Python - Day10 - 运算符 &基本数据类型 & 整形 & 字符串
Pycharm (2018.1)
#专业版 professional (百度搜索 pycharm server )
#不要汉化
project(文件夹)
解释器位置
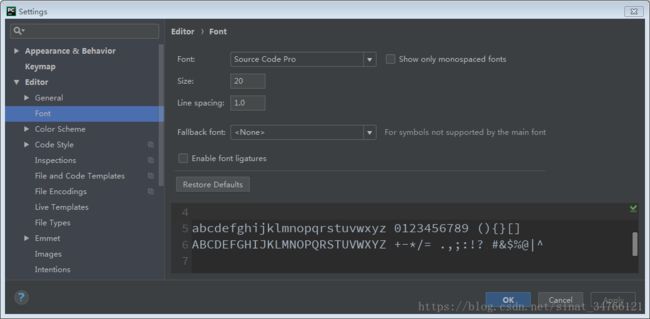
调整字体大小
利用滚轮调整字体大小
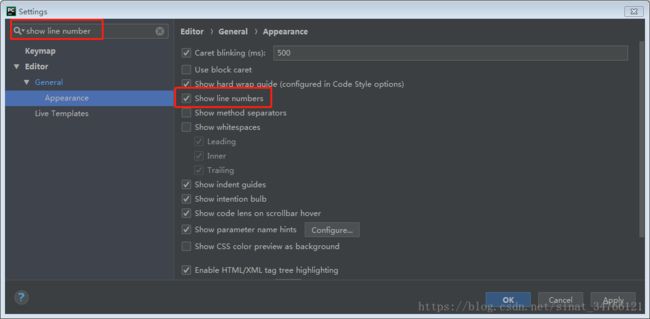
显示行号
1.运算符
数字运算符:
+ - * / ** %(取商) // (取余)
num=9%2 #取商
print(num)num=9//2 #取余
print(num)
赋值运算符:
count=a+b
count=count+a ==> count +=a
count=count-a ==> count -1=a
count=count*a ==>count *=a (乘法)
count=count/a ==> count /=a (除法)
count=count%a ==>count %=a (取模)
count=count**a ==> count **=a (幂赋值)
count=count//a ==> count xx=a (取整除)
字符串
#每个字叫一个字符,三个一起叫字符串(有三个字符)
#"郑建文" 字符串
#"郑建文"中的 "郑" 是字符
#"郑" 可以是一个字符串
成员运算:
1.in---- not in: 判断某个东西是否在某个东西里面(结果是一个布尔值 true/false)
1).in
eg.1:
name='郑建文'
if "正" in name:
print('OK')
else:
print('Error')![]()
eg.2:
name='郑建文'
if "建文" in name:
print('OK')
else:
print('Error')![]()
#子序列/子字符串
eg3:
name='郑建文'
if "郑文" in name:
print('OK')
else:
print('Error')![]()
eg4:
name='郑建文'
if "郑建" in name:
print('OK')
else:
print('Error')![]()
注释:
选中后,按住Ctrl+?
