LeetCode实战:相交链表
背景
- 为什么你要加入一个技术团队?
- 如何加入 LSGO 软件技术团队?
- 我是如何组织“算法刻意练习活动”的?
- 为什么要求团队的学生们写技术Blog
题目英文
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
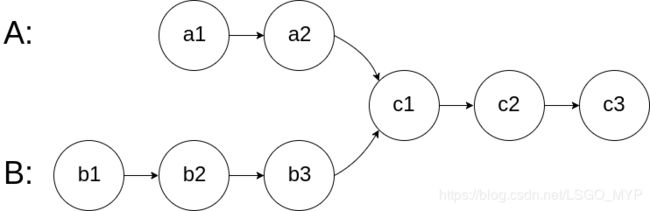
For example, the following two linked lists:
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
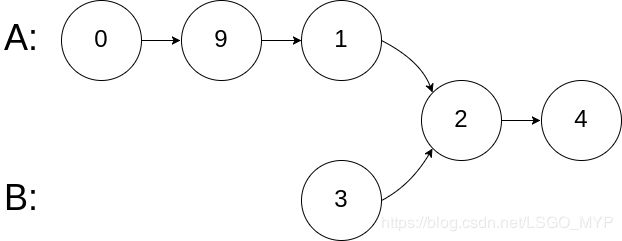
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
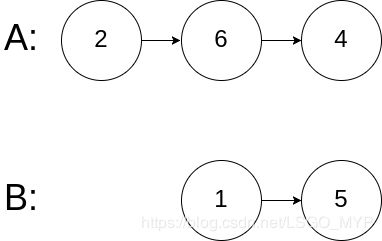
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
题目中文
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
- 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
算法实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution
{
public ListNode GetIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB)
{
HashSet<ListNode> hash = new HashSet<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = headA;
while (temp != null)
{
hash.Add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp != null)
{
if (hash.Contains(temp))
return temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
实验结果
- 状态:通过
- 45 / 45 个通过测试用例
- 执行用时: 172 ms, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
- 内存消耗: 37.6 MB, 在所有 C# 提交中击败了 5.88% 的用户
相关图文
1. “数组”类算法
- LeetCode实战:三数之和
- LeetCode实战:最接近的三数之和
- LeetCode实战:求众数
- LeetCode实战:缺失的第一个正数
- LeetCode实战:快乐数
- LeetCode实战:寻找两个有序数组的中位数
- LeetCode实战:盛最多水的容器
- LeetCode实战:删除排序数组中的重复项
- LeetCode实战:搜索旋转排序数组
- LeetCode实战:螺旋矩阵
- LeetCode实战:螺旋矩阵 II
2. “链表”类算法
- LeetCode实战:两数相加
- LeetCode实战:删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- LeetCode实战:两两交换链表中的节点
- LeetCode实战:旋转链表
- LeetCode实战:环形链表
3. “栈”类算法
- LeetCode实战:有效的括号
- LeetCode实战:最长有效括号
- LeetCode实战:逆波兰表达式求值
4. “队列”类算法
- LeetCode实战:设计循环双端队列
- LeetCode实战:滑动窗口最大值
- LeetCode实战:整数反转
- LeetCode实战:字符串转换整数 (atoi)
5. “递归”类算法
- LeetCode实战:爬楼梯
6. “位运算”类算法
- LeetCode实战:格雷编码
7. “字符串”类算法
- LeetCode实战:反转字符串
- LeetCode实战:翻转字符串里的单词
- LeetCode实战:最长公共前缀
- LeetCode实战:字符串相加
- LeetCode实战:字符串相乘
8. “树”类算法
- LeetCode实战:相同的树
- LeetCode实战:对称二叉树
- LeetCode实战:二叉树的最大深度
- LeetCode实战:将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
9. “哈希”类算法
- LeetCode实战:两数之和
10. “排序”类算法
- LeetCode实战:合并两个有序数组
- LeetCode实战:合并两个有序链表
- LeetCode实战:合并K个排序链表
11. “搜索”类算法
- LeetCode实战:搜索二维矩阵
- LeetCode实战:子集
12. “动态规划”类算法
- LeetCode实战:最长回文子串
- LeetCode实战:最大子序和
- LeetCode实战:不同路径
13. “回溯”类算法
- LeetCode实战:全排列
14. “数值分析”类算法
- LeetCode实战:回文数
- LeetCode实战:x 的平方根