Apollo库表及逻辑结构
目录
一、App、Cluster、Namespace、AppNamespace创建
1. App、AppNamespace创建流程
2. Cluster创建流程
3. AppNamespace vs. Namespace
二、Item、commit
流程
三、namespaceLock
四、发布配置(release、releaseHistory、releaseMessage)
1. admin侧API流程:
1)流向:
2)publish
3)mergeFromMasterAndPublishBranch
4)branch release
2. sendMessage
1)NotificationControllerV2#handleMessage()
2)客户端长轮询RemoteConfigRepostitory、RemoteConfigLongPollService
3)流程
3. publishEvent
五、instance、instanceConfig
六、serverConfig
1. 存储方式
2. 修改方式
七、认证与授权
1. 认证
2.授权(role)
八、consumer相关
九、注册发现
1. eureka
2. meta server
1)config server
2)admin server
一、App、Cluster、Namespace、AppNamespace创建
1. App、AppNamespace创建流程
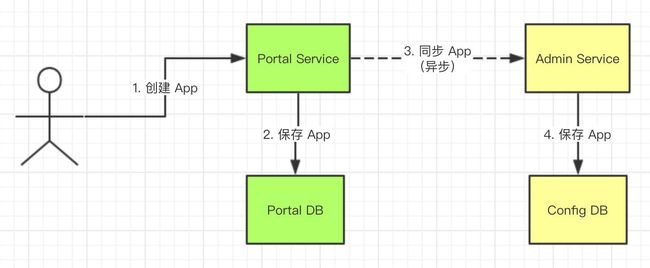
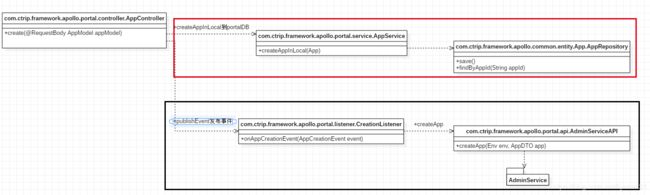
通过portal进行操作,(controller->service->publishEvent->通过listener调用到AdminService)->映射到admin侧API
在 Apollo 的架构中,一个环境( Env ) 对应一套 Admin Service 和 Config Service 。
而 Portal Service 会管理所有环境( Env ) 。因此,每次创建 App 后,需要进行同步。
或者说,App 在 Portal Service 中,表示需要管理的 App 。而在 Admin Service 和 Config Service 中,表示存在的 App 。
2. Cluster创建流程
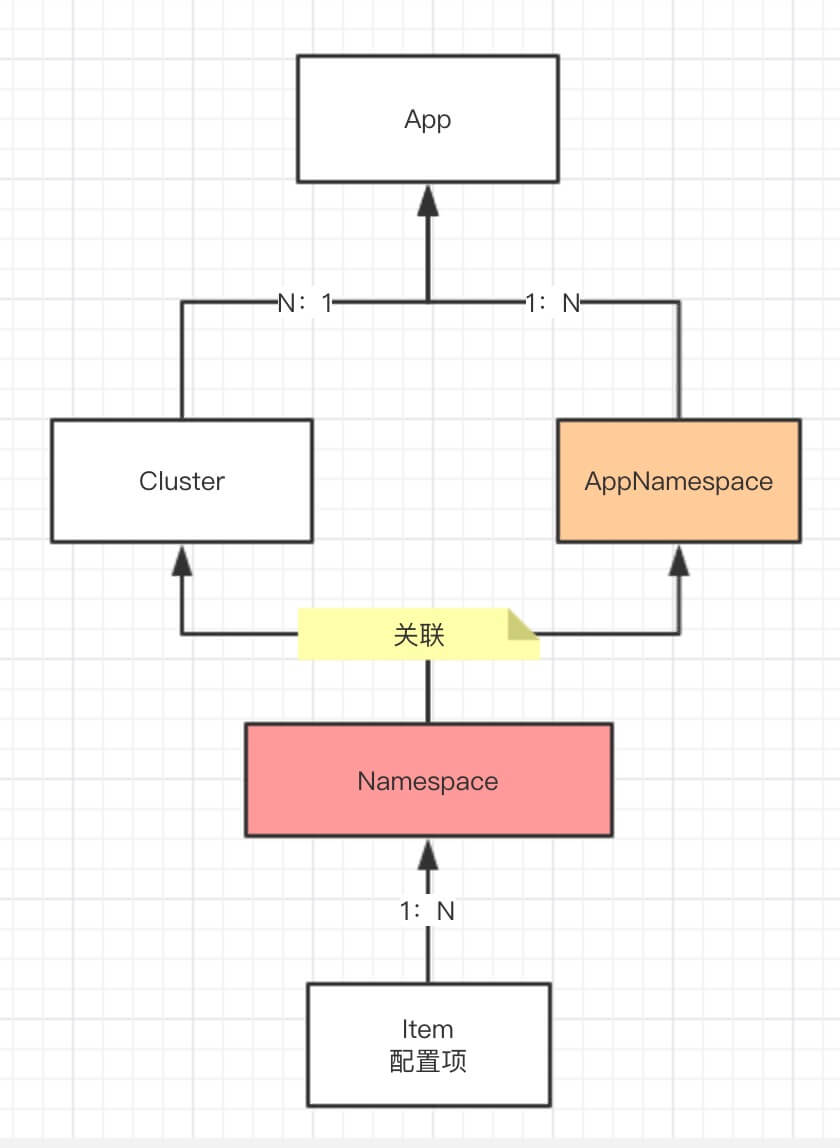
