Co-training 初探快切入
先做个总结
- co-training方法是一类半监督方法,是一个框架,核心就是利用少量已标记样本,通过两个(或多个)模型去学习,对未标记样本进行标记,挑选most confidently的样本加入已标记样本阵营。
- 目前主要存在两种方法:single-view 和 multi-view。最开始提出的是multi-view,就是对特征进行拆分,使用相同的模型,来保证模型间的差异性。后来论证了single-view方法,也就是采用不同种类的模型,但是采用全部特征,也是可以的。基于后一种方法,好多开始做集成方法,采用boosting方式,加入更多分类器,当然也是可以同时做特征的采样。
- co-training的性能是受选定的模型的影响的,比如分类任务,虽然是用多个弱分类器集成co-train,但是太弱也不行。要知道是把分类器对未知样本进行分类的结果作为label放入标记训练集里,分类器的结果不能代表ground truth,加进去后性能可想而知。下文有篇论文给出了Navie Bayes和SVM的差异,一个用co-training性能下降,起反作用,一个能提升性能(虽然很有可能是鬼扯)。
- 主要是处理数据集中,已标记样本少,或者标记不均衡,又想利用全部数据(未标记的样本)
以下是具体看论文的笔记,由于专注于了解这个领域,很多都略过,直接看任务和方法,处理什么问题,怎么处理之类的。
Active + Semi-Supervised Learning = Robust Multi-View Learning
I Muslea
, S Minton
, CA Knoblock
- ICML, 2002 - researchgate.net
We first show that existing semi-supervised algorithms are not robust over the whole spectrum of parameterized problems. Then we introduce a new multi-view algorithm, Co-EMT, which combines semi-supervised and active learning. Co-EMT outperforms the other algorithms both on the parameterized problems and on two additional real world domains. Our experiments suggest that Co-EMT’s robustness comes from active learning compensating for the correlation of the views.
相关方法的列举
Co-EM比较有意思,一个模型的M步得到的模型(其实是很调参),给另一个模型作为E步
文章中扯到了一个概念(好像是自己定义的) clumpiness ,没看懂,先跳过
直接看论文提出的方法
论文给出方法来源是 Co-Testing + Co-EM = Co-EMT
其实是加上Active Learning,对于模棱两可,模型结果不一致的样本,让人去标
Combining Labeled and Unlabeled Data with Co-Training
A Blum
, T Mitchell
- Proceedings of the eleventh annual conference on …, 1998 - dl.acm.org
Speci cally, the presence of two distinct views of each example suggests strategies in which
two learning algorithms are
trained separately on each view, and then each algorithm's predictions on new unlabeled examples are used to
enlarge the training set of the other.
Email Classification with Co-Training
Proceedings of the 2011 Conference of the …, 2011 - dl.acm.org
The main problems in text classification are
lack of labeled data, as well as the cost of labeling
the unlabeled data.
We address these problems by exploring co-training -
an algorithm that uses unlabeled data along with a few labeled examples to boost the performance of a classifier.
We experiment with co-training on the email domain.
Our results show that the performance of co-training depends on the learning algorithm it uses.
In particular, Support Vector Machines significantly outperforms Naive Bayes on email classification.
We address these problems by exploring co-training -
an algorithm that uses unlabeled data along with a few labeled examples to boost the performance of a classifier.
We experiment with co-training on the email domain.
Our results show that the performance of co-training depends on the learning algorithm it uses.
In particular, Support Vector Machines significantly outperforms Naive Bayes on email classification.
目的就是通过boost方法,用多个分类器扩充训练样本(标记样本)
Sometimes features describing the data are
redundant for a given task,
so that we can classify an example having only one set of features or another.
Such sets of features are called ”redundantly sufficient”.
so that we can classify an example having only one set of features or another.
Such sets of features are called ”redundantly sufficient”.
