Numpy入门教程:练习作业02
背景
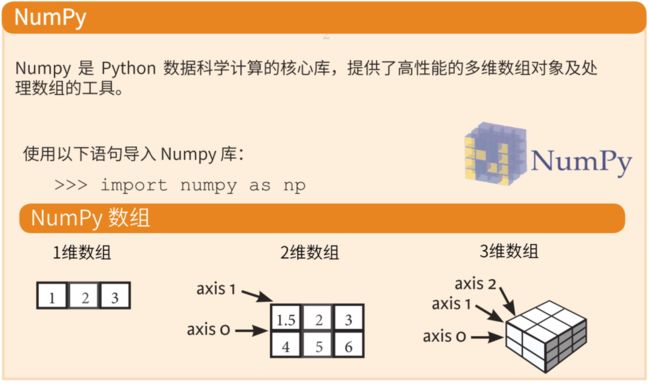
什么是 NumPy 呢?
NumPy 这个词来源于两个单词 – Numerical和Python。其是一个功能强大的 Python 库,可以帮助程序员轻松地进行数值计算,通常应用于以下场景:
- 执行各种数学任务,如:数值积分、微分、内插、外推等。因此,当涉及到数学任务时,它形成了一种基于 Python 的 MATLAB 的快速替代。
- 计算机中的图像表示为多维数字数组。NumPy 提供了一些优秀的库函数来快速处理图像。例如,镜像图像、按特定角度旋转图像等。
- 在编写机器学习算法时,需要对矩阵进行各种数值计算。如:矩阵乘法、求逆、换位、加法等。NumPy 数组用于存储训练数据和机器学习模型的参数。
练习作业
本次练习使用 鸢尾属植物数据集.\iris.data,在这个数据集中,包括了三类不同的鸢尾属植物:Iris Setosa,Iris Versicolour,Iris Virginica。每类收集了50个样本,因此这个数据集一共包含了150个样本。
- sepallength:萼片长度
- sepalwidth:萼片宽度
- petallength:花瓣长度
- petalwidth:花瓣宽度
以上四个特征的单位都是厘米(cm)。
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth species
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 Iris-setosa
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
.. ... ... ... ... ...
145 6.7 3.0 5.2 2.3 Iris-virginica
146 6.3 2.5 5.0 1.9 Iris-virginica
147 6.5 3.0 5.2 2.0 Iris-virginica
148 6.2 3.4 5.4 2.3 Iris-virginica
149 5.9 3.0 5.1 1.8 Iris-virginica
[150 rows x 5 columns]
21. 导入鸢尾属植物数据集,保持文本不变。
【知识点:输入和输出】
- 如何导入存在数字和文本的数据集?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=object, delimiter=',', skiprows=1)
print(iris_data[0:10])
# [['5.1' '3.5' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.9' '3.0' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.7' '3.2' '1.3' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.6' '3.1' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.0' '3.6' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.4' '3.9' '1.7' '0.4' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.6' '3.4' '1.4' '0.3' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.0' '3.4' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.4' '2.9' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.9' '3.1' '1.5' '0.1' 'Iris-setosa']]
22. 求出鸢尾属植物萼片长度的平均值、中位数和标准差(第1列,sepallength)
【知识点:统计相关】
- 如何计算numpy数组的均值,中位数,标准差?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
sepalLength = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0])
print(sepalLength[0:10])
# [5.1 4.9 4.7 4.6 5. 5.4 4.6 5. 4.4 4.9]
print(np.mean(sepalLength))
# 5.843333333333334
print(np.median(sepalLength))
# 5.8
print(np.std(sepalLength))
# 0.8253012917851409
23. 创建一种标准化形式的鸢尾属植物萼片长度,其值正好介于0和1之间,这样最小值为0,最大值为1(第1列,sepallength)。
【知识点:统计相关】
- 如何标准化数组?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
sepalLength = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0])
# 方法1
aMax = np.amax(sepalLength)
aMin = np.amin(sepalLength)
x = (sepalLength - aMin) / (aMax - aMin)
print(x[0:10])
# [0.22222222 0.16666667 0.11111111 0.08333333 0.19444444 0.30555556
# 0.08333333 0.19444444 0.02777778 0.16666667]
# 方法2
x = (sepalLength - aMin) / np.ptp(sepalLength)
print(x[0:10])
# [0.22222222 0.16666667 0.11111111 0.08333333 0.19444444 0.30555556
# 0.08333333 0.19444444 0.02777778 0.16666667]
24. 找到鸢尾属植物萼片长度的第5和第95百分位数(第1列,sepallength)。
【知识点:统计相关】
- 如何找到numpy数组的百分位数?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
sepalLength = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0])
x = np.percentile(sepalLength, [5, 95])
print(x) # [4.6 7.255]
25. 把iris_data数据集中的20个随机位置修改为np.nan值。
【知识点:随机抽样】
- 如何在数组中的随机位置修改值?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
# 方法1
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=object, delimiter=',', skiprows=1)
i, j = iris_data.shape
np.random.seed(20200621)
iris_data[np.random.randint(i, size=20), np.random.randint(j, size=20)] = np.nan
print(iris_data[0:10])