3. AppNamespace vs. Namespace
关系图如下:
数据流向如下:
- 在 App 下创建 AppNamespace 后,自动给 App 下每个 Cluster 创建 Namespace 。
- 在 App 下创建 Cluster 后,根据 App 下每个 AppNamespace 创建 Namespace 。
- 可删除 Cluster 下的 Namespace 。
总结来说:
- AppNamespace 是 App 下的每个 Cluster 默认创建的 Namespace 。
- Namespace 是 每个 Cluster 实际拥有的 Namespace 。
二、Item、commit
Item ,配置项,是 Namespace 下最小颗粒度的单位。在 Namespace 分成五种类型:properties yml yaml json xml 。其中:
- properties :每一行配置对应一条 Item 记录。
- 后四者:无法进行拆分,所以一个 Namespace 仅仅对应一条 Item 记录。
流程
如上。
每一次item的创建对应一个commit的创建
三、namespaceLock
Admin Service 锁定 Namespace 。可通过设置 ConfigDB 的 ServerConfi的 "namespace.lock.switch" 为 "true" 开启。效果如下:
- 一次配置修改只能是一个人
- 一次配置发布只能是另一个人
也就是说,开启后,一次配置修改并发布,需要两个人。
默认为 "false" ,即关闭。
在release的操作时用到
四、发布配置(release、releaseHistory、releaseMessage)
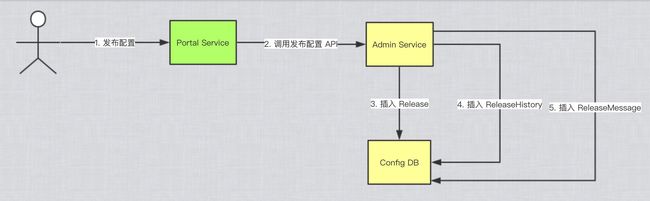
- 通过portal进行操作,(controller->service->调用到AdminService)->映射到admin侧API
- portal侧publishEvent->展示最后发布内容(Config)(publish后)
- admin侧sendMessage(releaseMessage)(publish后)
1. admin侧API流程:
1)流向:
controller->service#publish()->sendMessage()
2)publish
是否有 父namespace?