2).not in
name="郑建文"
if "文" not in name:
print("1")
else:
print("2")![]()
if True:
pass
while True:
pass
比较运算符
==
>
<
>=
<=
!=不等于
<>不等于
not True = False
v=not True
数据类型:布尔型 - bloo
真 True : if 1==1 / if 2>2
假 False
eg:
name="郑建文"
v="文1" not in name
print(v)![]()
name="郑建文"
v="文1" in name
print(v)![]()
=======================================================================
if True:
pass
while True:
pass
逻辑运算符:
v=user=='alex' and pwd='123' or ==1
v=user=='alex' or pwd='123'
v=not false
补充:
运算顺序:
1.先计算括号内的:(最好使用括号)
v=user=='alex' and (pwd='123' or ==1)
user="alex"
pwd="123"
v = user=='alex' and pwd == '123' or 1 == 1 and pwd == '99854'
print(v)![]()
user="alex"
pwd="123"
v = user=='ale' and pwd == '123' or 1 == 1 and pwd == '99854'
print(v)
2.一般执行顺序:从左到右(and 前是真,继续执行; or 前是真,后面不继续执行)
True OR==> True
True AND==>继续
False OR==>继续
False AND ==>False
user="alex"
pwd="123"
v = user='ale' and pwd == '123' or 1 == 2 and pwd == '99854' and 1==2
print(v)user="alex"
pwd="123"
v = user=='ale' and pwd == '123' or 1 == 1 and pwd == '99854'
print(v)先判断and前是否为真,
如果为真,判断and后是否为真;
为真,则为真
为假,则为假
如果为假,则默认and后均为假
总结:
运算结果为值
算数运算
a=10*10
赋值运算
a=a+1 a+=1
运算结果为布尔型:真或假 bloo
比较运算
a=1>5 bloo
逻辑运算
a=1>6 or 1==1
成员运算
a="问"in“郑建文”
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5444685.html
2.基本数据类型:相同的数据类型,有相同的功能
a=123
r=a.bit_length() #执行魔法,得到新值
print(r)数字没有upper属性
#字符串:女巫
name1="SHINee"
v1=name1.upper()
print(v1)![]()
数字(整形),int (所有的功能都放在int里->tips1,Ctrl+点击类型名称)
a1=123
a1=456
python 3 里,数字无论大小都用int类型,整形
python 2里,int是有范围的,超过范围,即为长整形 long
功能:
1.int,将字符串转换为数字(默认10进制)
a='123'
b=int(a)
print(b)![]()
a='123'
print(type(a),a)
b=int(a)
print(type(b),b)
num="0011"
v=int(num,base=16) #转换为16进制
print(v)
num="a"
v=int(num,base=16) #转换为16进制
print(v)
2.bit_lenght,当前数字的二进制的位数
age=3
#1 1
#2 10
#3 11
#4 100
#5 101
# 当前数字的二进制,至少用n位表示
r=age.bit_length()
print(r)![]()
字符串,str
1.首字母大写
test="aLex"
v=test.capitalize() #首字母大写
print(v)2.小写
test="aLex"
v1=test.casefold() #小写,更厉害,未知的对应关系
print(v1)
v2=test.lower()#处理普通的对应关系
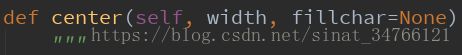
print(v2)3.center
设置宽度,并将内容居中
20指代总长度
* 空白未知填充,一个字符,可有可无
test="aLex"
v=test.center(20)
print(v)alex |
test="aLex"
v=test.center(20,"*")
print(v)********alex********
rjust/ljust:填充 r右边 l左边
test="alex"
v=test.rjust(20,"*")
print(v)****************alex
test="alex"
v=test.ljust(20,"*")
print(v)alex****************
zfill:不能指定字符,只能用0填充
test="alex"
v=test.zfill(20)
print(v)0000000000000000alex
4.count
def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None)去字符串中寻找子序列出现的次数
可设置起始位置,结束位置
test="aLexalexr"
v=test.count("ex")
print(v)
从第5个位置开始,第6个结束
test="aLexalexr"
v=test.count("ex",5,6)
print(v)
5.encode
6.decode
7.endswith
以...结束
test="aLexalexr"
v=test.endswith("a")
print(v)
test="aLexalexr"
v=test.endswith("xr")
print(v)
startswith
以....开始
test="alexalex"
v=test.find("ex",5,8)
print(v)
test="aLexalexr"
v=test.startswith("a")
print(v)
8.find
def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None)从开始往后找,找到第一个之后,获取其位置
>,<=区间
test="alexalex"
v=test.find("ex",5,8)
print(v)
9.format
格式化,将一个字符串中的占位符替换为指定的值
test="i am {name},age {a}"
print(test)
v=test.format(name="alex",a=19)
print(v)
按顺序替换
test="i am {0},age {1}"
print(test)
v=test.format("alex",19)
print(v)10.format_map
格式化,传入的值{"name":"alex","a":19}
test="i am {name},age {a}"
print(test)
v=test.format_map({"name":"alex","a":19})
print(v)test="i am {name},age {a}"
print(test)
v=test.format_map({"a":"alex","name":19})
print(v)
11.index(find可以代替,可以湖绿)
def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None)index,找不到会报错
test="aler"
v=test.index('ex')
print(v)
12.isalnum
字符串中是否只包含字母和数字
test="uasf890"
v=test.isalnum()
print(v)
def isalpha(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isalpha() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isdecimal(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isdecimal() -> bool
Return True if there are only decimal characters in S,
False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isdigit(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isdigit() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are digits
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isidentifier(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isidentifier() -> bool
Return True if S is a valid identifier according
to the language definition.
