入门学习-Python-小甲鱼学习资料-Day030-文件系统:介绍一个高大上的东西
根据视频自行练习
函数名 使用方法
getcwd() 返回当前工作目录
chdir(path) 改变工作目录
listdir(path=’.’) 列举指定目录中的文件名(’.‘表示当前目录,’…‘表示上一级目录)
mkdir(path) 创建单层目录,如该目录已存在抛出异常
makedirs(path) 递归创建多层目录,如该目录已存在抛出异常,注意:‘E:\a\b’和’E:\a\c’并不会冲突
remove(path) 删除文件
rmdir(path) 删除单层目录,如该目录非空则抛出异常
removedirs(path) 递归删除目录,从子目录到父目录逐层尝试删除,遇到目录非空则抛出异常
rename(old, new) 将文件old重命名为new
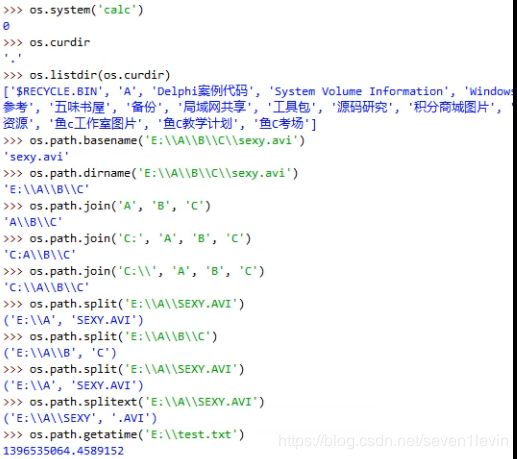
system(command) 运行系统的shell命令
walk(top) 遍历top路径以下所有的子目录,返回一个三元组:(路径, [包含目录], [包含文件])【具体实现方案请看:第30讲课后作业_】
以下是支持路径操作中常用到的一些定义,支持所有平台
os.curdir 指代当前目录(’.’)
os.pardir 指代上一级目录(’…’)
os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符(Win下为’\’,Linux下为’/’)
os.linesep 当前平台使用的行终止符(Win下为’\r\n’,Linux下为’\n’)
os.name 指代当前使用的操作系统(包括:‘posix’, ‘nt’, ‘mac’, ‘os2’, ‘ce’, ‘java’)
os.path模块中关于路径常用的函数使用方法
函数名 使用方法
basename(path) 去掉目录路径,单独返回文件名
dirname(path) 去掉文件名,单独返回目录路径
join(path1[, path2[, …]]) 将path1, path2各部分组合成一个路径名
split(path) 分割文件名与路径,返回(f_path, f_name)元组。如果完全使用目录,它也会将最后一个目录作为文件名分离,且不会判断文件或者目录是否存在
splitext(path) 分离文件名与扩展名,返回(f_name, f_extension)元组
getsize(file) 返回指定文件的尺寸,单位是字节
getatime(file) 返回指定文件最近的访问时间(浮点型秒数,可用time模块的gmtime()或localtime()函数换算)
getctime(file) 返回指定文件的创建时间(浮点型秒数,可用time模块的gmtime()或localtime()函数换算)
getmtime(file) 返回指定文件最新的修改时间(浮点型秒数,可用time模块的gmtime()或localtime()函数换算)
以下为函数返回 True 或 False
exists(path) 判断指定路径(目录或文件)是否存在
isabs(path) 判断指定路径是否为绝对路径
isdir(path) 判断指定路径是否存在且是一个目录
isfile(path) 判断指定路径是否存在且是一个文件
islink(path) 判断指定路径是否存在且是一个符号链接
ismount(path) 判断指定路径是否存在且是一个挂载点
samefile(path1, paht2) 判断path1和path2两个路径是否指向同一个文件
课后练习
import os
all_files = os.listdir(os.curdir)
type_dict=dict()