- 有:说明是 子namespace,进行灰度发布(publishBranchRelease -> branc release)
- 没有:主干发布master release->如果有 子namespace,将主干合并到 子namespace,并进行一次 子namespace 的发布(mergeFromMasterAndPublishBranch)
3)mergeFromMasterAndPublishBranch
获得 子namespace 的配置项map->获得 父namespace 的map->合并map(以 子map 为基础计算差异)->branch release
4)branch release
获得 父namespace 的最后有效release->创建 子namespace 的release对象->更新GrayReleaseRule->保存releaseHistory
2. sendMessage
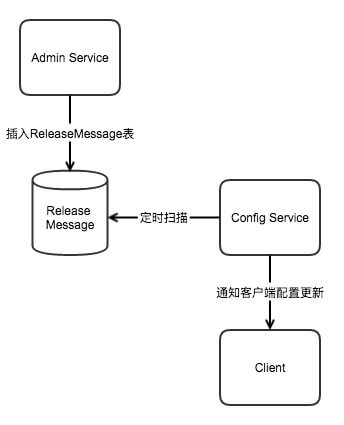
Admin Service 在配置发布后,需要通知所有的 Config Service 有配置发布,从而 Config Service 可以通知对应的客户端来拉取最新的配置。
通过数据库实现消息发布-订阅的模式
- DatebaseMessageSender#sendMessage()
向releaseMessage库表中通过 事务 操作插入发布的app、cluster、namespace消息 - config service侧ReleaseMessageSccaner#afterProperties()
1)启动线程每秒扫描数据库表(记录每次扫描的最大Id)
2)扫描到新消息,触发消息监听器 - NotificationControllerV2#handleMessage()
在ConfigServideAutoConfiguration中添加监听器;
消息监听器通知client
1)NotificationControllerV2#handleMessage()
在notification/v2中,当请求的 Namespace 暂无新通知时,会将该 Namespace 对应的 Watch Key (等价于 ReleaseMessage 的通知内容message字段)们,注册到deferredResults中(注册 Watch Key + DeferredResultWrapper 到 deferredResults)。等到 Namespace 配置发生变更时,在#handleMessage()中,进行通知。
- 读取并创建 DeferredResultWrapper 数组,避免并发问题。
- 创建 ApolloConfigNotification 对象,并调用ApolloConfigNotification#addMessage() 方法(单例模式避免多线程修改),添加通知消息明细ApolloNotificationMessages(ApolloConfigNotification维护一个列表)。
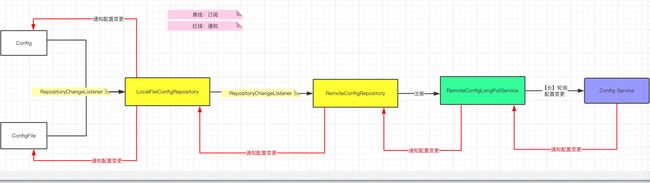
2)客户端长轮询RemoteConfigRepostitory、RemoteConfigLongPollService
流程:
- RemoteConfigRepository ,定时轮询 Config Service 的配置读取queryConfig()
- RemoteConfigLongPollService ,长轮询 Config Service 的配置变更通知notification/v2接口。当有新的通知时,触发 RemoteConfigRepository ,立即轮询 Config Service 的配置读取
配置更新
- RemoteConfigRepostitory构造函数中this.scheduleLongPollingRefresh()->...-> RemoteConfigLongPollService#doLongPollingRefresh()
注册到自己的RemoteConfigLongPollService中,实现配置的实时更新 - #doLongPollingRefresh()
1)HttpUtil#doGet()请求NotificationControllerV2
·NotificationControllerV2 不会立即返回结果,而是通过 Spring DeferredResult 把请求挂起。
·如果在 60 秒内没有该客户端关心的配置发布,那么会返回 Http 状态码 304 给客户端。
·如果有该客户端关心的配置发布,NotificationControllerV2 会调用 DeferredResult 的 setResult 方法,传入有配置变化的 namespace 信息,同时该请求会立即返回。客户端从返回的结果中获取到配置变化的 namespace 后,会立即请求 Config Service 获取该 namespace 的最新配置。
2)updateRemoteNotifications()、updateRemoteNotifications(),通过ApolloConfigNotification获取对应message列表,并通过mergeFrom()合并到本地的通知消息中。
3)notify()通知对应的 RemoteConfigRepository 们
配置读取
RemoteConfigRepostitory构造函数this.trySync()->sync()->loadApolloConfig()通过http调用ConfigController#queryConfig()
1: private ApolloConfig loadApolloConfig() {
2: // 限流
3: if (!m_loadConfigRateLimiter.tryAcquire(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
4: // wait at most 5 seconds
5: try {
6: TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
7: } catch (InterruptedException e) {
8: }
9: }
10: // 获得 appId cluster dataCenter 配置信息
11: String appId = m_configUtil.getAppId();
12: String cluster = m_configUtil.getCluster();
13: String dataCenter = m_configUtil.getDataCenter();
14: Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.Client.ConfigMeta", STRING_JOINER.join(appId, cluster, m_namespace));
15: // 计算重试次数
16: int maxRetries = m_configNeedForceRefresh.get() ? 2 : 1;
