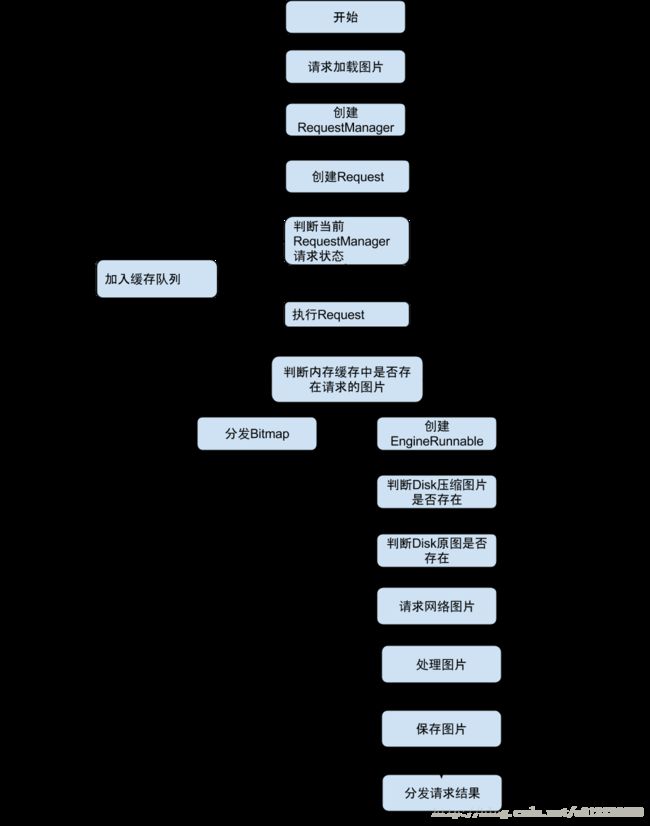
深入解析Glide源码
Glide 是 Google的开源项目, Glide具有获取、解码和展示视频剧照、图片、动画等功能,它还有灵活的API,这些API使开发者能够将Glide应用在几乎任何网络协议栈里。创建Glide的主要目的有两个,一个是实现平滑的图片列表滚动效果,另一个是支持远程图片的获取、大小调整和展示。本篇博客,我们一起深入分析Glide的源码。
总体设计
with方法
首先我们来看一下glide的一般使用方法
Glide.with(this)
.load("http://image.baidu.com/search/detail?ct=503316480&z=0&ipn=d&word=%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%87&hs=0&pn=0&spn=0&di=157484237350&pi=0&rn=1&tn=baiduimagedetail&is=0%2C0&ie=utf-8&oe=utf-8&cl=2&lm=-1&cs=4271053251%2C2424464488&os=2375022793%2C1835605452&simid=4247939438%2C550168575&adpicid=0&lpn=0&ln=30&fr=ala&fm=&sme=&cg=&bdtype=0&oriquery=&objurl=http%3A%2F%2Fpic55.nipic.com%2Ffile%2F20141208%2F19462408_171130083000_2.jpg&fromurl=ippr_z2C%24qAzdH3FAzdH3Fooo_z%26e3Bgtrtv_z%26e3Bv54AzdH3Fzi7wgptAzdH3F8c8n9d9_d_z%26e3Bip4s&gsm=0")
.into(mImageView);with方法主要就是用于创建RequestManager,这里是Glide通过Activity/Fragment生命周期管理Request原理所在,流程图如下:
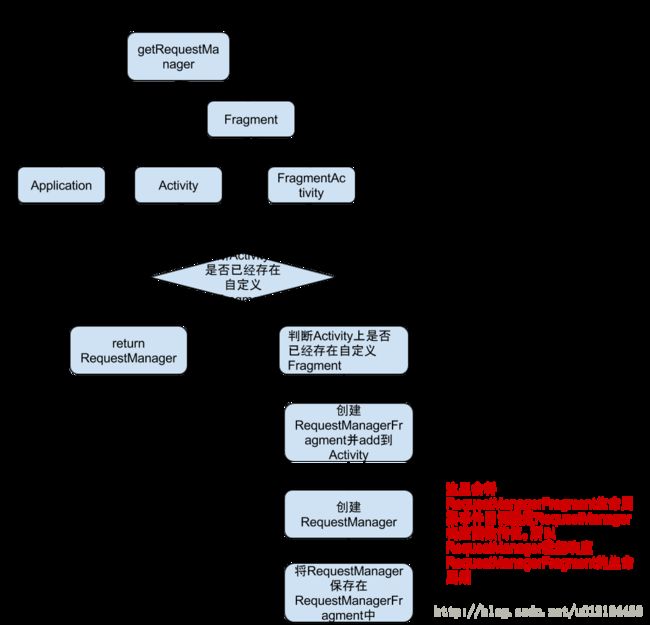
那我们就从with方法入手,with方法传入的参数可以是Context,Activity,Fragment或FragmentActiviy,以FragmentActiviy为例子
public static RequestManager with(FragmentActivity activity) {
RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get();
return retriever.get(activity);
}获取了RequestManagerRetriever,并调用了其get方法
public RequestManager get(FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();
return supportFragmentGet(activity, fm);
}
}判断是否在主线程中调用,如果是子线程中,则调用get(activity.getApplicationContext())
public RequestManager get(Context context) {
if (context == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You cannot start a load on a null Context");
} else if (Util.isOnMainThread() && !(context instanceof Application)) {
if (context instanceof FragmentActivity) {
return get((FragmentActivity) context);
} else if (context instanceof Activity) {
return get((Activity) context);
} else if (context instanceof ContextWrapper) {
return get(((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext());
}
}
return getApplicationManager(context);
}很明显传入的context是ApplicationContext,所以会调用getApplicationManager(context)
private RequestManager getApplicationManager(Context context) {
// Either an application context or we're on a background thread.
