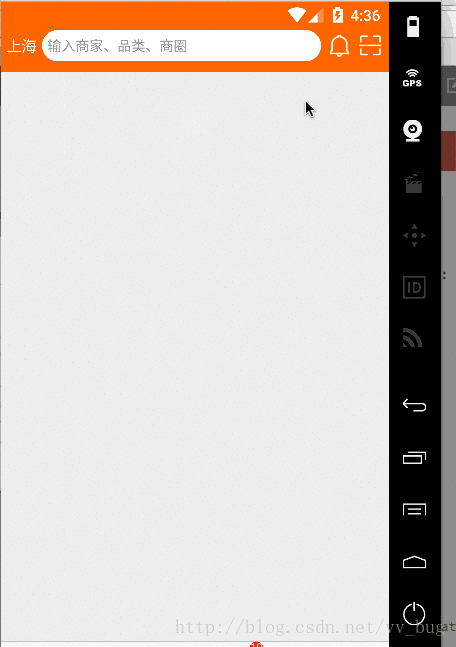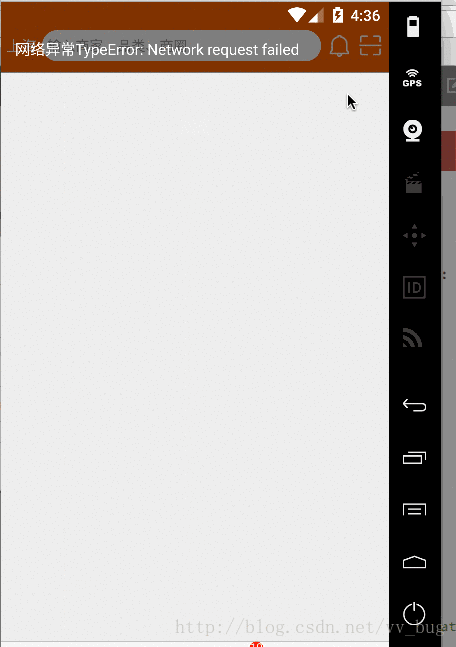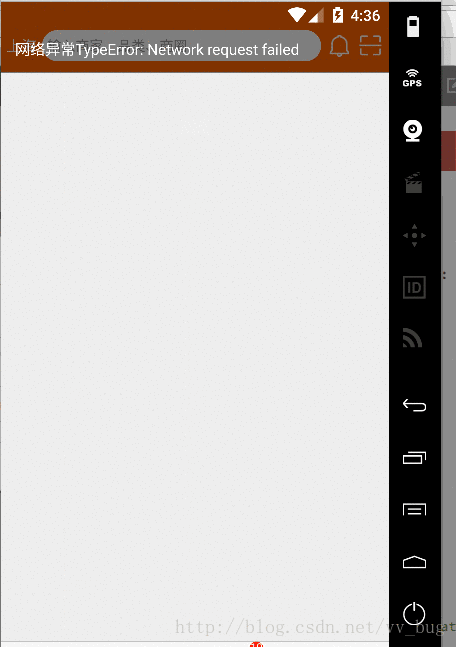
当我们设置timeout为1ss的时候:
let response = await fetch(url, {
headers: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.headers,
method: this.method,
body: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.body,
timeout:1
});我们看到,网络请求直接报错了超时了~~
然后我们设置为10s:
let response = await fetch(url, {
headers: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.headers,
method: this.method,
body: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.body,
timeout:10*1000
});运行结果:
可以看到,我们成功拿到了我们的数据了,也就是说我们设置的timeout起了效果的。。
最后附上BaseRequest.js的全部代码:
/**
* Created by leo on 17/2/21.
*/
/**
* @author YASIN
* @version [Android YASIN V01, ]
* @blog http://blog.csdn.net/vv_bug
* @description
*/
import AppConst from '../Constant/AppConstant';
import ResponseStatus from '../Constant/ResponseStatus';
import * as LoadingViewAction from '../Redux/Action/LoadingView';
import * as SnackBarAction from '../Redux/Action/SnackBar';
import store from '../Redux/Store';
import TimerMiXin from 'react-timer-mixin';
export default class BaseRequest {
// 构造
constructor(body, method) {
this.isCancled=false;
if (body == null) {
body = {};
}
Object.assign(body, {
version:AppConst.version
});
if (method == null || (method !== 'GET' || method !== 'POST')) {
method = 'POST';
}
this.body = JSON.stringify(body);
;
this.method = method;
this.headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
};
}
requestUrl() {
throw ({message: 'function requestUrl must be overrided!'});
}
showLoadingView(){
this.isShowing=true;
store.dispatch(LoadingViewAction.showLoadingView())
return this;
}
dismissLoadingView(){
TimerMiXin.setTimeout(()=>{
this.isShowing=false;
store.dispatch(LoadingViewAction.dismissLoadingView())
},100);
return this;
}
async start(successCallBack, failCallBack) {
try {
let url = AppConst.BASE_URL + this.requestUrl();
let response = await fetch(url, {
headers: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.headers,
method: this.method,
body: this.method == 'GET' ? null : this.body,
timeout:10
});
let responseJson = await response.json();
if(this.isShowing){
this.dismissLoadingView();
}
if (responseJson&&!this.isCancled) {
this.handleResponse(responseJson, successCallBack);
} else {
if (failCallBack&&!this.isCancled)failCallBack('请求失败');
}
} catch (erro) {
console.log('catch-->'+erro);
if(!this.isCancled)this.showSnackBar('网络异常'+erro);
if (failCallBack&&!this.isCancled)failCallBack('网络异常');
if(this.isShowing){
this.dismissLoadingView();
}
}
}
handleResponse(responseJson, successCallBack) {
if (ResponseStatus.SUCCESS == responseJson.code) {
if(successCallBack)successCallBack(responseJson);
}else if(responseJson.message&&responseJson.message.length>0){
this.showSnackBar(responseJson.message);
}
}
showSnackBar(text) {
TimerMiXin.setTimeout(()=>{
store.dispatch(SnackBarAction.showSnackBar(text))
},200);
}
isCancle(){
return this.isCancled;
}
setCancled(cancle:bool){
this.isCancled=cancle;
}
}end…….