17: long onErrorSleepTime = 0; // 0 means no sleep
18: Throwable exception = null;
19: // 获得所有的 Config Service 的地址
20: List configServices = getConfigServices();
21: String url = null;
22: // 循环读取配置重试次数直到成功。每一次,都会循环所有的 ServiceDTO 数组。
23: for (int i = 0; i < maxRetries; i++) {
24: // 随机所有的 Config Service 的地址
25: List randomConfigServices = Lists.newLinkedList(configServices);
26: Collections.shuffle(randomConfigServices);
27: // 优先访问通知配置变更的 Config Service 的地址。并且,获取到时,需要置空,避免重复优先访问。
28: // Access the server which notifies the client first
29: if (m_longPollServiceDto.get() != null) {
30: randomConfigServices.add(0, m_longPollServiceDto.getAndSet(null));
31: }
32: // 循环所有的 Config Service 的地址
33: for (ServiceDTO configService : randomConfigServices) {
34: // sleep 等待,下次从 Config Service 拉取配置
35: if (onErrorSleepTime > 0) {
36: logger.warn("Load config failed, will retry in {} {}. appId: {}, cluster: {}, namespaces: {}", onErrorSleepTime, m_configUtil.getOnErrorRetryIntervalTimeUnit(), appId, cluster, m_namespace);
37: try {
38: m_configUtil.getOnErrorRetryIntervalTimeUnit().sleep(onErrorSleepTime);
39: } catch (InterruptedException e) {
40: //ignore
41: }
42: }
43: // 组装查询配置的地址
44: url = assembleQueryConfigUrl(configService.getHomepageUrl(), appId, cluster, m_namespace, dataCenter, m_remoteMessages.get(), m_configCache.get());
45:
46: logger.debug("Loading config from {}", url);
47: // 创建 HttpRequest 对象
48: HttpRequest request = new HttpRequest(url);
49:
50: // 【TODO 6001】Tracer 日志
51: Transaction transaction = Tracer.newTransaction("Apollo.ConfigService", "queryConfig");
52: transaction.addData("Url", url);
53: try {
54: // 发起请求,返回 HttpResponse 对象
55: HttpResponse response = m_httpUtil.doGet(request, ApolloConfig.class);
56: // 设置 m_configNeedForceRefresh = false
57: m_configNeedForceRefresh.set(false);
58: // 标记成功
59: m_loadConfigFailSchedulePolicy.success();
60:
61: // 【TODO 6001】Tracer 日志
62: transaction.addData("StatusCode", response.getStatusCode());
63: transaction.setStatus(Transaction.SUCCESS);
64:
65: // 无新的配置,直接返回缓存的 ApolloConfig 对象
66: if (response.getStatusCode() == 304) {
67: logger.debug("Config server responds with 304 HTTP status code.");
68: return m_configCache.get();
69: }
70:
71: // 有新的配置,进行返回新的 ApolloConfig 对象
72: ApolloConfig result = response.getBody();
73: logger.debug("Loaded config for {}: {}", m_namespace, result);
74: return result;
75: } catch (ApolloConfigStatusCodeException ex) {
76: ApolloConfigStatusCodeException statusCodeException = ex;
77: // 若返回的状态码是 404 ,说明查询配置的 Config Service 不存在该 Namespace 。
78: // config not found
79: if (ex.getStatusCode() == 404) {
80: String message = String.format("Could not find config for namespace - appId: %s, cluster: %s, namespace: %s, " +
81: "please check whether the configs are released in Apollo!", appId, cluster, m_namespace);
82: statusCodeException = new ApolloConfigStatusCodeException(ex.getStatusCode(), message);
83: }
84: // 【TODO 6001】Tracer 日志
85: Tracer.logEvent("ApolloConfigException", ExceptionUtil.getDetailMessage(statusCodeException));
86: transaction.setStatus(statusCodeException);