if (applicationManager == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (applicationManager == null) {
// Normally pause/resume is taken care of by the fragment we add to the fragment or activity.
// However, in this case since the manager attached to the application will not receive lifecycle
// events, we must force the manager to start resumed using ApplicationLifecycle.
applicationManager = new RequestManager(context.getApplicationContext(),
new ApplicationLifecycle(), new EmptyRequestManagerTreeNode());
}
}
}
return applicationManager;
}创建了一个RequestManager,并将其返回,这里的ApplicationLifecycle很重要,下面会提到,再回到之前的get方法
public RequestManager get(FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();
return supportFragmentGet(activity, fm);
}
}如果在主线程中调用get方法,则会通过获取传入activity的FragmentManager,并将其传入到supportFragmentGet(activity, fm);方法中
RequestManager supportFragmentGet(Context context, FragmentManager fm) {
SupportRequestManagerFragment current = getSupportRequestManagerFragment(fm);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
requestManager = new RequestManager(context, current.getLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode());
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}首先是调用getSupportRequestManagerFragment方法获取一个SupportRequestManagerFragment,SupportRequestManagerFragment 是一个无界面的Fragment类,起到把请求和Activity生命周期同步的作用。
SupportRequestManagerFragment getSupportRequestManagerFragment(final FragmentManager fm) {
SupportRequestManagerFragment current = (SupportRequestManagerFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(
FRAGMENT_TAG);
if (current == null) {
current = pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.get(fm);
if (current == null) {
current = new SupportRequestManagerFragment();
pendingSupportRequestManagerFragments.put(fm, current);
fm.beginTransaction().add(current, FRAGMENT_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();
handler.obtainMessage(ID_REMOVE_SUPPORT_FRAGMENT_MANAGER, fm).sendToTarget();
}
}
return current;
}可以看到 getSupportRequestManagerFragment中,会先去判断传入的FragmentManager 中是否已经绑定了这个SupportRequestManagerFragment ,没有就将其创建,并添加到FragmentManager 中
我们可以看到SupportRequestManagerFragment 中,生命周期的方法,都会同步调用lifecycle的相应方法
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
lifecycle.onStart();
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
lifecycle.onStop();
}
而这个lifecycle就是ActivityFragmentLifecycle,它将用了观察者模式,可以发现addListener就是添加观察者,然后每一个生命周期方法,同步通知给每一个listener
@Override
public void addListener(LifecycleListener listener) {
lifecycleListeners.add(listener);
if (isDestroyed) {
listener.onDestroy();
} else if (isStarted) {
listener.onStart();
} else {
listener.onStop();
}
}
void onStart() {
isStarted = true;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onStart();
}
}
回到supportFragmentGet方法中
RequestManager supportFragmentGet(Context context, FragmentManager fm) {
SupportRequestManagerFragment current = getSupportRequestManagerFragment(fm);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
requestManager = new RequestManager(context, current.getLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode());
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}接下来就是获取SupportRequestManagerFragment 中的RequestManager,判断其是否存在,不在则进行创建,然后和SupportRequestManagerFragment 进行绑定,这里需要强调的是,构建RequestManager时,将SupportRequestManagerFragment 的lifecycle传入,我们看看RequestManager的构造函数里面
RequestManager(Context context, final Lifecycle lifecycle, RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode,
RequestTracker requestTracker, ConnectivityMonitorFactory factory) {
this.context = context.getApplicationContext();
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
this.treeNode = treeNode;
this.requestTracker = requestTracker;
this.glide = Glide.get(context);
this.optionsApplier = new OptionsApplier();
ConnectivityMonitor connectivityMonitor = factory.build(context,
new RequestManagerConnectivityListener(requestTracker));
// If we're the application level request manager, we may be created on a background thread. In that case we
// cannot risk synchronously pausing or resuming requests, so we hack around the issue by delaying adding
// ourselves as a lifecycle listener by posting to the main thread. This should be entirely safe.
