【数据结构】限定性线性表——栈与队列 总结
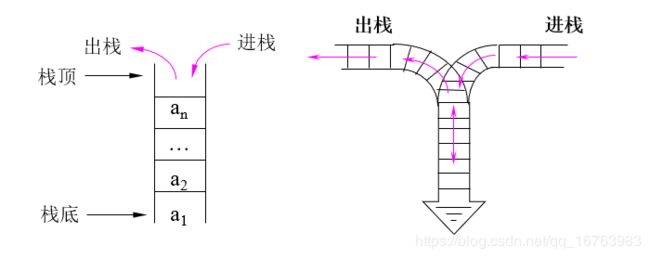
一、顺序栈 LIFO
(一)栈的声明
#define Stack_Size 100
typedef struct{
StackElementType elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}SeqStack;
(二)栈的操作
1、初始化栈——构造空栈 top == -1
void InitStack(SeqStack* S){
S->top=-1;
}
2、判栈空
int IsEmpty(SeqStack* S){
return (S->top == -1);
}
3、判栈满
int IsFull(SeqStack* S){
return (S->top == Stack_Size-1);
}
4、出栈
int Pop(SeqStack* S, StackElementType* x){
if(IsEmpty) return (FALSE);
else{
*x=S->elem[S->top];
S->top--;
return (TRUE);
}
}
5、取栈顶元素
在出栈的基础上,不弹出即可
int GetTop(SeqStack* S, StackElementType* x){
if(IsEmpty) return (FALSE);
else{
*x=S->elem[S->top];
}
}
二、链栈 LIFO
(一)栈的声明
typedef struct node{
StackElementType data;
struct node *next;
}LinkStackNode;
typedef LinkStackNode *LinkStack;
(二)栈的操作
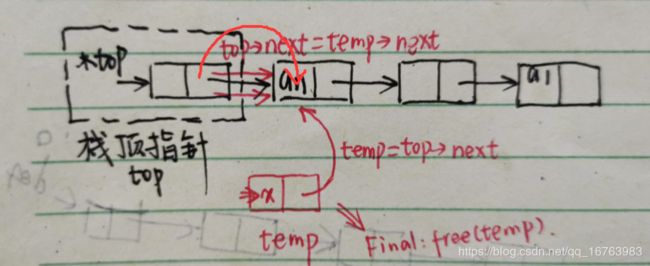
1、进栈
如下代码中的top即是栈顶指针
int Push(LinkStack top, StackElementType x){
LinkStackNode* temp;
temp=(LinkStackNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkStackNode));
if(temp==NULL) return (FALSE); //申请内存空间失败
temp->data=x;
//头插法
temp->next=top->next;
top->next=temp;
return (TRUE);
}
2、出栈
int Pop(LinkStack top, StackElementType *x){
LinkStackNode* temp=top->next;
if(temp==NULL) return (FALSE);
top->next=temp->next;
*x=temp->data;
free(temp);
return (TRUE);
}
(三)栈的应用
1、十进制转二进制
void Conversion10_2(int N){
Stack S;
int x;
while(N>0){
x=N%2;
Push(&S,x);
N/=2;
}
while(!IsEmpty(S)){
Pop(&S,&x);
cout<<x;
}
}
2、括号匹配问题
思路:遍历整个字符串,如果遇到左括号则入栈,遇到右括号则检查栈是否空,如空则右括号多余 return,非空则取栈顶,如与右括匹配,则继续遍历字符串,如不匹配则失败return!遍历完整个字符串后,再去检查一次栈,如果空了,说明匹配成功,如果非空,则左括号多余,失败于黎明之前。
void BracketMatch(char *str){
Stack S;
int i;
char ch;
InitStack(&S);
//扫描字符串
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++){
switch(str[i]){
case '(': case'[': case'{': //左括号入栈
Push(&S,str[i]);
case ')': case']': case'}':
if(IsEmpty(S)){
cout<<"右括号多余!";
return ;
}else{
GetTop(&S,&ch);
if(Match(ch,str[i])) Pop(&S,&ch);
else{
cout<<"左右括号不匹配!";
return ;
}
}
}
}
//扫描完后检查栈是否还有括号
if(!IsEmpty(S)) cout<<"左括号多余!";
else cout<<"左右括号完全匹配";
}
三、队列 FIFO
(一)链队列的声明
typedef struct Node{
QueueElementType data;
struct Node *next;
}LinkQueueNode;
//连续声明
typedef struct{
LinkQueueNode *front;
LinkQueueNode *rear;
}LinkQueue;
(二)队列的操作
1、队列初始化
int InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q){
Q->front=(LinkQueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
if(Q->front!=NULL){
Q->rear=Q->front; //初始化队列为空链,头指针即尾指针
Q->front->next=NULL;
return (TRUE);
}else{
return (FALSE);
}
}
2、入队
插入在尾部——尾插法
int EnterQueue(LinkQueue* Q, QueueElementType x){
LinkQueueNode* new_node;
new_node=(LinkQueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
if(new_node==NULL) return (FALSE);
new_node->data=x;
//尾插法在尾部
new_node->next=NULL; //插入在尾部
Q->rear->next=new_node;
Q->rear=new_node;
return (TRUE);
}
3、出队
其实就是先定位队头再用队头结点绕过的操作
int DeleteQueue(LinkQueueNode* Q, QueueElementType* x){
LinkQueueNode* p;
if(Q->front==Q->rear) return (FALSE); //空队
p=Q->font->next; //队头
Q->front->next=p->next; //绕过队头
if(Q->rear==p) Q->rear=Q->front; //队中只有一个元素,重置
*x=p->data;
free(p);
return (TRUE);
}
四、循环队列
用连续存储单元存放元素,类似于顺序栈,设队列数组是Queue[MAXSIZE],最后一个单元是Queue[MAXSIZE-1],后继是Queue[0],则
- rear+1==MAXSIZE时,rear=0
- rear=(rear+1) mod MAXSIZE
(一)循环队列的声明
const int MAXSIZE = 100;
typedef struct{
QueueElementType element[MAXSIZE];
int front;
int rear;
}SeqQueue;
(二)循环队列的操作
1、初始化队列
void InitQueue(SeqQueue* Q){
Q->front=Q->rear=0;
}
2、入队
int EnterQueue(SeqQueue* Q, QueueElementType x){
if((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE==Q->front) return (FALSE); //队满
Q->element[Q->rear]=x;
Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;
return (TRUE);
}
3、出队
int DeleteQueue(SeqQueue* Q, QueueElementType* x){
if(Q->front==Q->rear) return (FALSE); //队空
*x=Q->element[Q->front];
Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE;
return (TRUE);
}
本文更新至2020.7.5