JVM内存溢出-数据库连接对象大量累积
JVM内存溢出-数据库连接对象大量累积
题记
上周三晚上截单之前,部分订单交易处理缓慢,少量订单支付由于超时连接,直接导致支付失败。信息来源有二:其一是jvm内存监控,间断性预警内存使用率过高,而后降下来;重复循环。其二是运营团队反应的客户下单异常情况。由此,打开电脑,开始排查。
分析
- 由于项目对接新的渠道,近一周内没有新需求上线,基本排除新
bug引起的交易异常和内存预警; - 由于内存占用过高,周而复始,说明
GC后内存确实会降下来; - 交易延时,部分交易不可用可能是由于
GC时间过长直接导致的;
排查步骤
1.联系运维导出线上内存占比过高节点的dupm文件;
- 提供导出脚本如下
1、步骤:
ps -ef|grep tomcat 或 ps -ef|grep java
2、找到mbt-main 的进程pid
jmap -dump:format=b,file=/xxx/xxx/m.hprof
3、将生成的快照文件/xxx/xxx/heap.hprof 导出
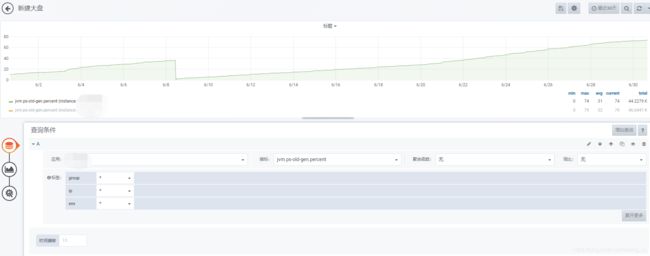
2.查看服务器监控包括CPU、JVM内存使用率
监控发现CPU使用正常
JVM内存使用
old区内存监控
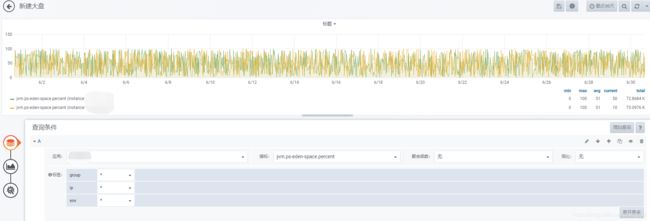
eden区内存监控
survivor区内存监控
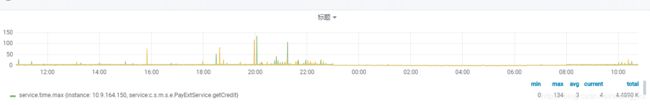
3.查看订单交易接口监控
交易监控正常时间均值在100ms以内
支付接口超时时间为2000ms
导致交易超时的原因,推测是full gc时间过长
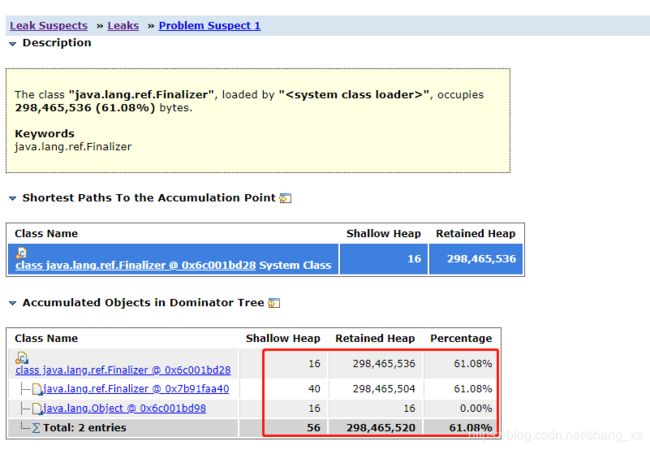
分析dump文件
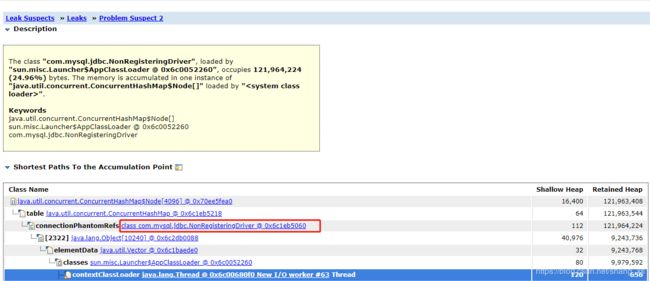
memory analyzer推测内存溢出原因
problem 2分析结果
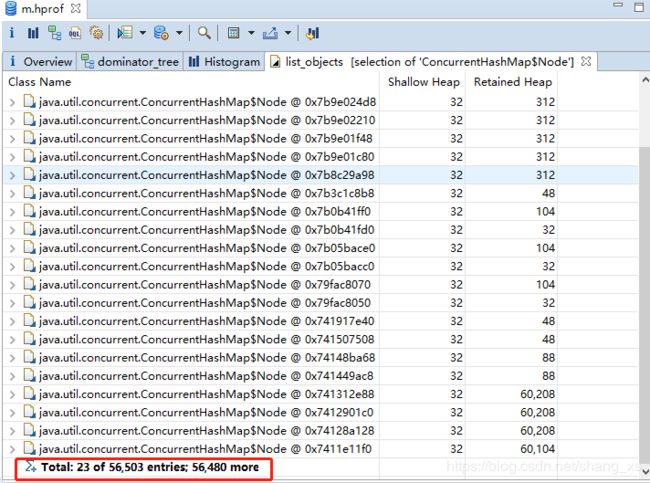
查看对象数
查看对象引用
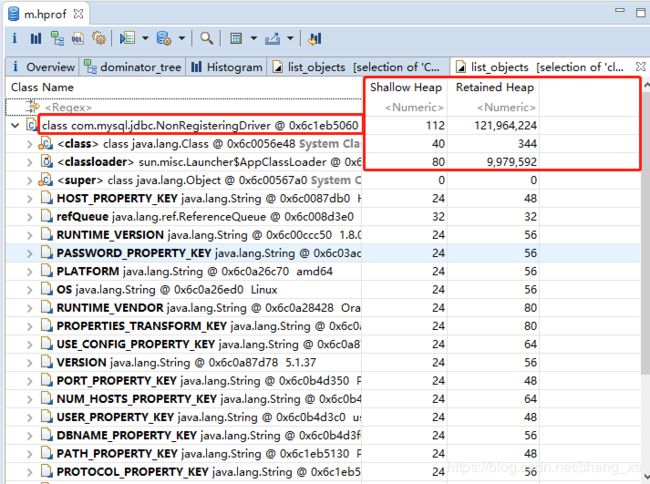
com.mysql.jdbc.NonRegisteringDriver$ConnectionPhantomReference 这个对象堆积了64992 个
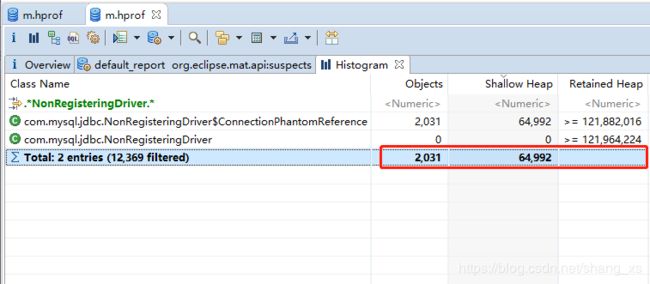
分析
com.mysql.jdbc.NonRegisteringDriver$ConnectionPhantomReference对象累计增长的原因
static class ConnectionPhantomReference extends PhantomReference<ConnectionImpl> {
private NetworkResources io;
ConnectionPhantomReference(ConnectionImpl connectionImpl, ReferenceQueue<ConnectionImpl> q) {
super(connectionImpl, q);
try {