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
lifecycle.addListener(RequestManager.this);
}
});
} else {
lifecycle.addListener(this);
}
lifecycle.addListener(connectivityMonitor);
}可以发现,lifecycle.addListener方法,将RequestManager自身添加到lifecycle中,这里的巧妙之处,在于,SupportRequestManagerFragment 的生命周期的方法,都会同步通知lifecycle的所有Listener,所以SupportRequestManagerFragment 的生命周期都可同步通知RequestManager,这就是glide的巧妙之处。
上面还做了判断,如果这个RequestManager是application级别的,将其post到主线程中,再调用 lifecycle.addListener(RequestManager.this);方法,保证生命周期的同步效果
到这里,with方法的逻辑就执行完毕了,那么总结一下这个方法的作用,通过with方法中的参数不同,调用RequestManagerRetriever的get方法,最终创建一个空的Fragment 名为SupportRequestManagerFragment 并绑定一个RequestManager
load方法
with方法返回的是一个RequestManager,那么load方法的逻辑显然就是在RequestManager中
public DrawableTypeRequest<String> load(String string) {
return (DrawableTypeRequest<String>) fromString().load(string);
}会先调用fromString再调用load方法
public DrawableTypeRequest fromString() {
return loadGeneric(String.class);
} private DrawableTypeRequest loadGeneric(Class modelClass) {
ModelLoader streamModelLoader = Glide.buildStreamModelLoader(modelClass, context);
ModelLoader fileDescriptorModelLoader =
Glide.buildFileDescriptorModelLoader(modelClass, context);
if (modelClass != null && streamModelLoader == null && fileDescriptorModelLoader == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown type " + modelClass + ". You must provide a Model of a type for"
+ " which there is a registered ModelLoader, if you are using a custom model, you must first call"
+ " Glide#register with a ModelLoaderFactory for your custom model class");
}
return optionsApplier.apply(
new DrawableTypeRequest(modelClass, streamModelLoader, fileDescriptorModelLoader, context,
glide, requestTracker, lifecycle, optionsApplier));
} loadGeneric方法中创建了两个ModelLoader,分别是streamModelLoader 和fileDescriptorModelLoader,然后通过他们构造了一个DrawableTypeRequest
其实就是通过工厂模式创建相应的类型的ModelLoader,我们以Glide.buildStreamModelLoader为例
public static ModelLoader buildStreamModelLoader(Class modelClass, Context context) {
return buildModelLoader(modelClass, InputStream.class, context);
} 这里传递了InputStream.class
public static <T, Y> ModelLoader<T, Y> buildModelLoader(Class<T> modelClass, Class<Y> resourceClass,
Context context) {
if (modelClass == null) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "Unable to load null model, setting placeholder only");
}
return null;
}
return Glide.get(context).getLoaderFactory().buildModelLoader(modelClass, resourceClass);
}通过Glide.get(context).getLoaderFactory()获取GenericLoaderFactory并调用其buildModelLoader创建InputStream.class对应的ModelLoader
public synchronized ModelLoader buildModelLoader(Class modelClass, Class resourceClass) {
ModelLoader result = getCachedLoader(modelClass, resourceClass);
if (result != null) {
// We've already tried to create a model loader and can't with the currently registered set of factories,
// but we can't use null to demonstrate that failure because model loaders that haven't been requested
// yet will be null in the cache. To avoid this, we use a special signal model loader.
if (NULL_MODEL_LOADER.equals(result)) {
return null;
} else {
return result;
}
}
final ModelLoaderFactory factory = getFactory(modelClass, resourceClass);
if (factory != null) {
result = factory.build(context, this);
cacheModelLoader(modelClass, resourceClass, result);
} else {
// We can't generate a model loader for the given arguments with the currently registered set of factories.