有些时候只需要少量其中基本特征就能做处理,特征可能会有冗余
co-traning的算法框架,太眼熟了不是么,就是上面的!通过分类器C_i不断的挑选most confidently 样本,作为已知样本加入训练集
文中用了两类分类器,
Naive Bayes 和 SVM,直接看结果
从上面两幅图不难看出,NB方法,在加入新标记样本后,在5-10轮可能会有小量的提升,但是总体是下降,也就是说通过co-training加入新标记样本影响的精度
但是SVM却是一直提升的情况,所有这就是这篇文章说的 co-training很受使用的模型的影响。(写文章的艺术,呵呵)
DCPE co-training for classification
Neurocomputing, 2012 - Elsevier
Co-training is a well-known semi-supervised learning technique that applies two basic learners to train the data source, which uses the most confident unlabeled data to augment labeled data in the learning process.
co-training这一类方法本质上说是半监督学习方法,利用两个或更多个分类器学习,扩充标记数据。
Briefly speaking, in co-training process, two learners work together to select the most confident unlabeled data to predict their labels. Then the unlabeled data with predicted labels are treated as new training data, and the process of prediction labels can be called label recovery [8]. The larger diversity or disagreement between the classifiers, the better performance can be obtained [9]. In its original form, co-training establishes two classifiers separately by learning on two sufficient and redundant views (feature subsets) of the data set. Co-training utilizes the diversity between two views of the data sets to perform the label propagation. Some co-training style algorithms, without the requirement of two views, have also been proposed recently [10,11]. These approaches suggested that co-training can use the diversities [12,13] between learners to recover the labels for the unlabeled training data
为了保证所用的模型之间的差异性,一般有两种方法来保证:
- 随机抽样特征子集(就像随机森林等集成方法一样),文中用词sufficient and redundant views (feature subsets) of the data set,但是前提是特征能够被划分,这种划分特征空间的叫做multi-view
- 不同种类的学习模型, 这种方式被叫做single view co-training,
- 文中还提到一种方法,没有细看。 Randomness isanewmethodtocreatethediversityin co-training. TherandomnessenabledCo-Forest [32] to esti- mate theconfidenceofrecovereddataandmaintainthe diversity inthelearningprocess.Co-Forestalgorithmhasbeen successfully usedinmedicaldiagnosis.
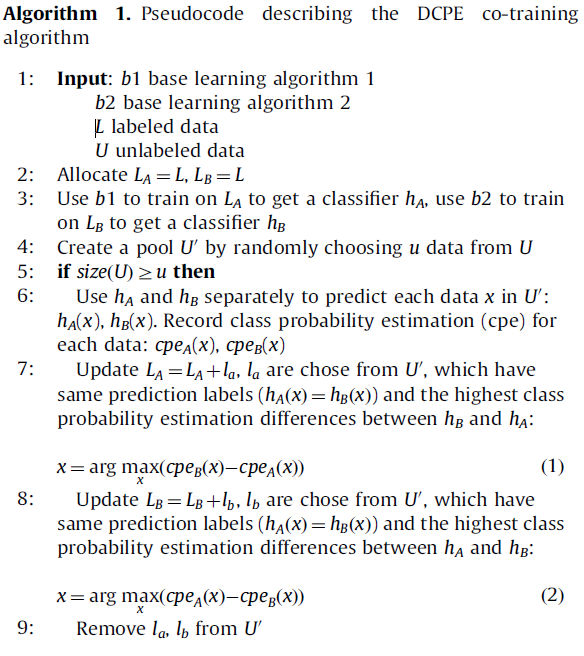
la和lb都是数据集,不断的从未标记数据集中选取u个放进带处理的集合U‘中,当size(U)>u是,用模型hA和hB对待处理集合U'做分类,按7和8中方法挑选confidence样本,作为新的标记样本分别放入la和lb中,扩充hA和hB的训练数据集
看完后,是不是感觉都差不多,时间跨度这么大,这么多人分这个坑。是的,表示很无语。。