生成对抗网络(GAN)简介以及Python实现
本篇博客简单介绍了生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks,GAN),并基于Keras实现深度卷积生成对抗网络(DCGAN)。
以往的生成模型都是预先假设生成样本服从某一分布族,然后用深度网络学习分布族的参数,最后从学习到的分布中采样生成新的样本。例如变分自编码器就是构建生成样本的密度函数 p ( x ∣ z , θ ) p(x|z,\theta) p(x∣z,θ),这种模型称为显示密度模型。
GAN并不学习密度函数,而是基于随机噪声,通过深度神经网络的层层包装,直接输出服从原始样本分布的新样本,这种模型称为隐式密度模型。
那么GAN如何保证生成的样本符合原始样本分布?这就需要用到对抗学习的思想。
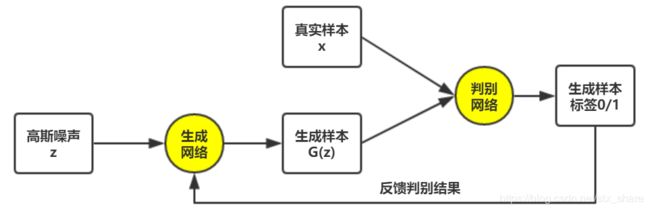
GAN网络结构
GAN网络由生成网络和判别网络组合而成,通常都由卷积层和全连接层构成。
- 生成网络负责根据输入的随机噪声 z z z,构建映射函数 G ( z ) G(z) G(z),使得生成样本尽量接近真实样本
- 判别网络负责比较真实样本 x x x与生成样本 G ( z ) G(z) G(z),判定出 G ( z ) G(z) G(z)不是来自真实样本分布,相当于一个二分类器
可见,生成网络与判别网络之间是对抗交互的。流程如下:
目标函数
判别网络输出样本来自真实分布的概率为 p ( y = 0 ∣ x ) = D ( x , ϕ ) p(y=0|x)=D(x, \phi) p(y=0∣x)=D(x,ϕ)式中, ϕ \phi ϕ为判别网络参数。注意:实际模型训练时,通常将真实样本标记为0,生成样本标记为1。
判别网络的目标函数用交叉熵表示:
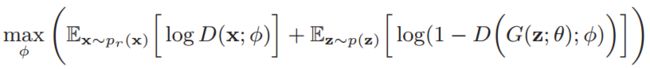
生成网络目标与之相反:
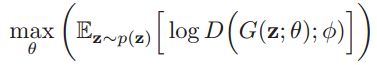
式中, θ \theta θ为生成网络参数。
注:以上公式图片均截图自 邱锡鹏《神经网络与深度学习》,详细推到过程请见此书
算法流程
生成网络与判别网络的训练是交叉进行的,判别网络训练K次后,生成网络训练1次。
- Input: 训练样本集D,最大迭代训练步数max_step,每次迭代判别网络训练次数K以及小批量样本数M
- Output: 生成网络参数
- 采用随机梯度下降训练判别网络K次,每次分别从样本集和生成网络采集M个样本
- 生成网络生成M个样本,基于最新的判别网络参数,训练生成网络一次
- 若达到最大迭代步数,终止,反之转步骤1
代码示例
# 实现简单的DCGAN(深度卷积生成对抗网络)
from keras.layers import Conv2D, Dense, Flatten, LeakyReLU, Reshape, Conv2DTranspose, \
BatchNormalization, Input, Dropout
from keras.models import Sequential, Model, load_model
from keras.optimizers import adam
from keras.utils import plot_model
import numpy as np
def uniform_sampling(n_sample, dim):
# 均匀分布采样
return np.random.uniform(0, 1, size=(n_sample, dim))
def normal_sampling(n_sample, dim):
# 均匀分布采样
return np.random.randn(n_sample, dim)
# 构建判别网络
d_model = Sequential()
d_model.add(BatchNormalization())
d_model.add(Dropout(0.3))
d_model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='same', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
d_model.add(LeakyReLU(0.2))
d_model.add(Dropout(0.3))
d_model.add(Conv2D(128, (3, 3), strides=2, padding='same')) # 用带步长卷积层替代池化层
d_model.add(LeakyReLU(0.2))
d_model.add(Dropout(0.3))
d_model.add(Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='same'))
d_model.add(LeakyReLU(0.2))
d_model.add(Dropout(0.3))
d_model.add(Conv2D(512, (3, 3), strides=2, padding='same'))
d_model.add(LeakyReLU(0.2))
d_model.add(Flatten())
d_model.add(Dropout(0.3))
d_model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) # 输出样本标记为1,即假样本的概率
# 构建生成网络
g_model = Sequential()
g_model.add(BatchNormalization())
g_model.add(Dense(7 * 7 * 256, activation='relu', input_dim=100))
g_model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 256)))
g_model.add(BatchNormalization())
g_model.add(Conv2DTranspose(128, 3, strides=2, padding='same', activation='relu')) # 反卷积
g_model.add(BatchNormalization())
g_model.add(Conv2DTranspose(64, 3, strides=2, padding='same', activation='relu'))
g_model.add(BatchNormalization())
g_model.add(Conv2DTranspose(32, 3, strides=1, padding='same', activation='relu'))
g_model.add(BatchNormalization())
g_model.add(Conv2DTranspose(1, 3, strides=1, padding='same', activation='tanh'))
class DCGAN:
def __init__(self, d_model, g_model,
input_dim=784, g_dim=100,
max_step=100, sample_size=256, d_iter=3, kind='normal'):
self.input_dim = input_dim # 图像的展开维度,即判别网络的输入维度
self.g_dim = g_dim # 随机噪声维度,即生成网络的输入维度
self.max_step = max_step # 整个模型的迭代次数
self.sample_size = sample_size # 训练过程中小批量采样的个数的一半
self.d_iter = d_iter # 每次迭代,判别网络训练的次数
self.kind = kind # 随机噪声分布类型