this.io = connectionImpl.getIO().getNetworkResources();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// if we somehow got here and there's really no i/o, we deal with it later
}
}
void cleanup() {
if (this.io != null) {
try {
this.io.forceClose();
} finally {
this.io = null;
}
}
}
}
查看数据库连接
public ConnectionImpl(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url) throws SQLException {
this.connectionCreationTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (databaseToConnectTo == null) {
databaseToConnectTo = "";
}
// Stash away for later, used to clone this connection for Statement.cancel and Statement.setQueryTimeout().
//
this.origHostToConnectTo = hostToConnectTo;
this.origPortToConnectTo = portToConnectTo;
this.origDatabaseToConnectTo = databaseToConnectTo;
try {
Blob.class.getMethod("truncate", new Class[] { Long.TYPE });
this.isRunningOnJDK13 = false;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException nsme) {
this.isRunningOnJDK13 = true;
}
this.sessionCalendar = new GregorianCalendar();
this.utcCalendar = new GregorianCalendar();
this.utcCalendar.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT"));
//
// Normally, this code would be in initializeDriverProperties, but we need to do this as early as possible, so we can start logging to the 'correct'
// place as early as possible...this.log points to 'NullLogger' for every connection at startup to avoid NPEs and the overhead of checking for NULL at
// every logging call.
//
// We will reset this to the configured logger during properties initialization.
