Java的List和Json转换以及StringRedisTemplate往redis存泛型对象
List转Json
List user= new ArrayList();
String str = JSON.toJSONString(user); Json 转List方法一
List user= JSON.parseArray(json,User.class);
如果是泛型方法需要使用TypeReference
Json 转List 方法二
String json = "[{}]";
List user= JSON.parseObject(json,new TypeReference>(){}); 泛型T
Json 转List方法三
List students = JSON.parseObject(listCache,new TypeReference>(){});
综合例子:Springboot环境下利用StringRedisTemplate往redis存泛型对象
一开始要注入下StringRedisTemplate
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;Redis获取值不存在就从数据库取出来json化存缓存,存在则直接反序列化json为List
List list;
String listCache=redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(listCache!=null){
list = JSON.parseObject(listCache,new TypeReference>(){});
}
else {
list = userService.getAllList();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSON.toJSONString(list), 60 * 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} 附录:TypeReference源码
package com.alibaba.fastjson;
import java.lang.reflect.GenericArrayType;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.lang.reflect.TypeVariable;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.util.ParameterizedTypeImpl;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils;
/**
* Represents a generic type {@code T}. Java doesn't yet provide a way to
* represent generic types, so this class does. Forces clients to create a
* subclass of this class which enables retrieval the type information even at
* runtime.
*
* For example, to create a type literal for {@code List}, you can
* create an empty anonymous inner class:
*
*
* TypeReference<List<String>> list = new TypeReference<List<String>>() {};
*
* This syntax cannot be used to create type literals that have wildcard
* parameters, such as {@code Class} or {@code List}.
*/
public class TypeReference {
static ConcurrentMap classTypeCache
= new ConcurrentHashMap(16, 0.75f, 1);
protected final Type type;
/**
* Constructs a new type literal. Derives represented class from type
* parameter.
*
* Clients create an empty anonymous subclass. Doing so embeds the type
* parameter in the anonymous class's type hierarchy so we can reconstitute it
* at runtime despite erasure.
*/
protected TypeReference(){
Type superClass = getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
Type type = ((ParameterizedType) superClass).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
Type cachedType = classTypeCache.get(type);
if (cachedType == null) {
classTypeCache.putIfAbsent(type, type);
cachedType = classTypeCache.get(type);
}
this.type = cachedType;
}
/**
* @since 1.2.9
* @param actualTypeArguments
*/
protected TypeReference(Type... actualTypeArguments){
Class thisClass = this.getClass();
Type superClass = thisClass.getGenericSuperclass();
ParameterizedType argType = (ParameterizedType) ((ParameterizedType) superClass).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
Type rawType = argType.getRawType();
Type[] argTypes = argType.getActualTypeArguments();
int actualIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; ++i) {
if (argTypes[i] instanceof TypeVariable &&
actualIndex < actualTypeArguments.length) {
argTypes[i] = actualTypeArguments[actualIndex++];
}
// fix for openjdk and android env
if (argTypes[i] instanceof GenericArrayType) {
argTypes[i] = TypeUtils.checkPrimitiveArray(
(GenericArrayType) argTypes[i]);
}
// 如果有多层泛型且该泛型已经注明实现的情况下,判断该泛型下一层是否还有泛型
if(argTypes[i] instanceof ParameterizedType) {
argTypes[i] = handlerParameterizedType((ParameterizedType) argTypes[i], actualTypeArguments, actualIndex);
}
}
Type key = new ParameterizedTypeImpl(argTypes, thisClass, rawType);
Type cachedType = classTypeCache.get(key);
if (cachedType == null) {
classTypeCache.putIfAbsent(key, key);
cachedType = classTypeCache.get(key);
}
type = cachedType;
}
private Type handlerParameterizedType(ParameterizedType type, Type[] actualTypeArguments, int actualIndex) {
Class thisClass = this.getClass();
Type rawType = type.getRawType();
Type[] argTypes = type.getActualTypeArguments();
for(int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; ++i) {
if (argTypes[i] instanceof TypeVariable && actualIndex < actualTypeArguments.length) {
argTypes[i] = actualTypeArguments[actualIndex++];
}
// fix for openjdk and android env
if (argTypes[i] instanceof GenericArrayType) {
argTypes[i] = TypeUtils.checkPrimitiveArray(
(GenericArrayType) argTypes[i]);
}
// 如果有多层泛型且该泛型已经注明实现的情况下,判断该泛型下一层是否还有泛型
if(argTypes[i] instanceof ParameterizedType) {
return handlerParameterizedType((ParameterizedType) argTypes[i], actualTypeArguments, actualIndex);
}
}
Type key = new ParameterizedTypeImpl(argTypes, thisClass, rawType);
return key;
}
/**
* Gets underlying {@code Type} instance.