87: // 设置最终的异常
88: exception = statusCodeException;
89: } catch (Throwable ex) {
90: // 【TODO 6001】Tracer 日志
91: Tracer.logEvent("ApolloConfigException", ExceptionUtil.getDetailMessage(ex));
92: transaction.setStatus(ex);
93: // 设置最终的异常
94: exception = ex;
95: } finally {
96: // 【TODO 6001】Tracer 日志
97: transaction.complete();
98: }
99: // 计算延迟时间
100: // if force refresh, do normal sleep, if normal config load, do exponential sleep
101: onErrorSleepTime = m_configNeedForceRefresh.get() ? m_configUtil.getOnErrorRetryInterval() : m_loadConfigFailSchedulePolicy.fail();
102: }
103:
104: }
105: // 若查询配置失败,抛出 ApolloConfigException 异常
106: String message = String.format("Load Apollo Config failed - appId: %s, cluster: %s, namespace: %s, url: %s", appId, cluster, m_namespace, url);
107: throw new ApolloConfigException(message, exception);
108: } 1: @RequestMapping(value = "/{appId}/{clusterName}/{namespace:.+}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
2: public ApolloConfig queryConfig(@PathVariable String appId, @PathVariable String clusterName,
3: @PathVariable String namespace,
4: @RequestParam(value = "dataCenter", required = false) String dataCenter,
5: @RequestParam(value = "releaseKey", defaultValue = "-1") String clientSideReleaseKey,
6: @RequestParam(value = "ip", required = false) String clientIp,
7: @RequestParam(value = "messages", required = false) String messagesAsString,
8: HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
9: String originalNamespace = namespace;
10: // 若 Namespace 名以 .properties 结尾,移除该结尾,并设置到 ApolloConfigNotification 中。例如 application.properties => application 。
11: // strip out .properties suffix
12: namespace = namespaceUtil.filterNamespaceName(namespace);
13: // 获得归一化的 Namespace 名字。因为,客户端 Namespace 会填写错大小写。
14: //fix the character case issue, such as FX.apollo <-> fx.apollo
15: namespace = namespaceUtil.normalizeNamespace(appId, namespace);
16:
17: // 若 clientIp 未提交,从 Request 中获取。
18: if (Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientIp)) {
19: clientIp = tryToGetClientIp(request);
20: }
21:
22: // 解析 messagesAsString 参数,创建 ApolloNotificationMessages 对象。
23: ApolloNotificationMessages clientMessages = transformMessages(messagesAsString);
24:
25: // 创建 Release 数组
26: List releases = Lists.newLinkedList();
27: // 获得 Namespace 对应的 Release 对象
28: String appClusterNameLoaded = clusterName;
29: if (!ConfigConsts.NO_APPID_PLACEHOLDER.equalsIgnoreCase(appId)) {
30: // 获得 Release 对象
31: Release currentAppRelease = configService.loadConfig(appId, clientIp, appId, clusterName, namespace, dataCenter, clientMessages);
32: if (currentAppRelease != null) {
33: // 添加到 Release 数组中。
34: releases.add(currentAppRelease);
35: // 获得 Release 对应的 Cluster 名字
36: // we have cluster search process, so the cluster name might be overridden
37: appClusterNameLoaded = currentAppRelease.getClusterName();
38: }
39: }
40: // 若 Namespace 为关联类型,则获取关联的 Namespace 的 Release 对象
41: // if namespace does not belong to this appId, should check if there is a public configuration
42: if (!namespaceBelongsToAppId(appId, namespace)) {
43: // 获得 Release 对象