Use keyword.iskeyword() to test for reserved identifiers
such as "def" and "class".
"""
return False
def islower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.islower() -> bool
Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isnumeric(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isnumeric() -> bool
Return True if there are only numeric characters in S,
False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isprintable(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isprintable() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are considered
printable in repr() or S is empty, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isspace(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isspace() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are whitespace
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def istitle(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.istitle() -> bool
Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one
character in S, i.e. upper- and titlecase characters may only
follow uncased characters and lowercase characters only cased ones.
Return False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isupper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isupper() -> bool
Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def join(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.join(iterable) -> str
Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
iterable. The separator between elements is S.
"""
return ""
def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
Return S left-justified in a Unicode string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
"""
return ""
def lower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.lower() -> str
Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
"""
return ""
def lstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.lstrip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
"""
return ""
def maketrans(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return a translation table usable for str.translate().
If there is only one argument, it must be a dictionary mapping Unicode
ordinals (integers) or characters to Unicode ordinals, strings or None.
Character keys will be then converted to ordinals.
If there are two arguments, they must be strings of equal length, and
in the resulting dictionary, each character in x will be mapped to the
character at the same position in y. If there is a third argument, it
must be a string, whose characters will be mapped to None in the result.
"""
pass
def partition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,
the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not
found, return S and two empty strings.
"""
pass
def replace(self, old, new, count=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring
old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
"""
return ""
def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Return -1 on failure.
"""
return 0
def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rindex(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Raises ValueError when the substring is not found.
"""
return 0
def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
"""
return ""
def rpartition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return
the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the
separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
"""
pass
def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rsplit(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings
Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and
working to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
splits are done. If sep is not specified, any whitespace string
is a separator.
"""
return []
def rstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rstrip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
"""
return ""
def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings
Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any
whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are
removed from the result.
"""
return []
def splitlines(self, keepends=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.splitlines([keepends]) -> list of strings
Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends
is given and true.
"""
return []
def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
"""
return False
def strip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.strip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing
whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
"""
return ""
def swapcase(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.swapcase() -> str
Return a copy of S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase
and vice versa.
"""
return ""
def title(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.title() -> str
Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case
characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case.
"""
return ""
def translate(self, table): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.translate(table) -> str
Return a copy of the string S in which each character has been mapped
through the given translation table. The table must implement
lookup/indexing via __getitem__, for instance a dictionary or list,
mapping Unicode ordinals to Unicode ordinals, strings, or None. If
this operation raises LookupError, the character is left untouched.
Characters mapped to None are deleted.
"""
return ""
def upper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.upper() -> str
Return a copy of S converted to uppercase.
"""
return ""
def zfill(self, width): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.zfill(width) -> str
Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
"""
return ""列表,list
元祖,tuple
字典,dict
布尔值,bool
Tips:
1.查看数据类型具有的功能,输入类型后,选中类型,Ctrl 键点击类型名称
2.函数中的值
有=的可带可不带,无=必须带