for each_file in all_files:
if os.path.isdir(each_file):
type_dict.setdefault('文件夹',0)
type_dict['文件夹'] +=1
else:
ext = os.path.splitext(each_file)[1]
type_dict.setdefault(ext,0)
type_dict[ext] += 1
for each_type in type_dict.keys():
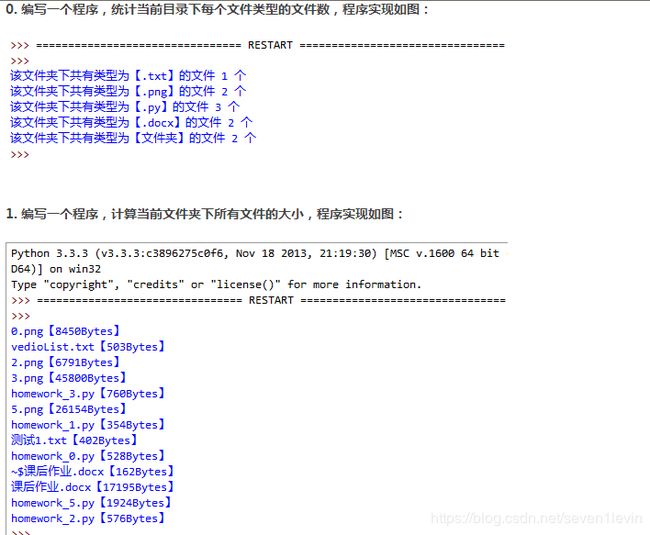
print('该文件夹下共有类型为【%s】的文件【%d】个' %(each_type,type_dict[each_type]))
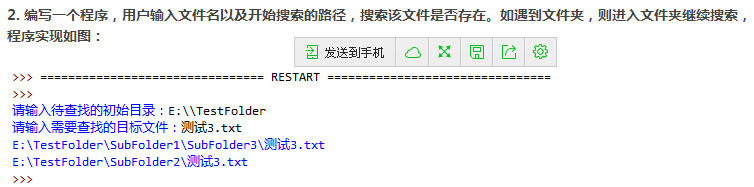
第1题
import os
all_files = os.listdir(os.curdir)
file_dict=dict()
for each_file in all_files:
if os.path.isfile(each_file):
file_size = os.path.getsize(each_file)
file_dict[each_file] = file_size
for each in file_dict.items():
print('%s [%d bytes]' %(each[0],each[1]))
第2题
def search_file(search_dir,goal):
os.chdir(search_dir)
for each_file in os.listdir(os.curdir):
if each_file == goal:
# 打印输出
print(os.getcwd()+os.sep+each_file)
if os.path.isdir(each_file):
# 递归调用
search_file(search_dir,goal)
os.chdir(os.pardir)
search_dir = input('请输入准备搜索的目录')
goal = input('请输入准备搜索的文件名')
search_file(search_dir,goal)
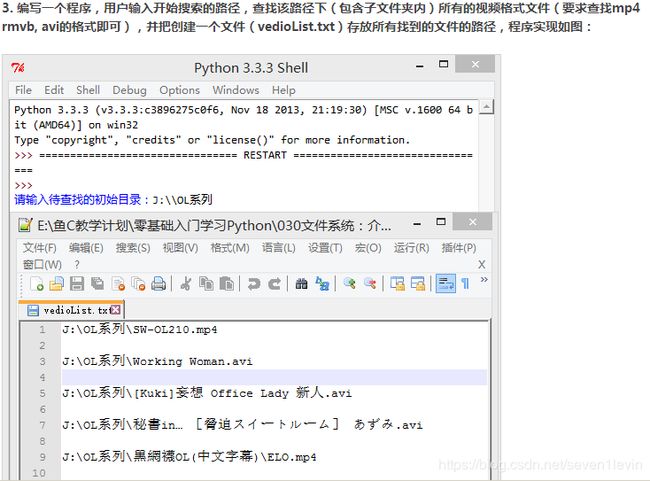
第3题
import sys
import os
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000)
def search_video(search_dir,v_type):
os.chdir(search_dir)
for each_file in os.listdir(os.curdir):
ext = os.path.splitext(each_file)[1]
if ext in v_type:
video_list.append(os.getcwd()+os.sep+each_file+os.linesep)
if os.path.isdir(each_file):
# 递归调用
search_video(search_dir,v_type)
os.chdir(os.pardir)
search_dir = input('请输入准备搜索的目录')
program_dir = os.getcwd()
v_type = ['.mp4','.rm','.rmvb','.avi','.mov']
video_list=[]
search_video(search_dir,v_type)
f = open(program_dir+os.sep+videolist.txt)
f.writelines(video_list)
f.close()