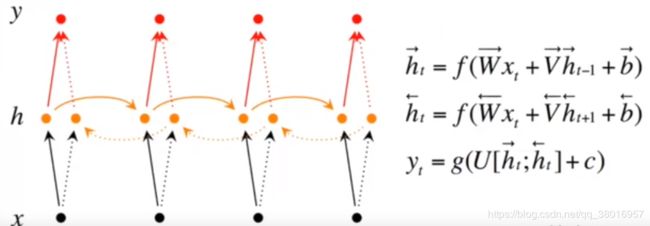
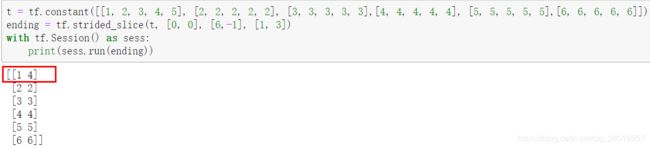
seq2seq+attention=>评论摘要
Summarizing Text with Amazon Reviews
数据集:Amazon 500000评论
本节内容:
- 数据预处理
- 构建Seq2Seq模型
- 训练网络
- 测试效果
seq2seq教程: https://github.com/j-min/tf_tutorial_plus/tree/master/RNN_seq2seq/contrib_seq2seq
https://www.jianshu.com/p/c0c5f1bdbb88
浏览数据集
将少量的含有缺失值的记录和其他属性dropout
1、数据预处理
re.sub(r'https?:\/\/.*[\r\n]*\, ' ', text)
- 连词转换:
“can’t’ve”: “cannot have”,
“'cause”: “because”,
“could’ve”: “could have”,
# 统计不重复的词的个数
def count_words(count_dict, text):
'''Count the number of occurrences of each word in a set of text'''
for sentence in text:
for word in sentence.split():
if word not in count_dict:
count_dict[word] = 1
else:
count_dict[word] += 1
# Find the number of times each word was used and the size of the vocabulary
word_counts = {}
count_words(word_counts, clean_summaries)
print("Size of Vocabulary:", len(word_counts))
count_words(word_counts, clean_texts)
print("Size of Vocabulary:", len(word_counts))
OUT:
Size of Vocabulary: 33809
Size of Vocabulary: 132884
我们的任务通过seq2seq完成encode-decod的操作,需要词向量作为输入,这里的词向量也可以用别人训练好的词向量喂入模型。github上有训练好的词向量
格式:[0]为单词 ,[1:]为向量
/c/en/absolute_value -0.0847 -0.1316 -0.0800 -0.0708 -0.2514 -0.1687 -…
现将单词和其向量转换为字典的格式
embeddings_index = {}
with open('numberbatch-en-17.04b.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
values = line.split(' ')
word = values[0]
embedding = np.asarray(values[1:], dtype='float32')
embeddings_index[word] = embedding
词库中的词不一样全都在词向量文件中,所以需要统计词库不在词向量文件中的单词,如果是词频大于20,且词向量文件中没有,就直接建立一个相同维度的向量训练即可。
统计miss单词的占比:
Number of words missing from CN: 3866
Percent of words that are missing from vocabulary: 2.91%
现将词频大于20的构建数字和单词的映射,方便计算机理解。
将标识符也加入词汇中,开始、PAD、unknow和结束符号
codes = ["","","",""]
int_to_vocab:

vocab_to_int:

做好词语和数字的映射之后,再将每一个语句中的单词转换为数字形式:有些词如词频小于20、还没有过滤掉的则替换为’unknown’
def convert_to_ints(text, word_count, unk_count, eos=False):
'''Convert words in text to an integer.
If word is not in vocab_to_int, use UNK's integer. ’unknown‘
Total the number of words and UNKs.
