PM Framework
Project management is the application of knowledge, skills ,tools and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements. For every project is constrained in different ways by its scope, time , and cost goal. These limitations are sometimes referred to in project management as the "triple constraint" However, to create a successful project, a project manager must consider scope, time, and cost and balance these three often-competing goals. He must consider the following:
- Scope: What work will be done as part of the project? what unique product, service, or result does the customer or sponsor expect from the project?
- Time: How long should it take to complete the project? what is the project's schedule?
- Cost: What should it cost to complete the project? what is the project's budget?
Project managers must not only strive to meet specific scope, time, cost, goals of projects, they must also facilitate the entire process to meet the needs and expectations of the people involved in or affected by project activities.
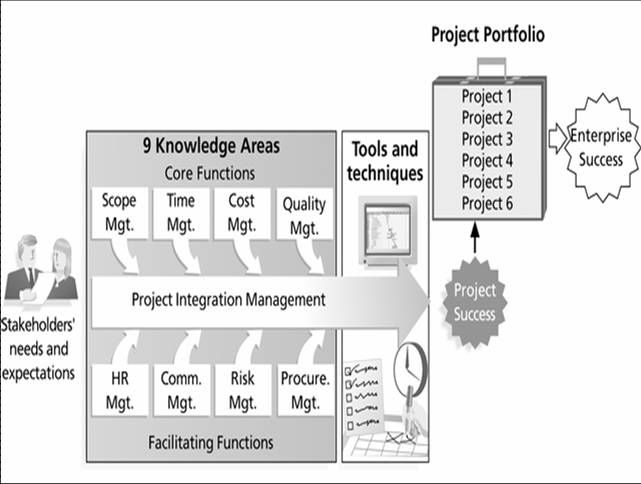
Figure below illustrates a project management framework. Key elements of this framework include the project stakeholders, project management knowledge areas, project management tools and technique, and the contribution of successful projects to the enterprise.
- Project integration management involves coordinating all of the other project management knowledge areas throughout a project' s life cycle.This integration ensures that all the elements of a project come together at the right times to complete a project successfully. There are seven main projects involved in project integration management:
-
- Develop the project charter: Work with stakeholders to create the document that formally authorizes a project—the charter.
- Develop the preliminary project scope statement: Work with stakeholders, especially users of the project’s products, services, or results, to develop the high-level scope requirements and create a preliminary project scope statement.
- Develop the project management plan: Coordinate all planning efforts to create a consistent, document—the project management plan.
- Direct and manage project execution: Carry out the project management plan by performing the activities included in it.
- Monitor and control the project work: Oversee project work to meet the performance objectives of the project.
- Perform integrated change control: Coordinate changes that affect the project’s
- Close the project: Finalize all project activities to formally close the project.
- Project scope management includes the processes involved in defining and controlling what work is or is not included in a project. There are five main processes involved in project scope management:
-
- Scope planning: Deciding how the scope will be defined, verified, and controlled.
- Scope definition: Reviewing the project charter and preliminary scope statement and adding more information as requirements are developed and change requests are approved.
- Creating the WBS: Subdividing the major project deliverables into smaller, more manageable components.
- Scope verification: Formalizing acceptance of the project scope. wbs
- Scope control: Controlling changes to project scope.
- Project time management, simply defined, involves the processes required to ensure timely completion of a project. There are six main processes in project time managements.
-
- Activity definition involves identifying the specific activities that the projet team member and stakeholder must perform to produce the project deliverables.
- Activity sequancing involves identifying and document the relationship between project activities
- Activity resource estimating involves estimating how many resources a project should we to perform project activity.
- Activity duration estimating involves estimating the number of work periods that are needed to complete indiviual activity
- Schedule development involve analysis above process
- Schedule control involves controlling and analysing change to the project schedule.
- Project cost management includes the processes required to ensure that a project team completes a project within an approved budget. Project Cost Management Processes:
-
- Cost estimating: Developing an approximation or estimate of the costs of the resources needed to complete a project.
- Cost budgeting: Allocating the overall cost estimate to individual work items to establish a baseline for measuring performance.
- Cost control: Controlling changes to the project budget.
- Project quality management is to ensure that the project will satisfy the needs for which it was undertaken. The project quality management involves three main process.
-
- Quality planning: Identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and how to satisfy them.
- Quality assurance: Periodically evaluating overall project performance to ensure the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards.
- Quality control: Monitoring specific project results to ensure that they comply with the relevant quality standards.
- Project human resource management includes the processes reuired to make the most effective use of the people involved with a project. Human resource management includes all project stakeholders: sponsors, customers, project team memebers, support staff, suppliers supporting the project, and so on. Human resource management includes the following four processes:
-
- Human resource planning: Identifying and documenting project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships.
- Acquiring the project team: Getting the needed personnal assigned to and working on the project.
- Developing the project team: Building individual and group skills to enhance project performance.
- Managing the project team: Tracking team member performance, motivating team members, providing timely feedback, resolving issues and conflicts, and coordinating changes to help enhance project performance.
- Project communications management is to ensure timely and appropriate generation, collection, dissemination, storage, and disposition of project information. There are four main processes in project communication management.
-
- Communications planning: Determining the information and communications needs of the stakeholders.
- Information distribution: Making needed information available to project stakeholders in a timely manner.
- Performance reporting: Collecting and disseminating performance information, including status reports, progress measurement, and forecasting.
- Managing stakeholders: Managing communications to satisfy the needs and expectations of project stakeholders and to resolve issues.
- Project risk management can b e viewed as minimizeing potential negative riks while maximizing potential positive risks. There are six major processes involved in risk management:
-
- Risk management planning: Deciding how to approach and plan the risk management activities for the project.
- Risk identification: Determining which risks are likely to affect a project and documenting the characteristics of each.
- Qualitative risk analysis: Prioritizing risks based on their probability and impact of occurrence.
- Quantitative risk analysis: Numerically estimating the effects of risks on project objectives.
- Risk response planning: Taking steps to enhance opportunities and reduce threats to meeting project objectives.
- Risk monitoring and control: Monitoring identified and residual risks, identifying new risks, carrying out risk response plans, and evaluating the effectiveness of risk strategies throughout the life of the project.
- Project procurement management includes the processes required to acquire goods and services for a project from outside the performing organization. There are six main processes of project procurement management.
-
- Planning purchases involves what to procure, when and how.
- Planning contracting involves describing requirement for the products or servics desired from the procurement and identifying potential sellers.
- Requesting seller response involves obtaining appropriate information from sellers.
- Selecting seller involves choosing from among potential suppliers through a process of evaluating and negotiating the contract.
- Administering the contract involves managing the relationship with the selected seller.
- Closing the contract involves completion and settlement of each contract.