多线程与高并发(一):单机高并发应该掌握的线程基础:线程状态,异常与锁等
多线程复习
多线程的基本概念
什么是一个线程?如何开启一个线程?
package com.mashibing.juc.c_000;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class T01_WhatIsThread {
private static class T1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("T1");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//new T1().run();//这是普通的函数调用
new T1().start();//这是开启一个线程
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main");
}
}
}
面试题:请你告诉我启动线程的三种方式
- 继承Thread,重写run方法
- 实现Runnable接口,重写run方法(或Lambda表达式)
- 通过线程池来启动(实际上也是以上两种之一)
package com.mashibing.juc.c_000;
public class T02_HowToCreateThread {
static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello MyThread!");
}
}
static class MyRun implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello MyRun!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyThread().start(); // 第一种
new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); // 第二种(1)
new Thread(()->{ // 第二种(2)
System.out.println("Hello Lambda!");
}).start();
}
}
//请你告诉我启动线程的三种方式 1:Thread 2: Runnable 3:Executors.newCachedThrad
Sleep Yield Join 的含义
- sleep:睡眠,当前线程暂停一段时间,让给别的线程去执行。睡眠时间到,自动复活
- yield:当前线程正在执行的时候,停下来进入等待队列,回到等待队列里。系统调度算法去决定哪个线程继续运行(有可能还是自己)
- join:在自己当前线程加入你调用的join线程,本线程等待等调用的线程运行完了,自己再去执行。(自己join自己没有意义)
package com.mashibing.juc.c_000;
public class T03_Sleep_Yield_Join {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// testSleep();
// testYield();
testJoin();
}
static void testSleep() {
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("A" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
//TimeUnit.Milliseconds.sleep(500)
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
static void testYield() {
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("A" + i);
if(i%10 == 0) Thread.yield();
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("------------B" + i);
if(i%10 == 0) Thread.yield();
}
}).start();
}
static void testJoin() {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("A" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
//TimeUnit.Milliseconds.sleep(500)
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("A" + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
//TimeUnit.Milliseconds.sleep(500)
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
线程状态
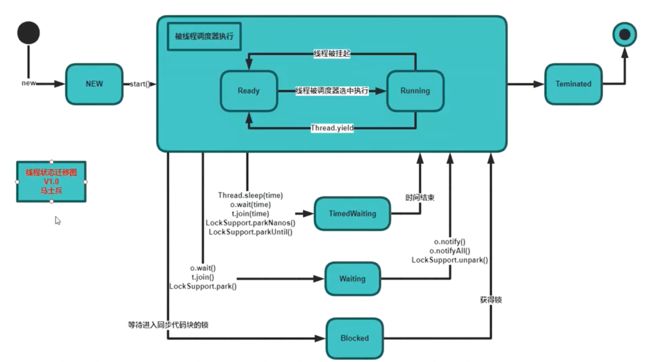
如何关闭线程?
不要使用stop()关闭线程,要让线程自己去结束。
package com.mashibing.juc.c_000;
public class T04_ThreadState {
static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(this.getState());
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new MyThread();
System.out.println(t.getState());
t.start();
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(t.getState());
}
}
Interrupt 的含义
当 catch 到 InterruptedException 时,应该在逻辑中写好处理方式:让线程停止或者继续运行
Syncronized 复习
给一个变量/一段代码加锁的含义是:线程拿到锁之后,才能修改一个变量/执行一段代码
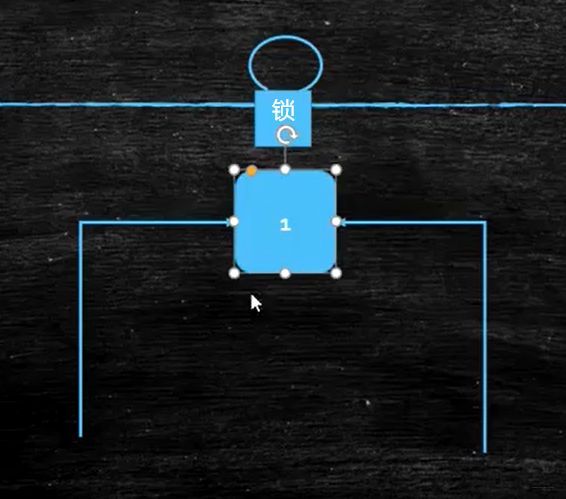
/**
* synchronized关键字
* 对某个对象加锁
*/
package com.mashibing.juc.c_001;
public class T {
private int count = 10;
private Object o = new Object();
public void m() {
synchronized(o) { //任何线程要执行下面的代码,必须先拿到o的锁
count--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " count = " + count);
}
}
}
/**
* synchronized关键字
* 对某个对象加锁
* @author mashibing
*/
package com.mashibing.juc.c_002;
public class T {
private int count = 10;
public void m() {
synchronized(this) { //任何线程要执行下面的代码,必须先拿到this的锁
count--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " count = " + count);
}
}
}
/**
* synchronized关键字
* 对某个对象加锁
* @author mashibing
*/
package com.mashibing.juc.c_003;
public class T {
private int count = 10;
public synchronized void m() { //等同于在方法的代码执行时要synchronized(this)
count--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " count = " + count);
}
}
/**
* synchronized关键字
* 对某个对象加锁
* @author mashibing
*/
package com.mashibing.juc.c_004;
public class T {
private static int count = 10;
public synchronized static void m() { //这里等同于synchronized(FineCoarseLock.class)
count--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " count = " + count);
}
public static void mm() {
synchronized(T.class) { //考虑一下这里写synchronized(this)是否可以?
count --;
}
}
}
测试将syncronized方法和非syncronized方法一起调用:非syncronized方法并没有被阻塞
/**
* 同步和非同步方法是否可以同时调用?
* @author mashibing
*/
package com.mashibing.juc.c_007;
public class T {
public synchronized void m1() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " m1 start...");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " m1 end");
}
public void m2() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " m2 ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
T t = new T();
/*new Thread(()->t.m1(), "t1").start();
new Thread(()->t.m2(), "t2").start();*/
new Thread(t::m1, "t1").start();
new Thread(t::m2, "t2").start();
/*
//1.8之前的写法
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
t.m1();
}
});
*/
}
}
示例:脏读
/**
* 面试题:模拟银行账户
* 对业务写方法加锁
* 对业务读方法不加锁
* 这样行不行?
*
* 容易产生脏读问题(dirtyRead)
*/
package com.mashibing.juc.c_008;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Account {
String name;
double balance;
public synchronized void set(String name, double balance) {
this.name = name;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.balance = balance;
}
public /*synchronized*/ double getBalance(String name) {
return this.balance;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account a = new Account();
new Thread(()->a.set("zhangsan", 100.0)).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(a.getBalance("zhangsan"));
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(a.getBalance("zhangsan"));
}
}