# [['5.1' '3.5' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.9' '3.0' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.7' '3.2' '1.3' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.6' '3.1' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.0' '3.6' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.4' nan '1.7' '0.4' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.6' '3.4' '1.4' '0.3' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.0' '3.4' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.4' '2.9' '1.4' '0.2' nan]
# ['4.9' '3.1' '1.5' '0.1' 'Iris-setosa']]
# 方法2
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=object, delimiter=',', skiprows=1)
i, j = iris_data.shape
np.random.seed(20200620)
iris_data[np.random.choice(i, size=20), np.random.choice(j, size=20)] = np.nan
print(iris_data[0:10])
# [['5.1' '3.5' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.9' '3.0' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.7' '3.2' '1.3' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.6' '3.1' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# [nan '3.6' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.4' '3.9' '1.7' '0.4' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.6' '3.4' '1.4' '0.3' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['5.0' '3.4' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.4' '2.9' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa']
# ['4.9' '3.1' '1.5' nan 'Iris-setosa']]
26. 在iris_data的sepallength中查找缺失值的个数和位置(第1列)。
【知识点:逻辑函数、搜索】
- 如何在numpy数组中找到缺失值的位置?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0, 1, 2, 3])
i, j = iris_data.shape
np.random.seed(20200621)
iris_data[np.random.randint(i, size=20), np.random.randint(j, size=20)] = np.nan
sepallength = iris_data[:, 0]
x = np.isnan(sepallength)
print(sum(x)) # 6
print(np.where(x))
# (array([ 26, 44, 55, 63, 90, 115], dtype=int64),)
27. 筛选具有 sepallength(第1列)< 5.0 并且 petallength(第3列)> 1.5 的 iris_data行。
【知识点:搜索】
- 如何根据两个或多个条件筛选numpy数组?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0, 1, 2, 3])
sepallength = iris_data[:, 0]
petallength = iris_data[:, 2]
index = np.where(np.logical_and(petallength > 1.5, sepallength < 5.0))
print(iris_data[index])
# [[4.8 3.4 1.6 0.2]
# [4.8 3.4 1.9 0.2]
# [4.7 3.2 1.6 0.2]
# [4.8 3.1 1.6 0.2]
# [4.9 2.4 3.3 1. ]
# [4.9 2.5 4.5 1.7]]
28. 选择没有任何 nan 值的 iris_data行。
【知识点:逻辑函数、搜索】
- 如何从numpy数组中删除包含缺失值的行?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0, 1, 2, 3])
i, j = iris_data.shape
np.random.seed(20200621)
iris_data[np.random.randint(i, size=20), np.random.randint(j, size=20)] = np.nan
x = iris_data[np.sum(np.isnan(iris_data), axis=1) == 0]
print(x[0:10])
# [[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]
# [4.9 3. 1.4 0.2]
# [4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2]
# [4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2]
# [5. 3.6 1.4 0.2]
# [4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3]
# [5. 3.4 1.5 0.2]
# [4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1]
# [5.4 3.7 1.5 0.2]
# [4.8 3.4 1.6 0.2]]
29. 计算 iris_data 中sepalLength(第1列)和petalLength(第3列)之间的相关系数。
【知识点:统计相关】
- 如何计算numpy数组两列之间的相关系数?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0, 1, 2, 3])
sepalLength = iris_data[:, 0]
petalLength = iris_data[:, 2]
# 方法1
m1 = np.mean(sepalLength)
m2 = np.mean(petalLength)
cov = np.dot(sepalLength - m1, petalLength - m2)
std1 = np.sqrt(np.dot(sepalLength - m1, sepalLength - m1))
std2 = np.sqrt(np.dot(petalLength - m2, petalLength - m2))
print(cov / (std1 * std2)) # 0.8717541573048712
# 方法2
x = np.mean((sepalLength - m1) * (petalLength - m2))
y = np.std(sepalLength) * np.std(petalLength)
print(x / y) # 0.8717541573048712
# 方法3
x = np.cov(sepalLength, petalLength, ddof=False)
y = np.std(sepalLength) * np.std(petalLength)
print(x[0, 1] / y) # 0.8717541573048716
# 方法4
x = np.corrcoef(sepalLength, petalLength)
print(x)
