用off-cpu火焰图调查Linux性能问题
来源
https://www.memsql.com/blog/linux-off-cpu-investigation/
《investigating Linux Performance with Off-CPU Flame Graphs》
本文用off-cpu火焰图分析一个程序的延迟(主要在拿锁上),找出来瓶颈,并消除的故事。本文非常值得一读,但是阅码场没有足够的时间将其翻译为中文,希望童鞋们直接读英文。
The Setup
As a performance engineer at MemSQL, one of my primary responsibilities is to ensure that customer Proof of Concepts (POCs) run smoothly. I was recently asked to assist with a big POC, where I was surprised to encounter an uncommon Linux performance issue. I was running a synthetic workload of 16 threads (one for each CPU core). Each one simultaneously executed a very simple query (select count(*) from t where i > 5) against a columnstore table.
In theory, this ought to be a CPU bound operation since it would be reading from a file that was already in disk buffer cache. In practice, our cores were spending about 50% of their time idle
In this post, I’ll walk through some of the debugging techniques and reveal exactly how we reached resolution.
What were our threads doing?
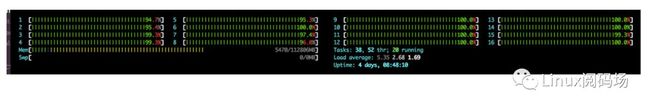
After confirming that our workload was indeed using 16 threads, I looked at the state of our various threads. In every refresh of my htop window, I saw that a handful of threads were in the D state corresponding to “Uninterruptible sleep”:
Why were we going off CPU?
At this point, I generated an off-cpu flamegraph using Linux perf_events to see why we entered this state. Off-CPU means that instead of looking at what is keeping the CPU busy, you look at what is preventing it from being busy by things happening elsewhere (e.g. waiting for IO or a lock). The normal way to generate these visualizations is to use perf inject -s, but the machine I tested on did not have a new enough version of perf. Instead I had to use an awk script I had previously written:
$ sudo perf record --call-graph=fp -e 'sched:sched_switch' -e 'sched:sched_stat_sleep' -e 'sched:sched_stat_blocked' --pid $(pgrep memsqld | head -n 1) -- sleep 1
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 1.343 MB perf.data (~58684 samples) ]
$ sudo perf script -f time,comm,pid,tid,event,ip,sym,dso,trace -i sched.data | ~/FlameGraph/stackcollapse-perf-sched.awk | ~/FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl --color=io --countname=us >off-cpu.svg
Note: recording scheduler events via perf record can have a very large overhead and should be used cautiously in production environments. This is why I wrap the perf record around a sleep 1 to limit the duration.
In an off-cpu flamegraph, the width of a bar is proportional to the total time spent off cpu. Here we see a lot of time is spent in rwsem_down_write_failed.
From the repeated calls to rwsem_down_read_failed and rwsem_down_write_failed, we see that culprit was mmapcontending in the kernel on the mm->mmap_sem lock:
down_write(&mm->mmap_sem);
ret = do_mmap_pgoff(file, addr, len, prot, flag, pgoff,&populate);
up_write(&mm->mmap_sem);
This was causing every mmap syscall to take 10-20ms (almost half the latency of the query itself). MemSQL was so fast that that we had inadvertently written a benchmark for Linux mmap!
The fix was simple — we switched from using mmap to using the traditional file read interface. After this change, we nearly doubled our throughput and became CPU bound as we expected:
For more information and discussion around Linux performance, check out the original post on my personal blog.
Download MemSQL Community Edition to run your own performance tests for free today: memsql.com/download
Alex Reece is a systems and performance engineer. He believes in active benchmarking, root cause analysis, and fast code.
"Linux阅码场"是专业的Linux及系统软件技术交流社区,企业和Linux人才的连接枢纽。
查看我们精华技术文章请移步:
Linux阅码场原创精华文章汇总
求职招聘请移步:
阅码场: 连接企业和Linux/嵌入式人才的平台总线
扫描二维码关注我们
![]()