*/
public Type getType() {
return type;
}
public final static Type LIST_STRING = new TypeReference>() {}.getType();
}
TypeReference的存在是因为java中子类可以获取到父类泛型的真实类型。
其中核心的方法是:getActualTypeArguments,它可以得到父类的反省类型
ParameterizedType是一个记录类型泛型的接口, 继承自Type,一共三方法:
Type[] getActualTypeArguments(); //返回泛型类型数组
Type getRawType(); //返回原始类型Type
Type getOwnerType(); //返回 Type 对象,表示此类型是其成员之一的类型。
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/609441
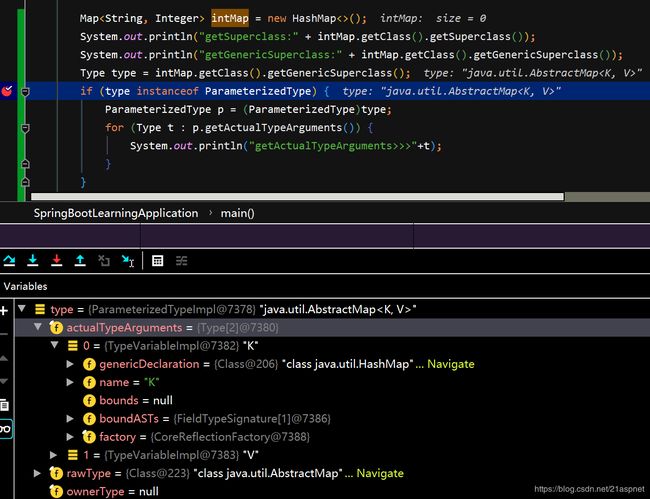
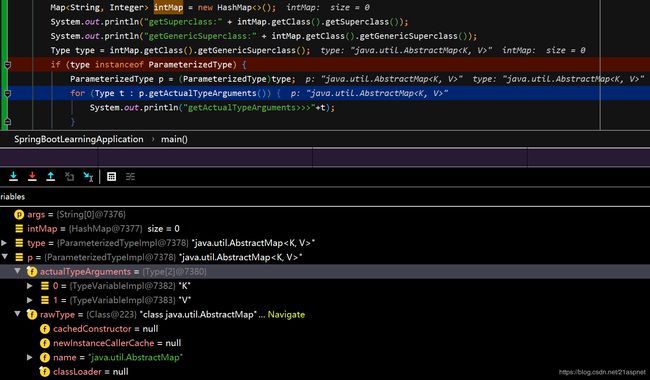
Map intMap = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println("getSuperclass:" + intMap.getClass().getSuperclass());
System.out.println("getGenericSuperclass:" + intMap.getClass().getGenericSuperclass());
Type type = intMap.getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {
ParameterizedType p = (ParameterizedType)type;
for (Type t : p.getActualTypeArguments()) {
System.out.println("getActualTypeArguments>>>"+t);
}
}
扩展阅读Java如何获得泛型类的真实类型:
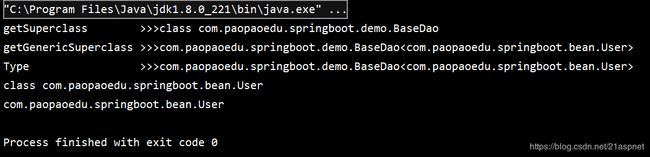
package com.paopaoedu.springboot.demo;
import com.paopaoedu.springboot.bean.User;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
public class BaseDao{
private Class clazz;
// 使用反射技术得到T的真实类型
public Class getRealType(){
Class c=this.getClass();
//getSuperclass()获得该类的父类
System.out.println("getSuperclass >>>"+c.getSuperclass());
//getGenericSuperclass()获得带有泛型的父类
System.out.println("getGenericSuperclass >>>"+c.getGenericSuperclass());
//Type是 Java 编程语言中所有类型的公共高级接口。它们包括原始类型、参数化类型、数组类型、类型变量和基本类型。
Type type=c.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println("Type >>>"+type);
//ParameterizedType参数化类型,即泛型
// 获取当前new的对象的泛型的父类类型
ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType) this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
// 获取第一个类型参数的真实类型
this.clazz = (Class) pt.getActualTypeArguments()[0];
c=(Class) pt.getActualTypeArguments()[0];
System.out.println(c);
return clazz;
}
}
class userdemo extends BaseDao{
public static void main(String[] args) {
userdemo classB = new userdemo();
Class realType = classB.getRealType();
System.out.println(realType.getName());
}
}