44: Release publicRelease = this.findPublicConfig(appId, clientIp, clusterName, namespace, dataCenter, clientMessages);
45: // 添加到 Release 数组中
46: if (!Objects.isNull(publicRelease)) {
47: releases.add(publicRelease);
48: }
49: }
50: // 若获得不到 Release ,返回状态码为 404 的响应
51: if (releases.isEmpty()) {
52: response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, String.format("Could not load configurations with appId: %s, clusterName: %s, namespace: %s",
53: appId, clusterName, originalNamespace));
54: Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.Config.NotFound", assembleKey(appId, clusterName, originalNamespace, dataCenter));
55: return null;
56: }
57:
58: // 记录 InstanceConfig
59: auditReleases(appId, clusterName, dataCenter, clientIp, releases);
60:
61: // 计算 Config Service 的合并 ReleaseKey
62: String mergedReleaseKey = releases.stream().map(Release::getReleaseKey).collect(Collectors.joining(ConfigConsts.CLUSTER_NAMESPACE_SEPARATOR));
63: // 对比 Client 的合并 Release Key 。若相等,说明没有改变,返回状态码为 302 的响应
64: if (mergedReleaseKey.equals(clientSideReleaseKey)) {
65: // Client side configuration is the same with server side, return 304
66: response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
67: Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.Config.NotModified", assembleKey(appId, appClusterNameLoaded, originalNamespace, dataCenter));
68: return null;
69: }
70:
71: // 创建 ApolloConfig 对象
72: ApolloConfig apolloConfig = new ApolloConfig(appId, appClusterNameLoaded, originalNamespace, mergedReleaseKey);
73: // 合并 Release 的配置,并将结果设置到 ApolloConfig 中
74: apolloConfig.setConfigurations(mergeReleaseConfigurations(releases));
75:
76: // 【TODO 6001】Tracer 日志
77: Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.Config.Found", assembleKey(appId, appClusterNameLoaded, originalNamespace, dataCenter));
78: return apolloConfig;
79: } 3)流程
3. publishEvent
五、instance、instanceConfig
实例( Instance ),实际就是 Apollo 的客户端。
instance调用:
- Admin侧InstanceConfig中get获取
- Config侧ConfigController#queryConfig()->InstanceConfigAuditUtil->create()中save保存
instanceConfig调用:
- Config侧ConfigController#queryConfig()->InstanceConfigAuditUtil->create()中save保存
- Namespace#batchDelete()
| instance | instanceConfig | |
| appId |
<-instanceId-> | configAppId |
六、serverConfig
1. 存储方式
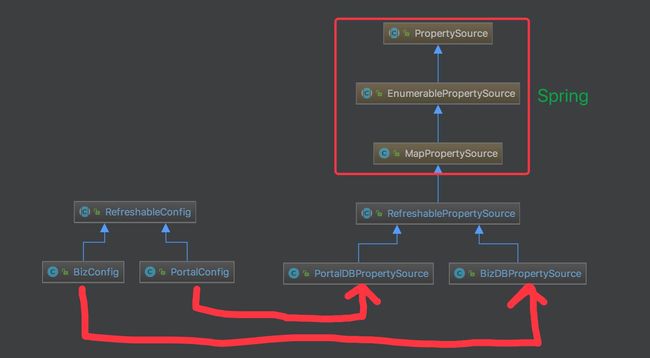
serviceConfig封装成PropertySource(根据name和source存储配置属性):
public abstract class RefreshablePropertySource extends MapPropertySource {
public RefreshablePropertySource(String name, Map source) {
super(name, source);
}
@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
return this.source.get(name);
}
/**
* refresh property
*/
protected abstract void refresh();
/**
* 实现方法
* @Override
protected void refresh() {
// 获得所有的 ServerConfig 记录
Iterable dbConfigs = serverConfigRepository.findAll();
// 缓存,更新到属性源
for (ServerConfig config : dbConfigs) {
String key = config.getKey();
Object value = config.getValue();
// 打印日志
if (this.source.isEmpty()) {
logger.info("Load config from DB : {} = {}", key, value);
} else if (!Objects.equals(this.source.get(key), value)) {