self.d_model = d_model # 判别模型
self.g_model = g_model # 生成模型
self.m_model = self.merge_model() # 合并模型
self.optimizer = adam(lr=0.0002, beta_1=0.5)
self.d_model.compile(optimizer=self.optimizer, loss='binary_crossentropy')
def merge_model(self):
# 合并生成网络与判别网络
noise = Input(shape=(self.g_dim,))
gen_sample = self.g_model(noise)
self.d_model.trainable = False # 固定判别网络,训练合并网络等同与训练生成网络
d_output = self.d_model(gen_sample)
m_model = Model(noise, d_output) # 模型输出生成样本的预测结果,越接近0越好
m_model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy')
return m_model
def gen_noise(self, num_sample):
# 生成随机噪声数据
if self.kind == 'normal':
f = normal_sampling
elif self.kind == 'uniform':
f = uniform_sampling
else:
raise ValueError('暂不支持分布{}'.format(self.kind))
return f(num_sample, self.g_dim)
def gen_real_data(self, train_data):
# 真实样本采样
n_samples = train_data.shape[0]
inds = np.random.randint(0, n_samples, size=self.sample_size)
real_data = train_data[inds]
real_label = np.random.uniform(0, 0.3,
size=(self.sample_size,)) # 用0-0.3随机数代替标记0
return real_data, real_label
def gen_fake_data(self):
# 生成样本
noise = self.gen_noise(self.sample_size)
fake_data = g_model.predict(noise) # 生成网络生成M个样本,标记为0
fake_label = np.random.uniform(0.7, 1.2,
size=(self.sample_size,)) # 用0.7-1.2随机数代替标记1
return fake_data, fake_label
def fit(self, train_data):
# 轮流训练判别网络和生成网络
for i in range(self.max_step):
for _ in range(self.d_iter): # 训练判别网络
real_data, real_label = self.gen_real_data(train_data)
d_model.train_on_batch(real_data, real_label)
fake_data, fake_label = self.gen_fake_data()
d_model.train_on_batch(fake_data, fake_label)
# 训练生成网络
noise = self.gen_noise(self.sample_size)
expected_label = np.random.uniform(0, 0.3, size=(self.sample_size,)) # 期望输出0
self.d_model.trainable = False
self.m_model.compile(optimizer=self.optimizer, loss='binary_crossentropy')
gan_loss = self.m_model.train_on_batch(noise, expected_label)
print('第{0}次迭代训练损失值:{1:.3f}'.format(i + 1, gan_loss))
return
def gen_samples(self, num):
# 生成网络生成数据
z = self.gen_noise(num)
imgs = g_model.predict(z)
return imgs
def save_model(self):
# 保存训练后的模型
self.d_model.save('d_model.hdf5')
self.g_model.save('g_model.hdf5')
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
# d_model = load_model('D:\Machine_Learning\deep_learning_algorithm\gan\d_model.hdf5')
# g_model = load_model('D:\Machine_Learning\deep_learning_algorithm\gan\g_model.hdf5')
# plot_model(d_model, 'd_model.png')
# plot_model(g_model, 'g_model.png')
model = DCGAN(d_model, g_model, max_step=10, sample_size=1000, d_iter=2)
# 导入数据
input_dim = 28 * 28 * 1 # 单通道28像素的图像
f = np.load(r'D:\Machine_Learning\deep_learning_algorithm\data\mnist.npz')
x_train, y_train = f['x_train'], f['y_train']
f.close()
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, [-1, input_dim])
x_train = (x_train.astype('float32') - 127.5) / 127.5 # 规范化到(-1,1)
x_train = x_train.reshape((x_train.shape[0], 28, 28, 1)) # 转换成卷积网络层标准的数据格式
# 训练
model.fit(x_train)
model.save_model()
# 生成样本并可视化
imgs = model.gen_samples(10)
def plot_img(gen_imgs):
# 对比重构前后的图像
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
ax = plt.subplot(1, n, i + 1)
plt.imshow(gen_imgs[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
return
plot_img(imgs)
参考资料
- 邱锡鹏《神经网络与深度学习》
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06434.pdf
- https://github.com/soumith/ganhacks
- https://blog.csdn.net/theonegis/article/details/80115340
注:代码未经严格测试训练,仅作示例,如有不当之处请指正。