Add EOS token to the end of texts'''
ints = []
for sentence in text:
sentence_ints = []
for word in sentence.split():
word_count += 1
if word in vocab_to_int:
sentence_ints.append(vocab_to_int[word])
else:
sentence_ints.append(vocab_to_int["" ])
unk_count += 1
if eos:
sentence_ints.append(vocab_to_int["" ])
ints.append(sentence_ints)
return ints, word_count, unk_count
得到数字表示的句子:
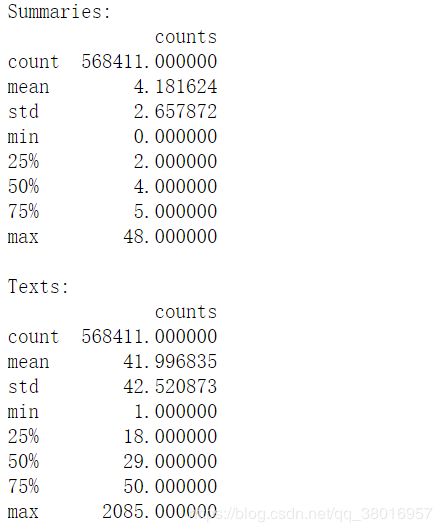
为了更能清晰的观察数据,将每个句子的长度转换DataFrame,再用describe函数查看具体情况
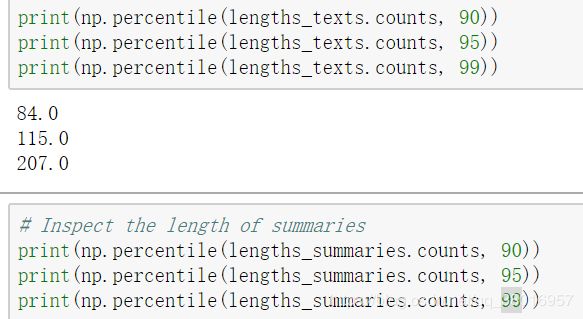
查看%90、95、99分位的数值
现在再对句子进行一次过滤,
- 1、对summaries和text过滤:
一句话中unk太多,设定阈值过滤一些句子 - 2、对summaries和text的长度排序,只取%90分位以下的长度值即可
sorted_summaries = []
sorted_texts = []
max_text_length = 84
max_summary_length = 13
min_length = 2
unk_text_limit = 1
unk_summary_limit = 0
for length in range(min(lengths_texts.counts), max_text_length):
for count, words in enumerate(int_summaries):
if (len(int_summaries[count]) >= min_length and
len(int_summaries[count]) <= max_summary_length and
len(int_texts[count]) >= min_length and
unk_counter(int_summaries[count]) <= unk_summary_limit and
unk_counter(int_texts[count]) <= unk_text_limit and
length == len(int_texts[count])
):
sorted_summaries.append(int_summaries[count])
到这里,就完成了对数据的筛选,处理部分,接下来构造Seq2Seq模型
2、构造Seq2Seq模型
Bidirectional RNNs(双向网络)的改进之处便是,假设当前的输出(第t步的输出)不仅仅与前面的序列有关,并且还与后面的序列有关。
例如:预测一个语句中缺失的词语那么就需要根据上下文来进行预测。Bidirectional RNNs是一个相对较简单的RNNs,是由两个RNNs上下叠加在一起组成的。输出由这两个RNNs的隐藏层的状态决定的
(1)数据输入
将数据切分,在每个句子前加‘’标识符
def process_encoding_input(target_data, vocab_to_int, batch_size):
'''Remove the last word id from each batch and concat the to the begining of each batch'''
ending = tf.strided_slice(target_data, [0, 0], [batch_size, -1], [1, 1])
dec_input = tf.concat([tf.fill([batch_size, 1], vocab_to_int['' ]), ending], 1)
return dec_input
(2)encoding_layer
动态双向RNN,输出enc_output, enc_state
def encoding_layer(rnn_size, sequence_length, num_layers, rnn_inputs, keep_prob):
'''Create the encoding layer'''
for layer in range(num_layers):
with tf.variable_scope('encoder_{}'.format(layer)):
cell_fw = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(rnn_size,
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=2))
cell_fw = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(cell_fw,
input_keep_prob = keep_prob)
cell_bw = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(rnn_size,
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=2))
cell_bw = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(cell_bw,
input_keep_prob = keep_prob)
enc_output, enc_state = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(cell_fw,
cell_bw,
rnn_inputs,
sequence_length,# 一个batchSize的大小
dtype=tf.float32)
# Join outputs since we are using a bidirectional RNN
enc_output = tf.concat(enc_output,2)
return enc_output, enc_state
(3)训练,辅助层
1、训练:training_decoding_layer:
tf.contrib.seq2seq.
TrainingHelper
BasicDecoder
dynamic_decode
2、测试:inference_decoding_layer
tf.contrib.seq2seq.
GreedyEmbeddingHelper
BasicDecoder
dynamic_decode
(4)decoding_layer
LSTMCell
BahdanauAttention
AttentionWrapper
with tf.variable_scope("decode"):
training_logits = training_decoding_layer(dec_embed_input,
summary_length,
dec_cell,
initial_state,
output_layer,
vocab_size,
max_summary_length)
with tf.variable_scope("decode", reuse=True):
inference_logits = inference_decoding_layer(embeddings,
vocab_to_int['' ],
vocab_to_int['' ],
dec_cell,
initial_state,
output_layer,
max_summary_length,
batch_size)
(5)seq2seq_model
将上面建立的操作结合
(6)Graph built
get_batches 得到batch
pad_sentence_batch 将长度不够的句子用’PAD‘补齐
tf.contrib.seq2seq.sequence_loss
tf.train.AdamOptimizer