# [[1. 0.87175416]
# [0.87175416 1. ]]
30. 找出iris_data是否有任何缺失值。
【知识点:逻辑函数】
- 如何查找给定数组是否具有空值?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0, 1, 2, 3])
x = np.isnan(iris_data)
print(np.any(x)) # False
31. 在numpy数组中将所有出现的nan替换为0。
【知识点:逻辑函数】
- 如何在numpy数组中用0替换所有缺失值?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0, 1, 2, 3])
i, j = iris_data.shape
np.random.seed(20200621)
iris_data[np.random.randint(i, size=20), np.random.randint(j, size=20)] = np.nan
iris_data[np.isnan(iris_data)] = 0
print(iris_data[0:10])
# [[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]
# [4.9 3. 1.4 0.2]
# [4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2]
# [4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2]
# [5. 3.6 1.4 0.2]
# [5.4 0. 1.7 0.4]
# [4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3]
# [5. 3.4 1.5 0.2]
# [4.4 2.9 0. 0.2]
# [4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1]]
32. 找出鸢尾属植物物种中的唯一值和唯一值出现的数量。
【知识点:数组操作】
- 如何在numpy数组中查找唯一值的计数?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=object, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[4])
x = np.unique(iris_data, return_counts=True)
print(x)
# (array(['Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica'], dtype=object), array([50, 50, 50], dtype=int64))
33. 将 iris_data 的花瓣长度(第3列)以形成分类变量的形式显示。定义:Less than 3 --> ‘small’;3-5 --> ‘medium’;’>=5 --> ‘large’。
【知识点:统计相关】
- 如何将数字转换为分类(文本)数组?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=float, delimiter=',', skiprows=1, usecols=[0, 1, 2, 3])
petal_length_bin = np.digitize(iris_data[:, 2], [0, 3, 5, 10])
label_map = {1: 'small', 2: 'medium', 3: 'large', 4: np.nan}
petal_length_cat = [label_map[x] for x in petal_length_bin]
print(petal_length_cat[0:10])
# ['small', 'small', 'small', 'small', 'small', 'small', 'small', 'small', 'small', 'small']
34. 在 iris_data 中创建一个新列,其中 volume 是 (pi x petallength x sepallength ^ 2)/ 3。
【知识点:数组操作】
- 如何从numpy数组的现有列创建新列?
【答案】
import numpy as np
outfile = r'.\iris.data'
iris_data = np.loadtxt(outfile, dtype=object, delimiter=',', skiprows=1)
sepalLength = iris_data[:, 0].astype(float)
petalLength = iris_data[:, 2].astype(float)
volume = (np.pi * petalLength * sepalLength ** 2) / 3
volume = volume[:, np.newaxis]
iris_data = np.concatenate([iris_data, volume], axis=1)
print(iris_data[0:10])
# [['5.1' '3.5' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa' 38.13265162927291]
# ['4.9' '3.0' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa' 35.200498485922445]
# ['4.7' '3.2' '1.3' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa' 30.0723720777127]
# ['4.6' '3.1' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa' 33.238050274980004]
# ['5.0' '3.6' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa' 36.65191429188092]
# ['5.4' '3.9' '1.7' '0.4' 'Iris-setosa' 51.911677007917746]
# ['4.6' '3.4' '1.4' '0.3' 'Iris-setosa' 31.022180256648003]
# ['5.0' '3.4' '1.5' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa' 39.269908169872416]
# ['4.4' '2.9' '1.4' '0.2' 'Iris-setosa' 28.38324242763259]
# ['4.9' '3.1' '1.5' '0.1' 'Iris-setosa' 37.714819806345474]]
35. 随机抽鸢尾属植物的种类,使得Iris-setosa的数量是Iris-versicolor和Iris-virginica数量的两倍。
【知识点:随机抽样】
- 如何在numpy中进行概率抽样?
【答案】
import numpy as np
species = np.array(['Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica'])
species_out = np.random.choice(species, 10000, p=[0.5, 0.25, 0.25])
print(np.unique(species_out, return_counts=True))
# (array(['Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica'], dtype='
当前活动
我是 终身学习者“老马”,一个长期践行“结伴式学习”理念的 中年大叔。
我崇尚分享,渴望成长,于2010年创立了“LSGO软件技术团队”,并加入了国内著名的开源组织“Datawhale”,也是“Dre@mtech”、“智能机器人研究中心”和“大数据与哲学社会科学实验室”的一员。
愿我们一起学习,一起进步,相互陪伴,共同成长。
后台回复「搜搜搜」,随机获取电子资源!
欢迎关注,请扫描二维码:
![]()