//
this.log = LogFactory.getLogger(getLogger(), LOGGER_INSTANCE_NAME, getExceptionInterceptor());
this.openStatements = new HashMap<Statement, Statement>();
if (NonRegisteringDriver.isHostPropertiesList(hostToConnectTo)) {
Properties hostSpecificProps = NonRegisteringDriver.expandHostKeyValues(hostToConnectTo);
Enumeration<?> propertyNames = hostSpecificProps.propertyNames();
while (propertyNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String propertyName = propertyNames.nextElement().toString();
String propertyValue = hostSpecificProps.getProperty(propertyName);
info.setProperty(propertyName, propertyValue);
}
} else {
if (hostToConnectTo == null) {
this.host = "localhost";
this.hostPortPair = this.host + ":" + portToConnectTo;
} else {
this.host = hostToConnectTo;
if (hostToConnectTo.indexOf(":") == -1) {
this.hostPortPair = this.host + ":" + portToConnectTo;
} else {
this.hostPortPair = this.host;
}
}
}
this.port = portToConnectTo;
this.database = databaseToConnectTo;
this.myURL = url;
this.user = info.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.USER_PROPERTY_KEY);
this.password = info.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.PASSWORD_PROPERTY_KEY);
if ((this.user == null) || this.user.equals("")) {
this.user = "";
}
if (this.password == null) {
this.password = "";
}
this.props = info;
initializeDriverProperties(info);
// We store this per-connection, due to static synchronization issues in Java's built-in TimeZone class...
this.defaultTimeZone = TimeUtil.getDefaultTimeZone(getCacheDefaultTimezone());
this.isClientTzUTC = !this.defaultTimeZone.useDaylightTime() && this.defaultTimeZone.getRawOffset() == 0;
if (getUseUsageAdvisor()) {
this.pointOfOrigin = LogUtils.findCallingClassAndMethod(new Throwable());
} else {
this.pointOfOrigin = "";
}
try {
this.dbmd = getMetaData(false, false);
initializeSafeStatementInterceptors();
createNewIO(false);
unSafeStatementInterceptors();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
cleanup(ex);
// don't clobber SQL exceptions
throw ex;
} catch (Exception ex) {
cleanup(ex);
StringBuilder mesg = new StringBuilder(128);
if (!getParanoid()) {
mesg.append("Cannot connect to MySQL server on ");
mesg.append(this.host);
mesg.append(":");
mesg.append(this.port);
mesg.append(".\n\n");
mesg.append("Make sure that there is a MySQL server ");
mesg.append("running on the machine/port you are trying ");
mesg.append("to connect to and that the machine this software is running on ");
mesg.append("is able to connect to this host/port (i.e. not firewalled). ");
mesg.append("Also make sure that the server has not been started with the --skip-networking ");
mesg.append("flag.\n\n");
} else {
mesg.append("Unable to connect to database.");
}
SQLException sqlEx = SQLError.createSQLException(mesg.toString(), SQLError.SQL_STATE_COMMUNICATION_LINK_FAILURE, getExceptionInterceptor());
sqlEx.initCause(ex);
throw sqlEx;
}
NonRegisteringDriver.trackConnection(this);
}
分析
调用链路:ConnectionImpl -> createNewIO->NonRegisteringDriver.trackConnection->NonRegisteringDriver.connectionPhantomRefs
protected static final ConcurrentHashMap<ConnectionPhantomReference, ConnectionPhantomReference> connectionPhantomRefs = new ConcurrentHashMap<ConnectionPhantomReference, ConnectionPhantomReference>();
// 加入
protected static void trackConnection(Connection newConn) {
ConnectionPhantomReference phantomRef = new ConnectionPhantomReference((ConnectionImpl) newConn, refQueue);
connectionPhantomRefs.put(phantomRef, phantomRef);
}
分析 ConnectionPhantomReference -> PhantomReference
- 创建对象,使用
Phantom Reference - 对象不可达
GC发生只有Phantom Reference引用,检查是否需要执行Finalize- 对象已处于
Finalized状态 GC发现,认为它是Phantom可达对象,则加入Reference的Pending链表ReferenceHandler将Pending链表表头加入ReferenceQueue- 手动清除
Phantom Reference,使对象成为完全不可达对象 GC发现对象不可达,回收对象所占的空间
代码示例
public class Test {
public static boolean isRun = true;
@SuppressWarnings("static-access")
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String abc = new String("abc");
System.out.println(abc.getClass() + "@" + abc.hashCode());
final ReferenceQueue<String> referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue<String>();
new Thread() {
public void run() {
while (isRun) {
Object obj = referenceQueue.poll();
if (obj != null) {
try {
Field rereferent = Reference.class
.getDeclaredField("referent");
rereferent.setAccessible(true);
Object result = rereferent.get(obj);
System.out.println("gc will collect:"
+ result.getClass() + "@"
+ result.hashCode() + "\t"
+ (String) result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}.start();
PhantomReference<String> abcWeakRef = new PhantomReference<String>(abc,
referenceQueue);
abc = null;
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
System.gc();
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
isRun = false;
}
}
解决方案
经调研、排查问题产生的根源是数据库连接对象堆积,导致full gc时间过长。
- 采用
JDK1.8+支持的G1垃圾收集器 - 根据当前
JVM采用的垃圾收集器配置触发full gc策略的参数 - 代码实现
System.gc();不能保证GC时效性