logger.info("Load config from DB : {} = {}. Old value = {}", key, value, this.source.get(key));
}
// 更新到属性源
this.source.put(key, value);
}
}
**/
} - portal侧:key-value存储,PortalDBPropertySource继承自MapPropertySource(name<-->source(map))
PortalDBPropertySource中的refresh()方法将配置属性从库中查询放到source中进行缓存 - config侧:key-value存储、cluster字段(在多机房部署时,往往希望 config service 和 admin service 只向同机房的 eureka 注册,要实现这个效果,需要利用 ServerConfig 表中的cluster字段。)
BizDBPropertySource类似PortalDBPropertySource,增加了cluster属性的更新。
RefreshableConfig的实现类(Biz和Portal)在初始化#setup()中调用RefreshablePropertySource实现类(Biz和Portal)的#refresh(),60s(CONFIG_REFRESH_INTERVAL)刷新一次配置:
1: @PostConstruct
2: public void setup() {
3: // 获得 RefreshablePropertySource 数组
4: propertySources = getRefreshablePropertySources();
5: if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(propertySources)) {
6: throw new IllegalStateException("Property sources can not be empty.");
7: }
8:
9: // add property source to environment
10: for (RefreshablePropertySource propertySource : propertySources) {
11: propertySource.refresh();
12: environment.getPropertySources().addLast(propertySource);
13: }
14:
15: // 创建 ScheduledExecutorService 对象
16: // task to update configs
17: ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, ApolloThreadFactory.create("ConfigRefresher", true));
18: // 提交定时任务,每分钟刷新一次 RefreshablePropertySource 数组
19: executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
20: try {
21: propertySources.forEach(RefreshablePropertySource::refresh);
22: } catch (Throwable t) {
23: logger.error("Refresh configs failed.", t);
24: Tracer.logError("Refresh configs failed.", t);
25: }
26: }, CONFIG_REFRESH_INTERVAL, CONFIG_REFRESH_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
27: }config service 和 admin servicBizDBPropertySourcee 会读取所在机器的 /opt/settings/server.properties(Mac/Linux)或 C:\opt\settings\server.properties(Windows)中的 idc 属性,如果该 idc 有对应的eureka.service.url 配置,那么就会向该机房的 eureka 注册 。
2. 修改方式
1. protal侧通过ServerConfigController对serverConfig进行创建或修改
2. config侧无修改入口,库表中有eureka地址、item配置、namespace配置、config配置,从库表中查询时,BizConfig会有默认值的传参及配置
七、认证与授权
1. 认证
authorities表,用户的权限管理
基于spring profile特性,实现SPI
2.授权(role)
- role:权限+appId+namespace
- permission:appId(+namespace)
- rolePermission
- userRole
- users
操作授权,授权的是user的role
role的permission在app、namespace初始化的时候进行关联
八、consumer相关
第三方应用
通过openapi调用
九、注册发现
1. eureka
apollo-adminservice 和 apollo-configservice 项目,引入 apollo-biz 项目,启动 Eureka Client ,向 Eureka Server 注册自己为实例。通过 .properties 配置实例名
2. meta server
- controller提供了三个 API ,
services/meta、services/config、services/admin获得 Meta Service、Config Service、Admin Service 集群地址。实际上,services/meta暂时是不可用的,获取不到实例,因为 Meta Service 目前内嵌在 Config Service 中。 - 在每个 API 中,调用 DiscoveryService 调用对应的方法,获取服务集群。
考虑到高可用,Meta Service 必须集群。因为 Meta Service 自身扮演了目录服务的角色,所以引入 Proxy Server 。
1)config server
- 初始时,从 Meta Service 获取 Config Service 集群地址进行缓存。
- 定时任务,每 5 分钟,从 Meta Service 获取 Config Service 集群地址刷新缓存。
2)admin server
- 初始时,创建延迟 1 秒的任务,从 Meta Service 获取 Config Service 集群地址进行缓存。
- 获取成功时,创建延迟 5 分钟的任务,从 Meta Service 获取 Config Service 集群地址刷新缓存。
- 获取失败时,创建延迟 10 秒的任务,从 Meta Service 获取 Config Service 集群地址刷新缓存。