cacheNullLoader(modelClass, resourceClass);
}
return result;
} getCachedLoader方法判断InputStream.class对应的ModelLoader是否已经创建过,也就是是否存在内存缓存中,有则返回
然后调用了getFactory方法,根据InputStream.class,创建其对应的ModelLoaderFactory
private ModelLoaderFactory getFactory(Class modelClass, Class resourceClass) {
Map/*Y*/, ModelLoaderFactory/*T, Y*/> resourceToFactories = modelClassToResourceFactories.get(modelClass);
ModelLoaderFactory/*T, Y*/ result = null;
if (resourceToFactories != null) {
result = resourceToFactories.get(resourceClass);
}
if (result == null) {
for (Class registeredModelClass : modelClassToResourceFactories.keySet()) {
// This accounts for model subclasses, our map only works for exact matches. We should however still
// match a subclass of a model with a factory for a super class of that model if if there isn't a
// factory for that particular subclass. Uris are a great example of when this happens, most uris
// are actually subclasses for Uri, but we'd generally rather load them all with the same factory rather
// than trying to register for each subclass individually.
if (registeredModelClass.isAssignableFrom(modelClass)) {
Map/*Y*/, ModelLoaderFactory/*T, Y*/> currentResourceToFactories =
modelClassToResourceFactories.get(registeredModelClass);
if (currentResourceToFactories != null) {
result = currentResourceToFactories.get(resourceClass);
if (result != null) {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
} 可以发现ModelLoaderFactory是保存在一个叫resourceToFactories的Map 中,而这个Map又是存储在名叫modelClassToResourceFactories的Map 中
然后是调用ModelLoaderFactory的build方法创建ModelLoader,然后通过cacheModelLoader方法将ModelLoader进行缓存起来
private void cacheModelLoader(Class modelClass, Class resourceClass, ModelLoader modelLoader) {
Map/*Y*/, ModelLoader/*T, Y*/> resourceToLoaders = cachedModelLoaders.get(modelClass);
if (resourceToLoaders == null) {
resourceToLoaders = new HashMap/*Y*/, ModelLoader/*T, Y*/>();
cachedModelLoaders.put(modelClass, resourceToLoaders);
}
resourceToLoaders.put(resourceClass, modelLoader);
} fromString的流程就分析完毕,然后回到RequestManager的load方法
public DrawableTypeRequest<String> load(String string) {
return (DrawableTypeRequest<String>) fromString().load(string);
}
fromString返回DrawableTypeRequest,所以load方法在DrawableTypeRequest中
@Override
public DrawableRequestBuilder load(ModelType model) {
super.load(model);
return this;
} public GenericRequestBuilder load(ModelType model) {
this.model = model;
isModelSet = true;
return this;
} 只是对我们传进来的图片的uri进行赋值
Into方法
into方法是加载图片的发起点,其逻辑在DrawableRequestBuilder类中
public Target into(ImageView view) {
return super.into(view);
} 调用了GenericRequestBuilder的into方法
ublic Target into(ImageView view) {
Util.assertMainThread();
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must pass in a non null View");
}
if (!isTransformationSet && view.getScaleType() != null) {
switch (view.getScaleType()) {
case CENTER_CROP:
applyCenterCrop();
break;
case FIT_CENTER:
case FIT_START:
case FIT_END:
applyFitCenter();
break;
//$CASES-OMITTED$
default:
// Do nothing.
}
}
return into(glide.buildImageViewTarget(view, transcodeClass));
} 根据不同的ImageView 的ScaleType有不同的处理逻辑,applyCenterCrop()方法和 applyFitCenter()的实现都是在子类DrawableRequestBuilder中
public DrawableRequestBuilder fitCenter() {
return transform(glide.getDrawableFitCenter());
} 然后调用了transform方法
public DrawableRequestBuilder transform(Transformation... transformation) {
super.transform(transformation);
return this;
} public GenericRequestBuilder transform(
Transformation... transformations) {
isTransformationSet = true;
if (transformations.length == 1) {
transformation = transformations[0];
} else {
transformation = new MultiTransformation(transformations);
}
return this;
} 其实就是对GenericRequestBuilder中的transformation 进行赋值,而这个transformation 是通过glide.getDrawableFitCenter()方法进行赋值
GifBitmapWrapperTransformation getDrawableFitCenter() {
return drawableFitCenter;
}而这个drawableFitCenter是在Glide的构造函数中进行赋值的
bitmapFitCenter = new FitCenter(bitmapPool);
drawableFitCenter = new GifBitmapWrapperTransformation(bitmapPool, bitmapFitCenter);
FitCenter是BitmapTransformation的子类,BitmapTransformation 实现了Transformation
接下来看一下GifBitmapWrapperTransformation的创建过程
public GifBitmapWrapperTransformation(BitmapPool bitmapPool, Transformation bitmapTransformation) {
this(bitmapTransformation, new GifDrawableTransformation(bitmapTransformation, bitmapPool));
} 传入了FitCenter和BitmapPool (此类很重要,后面会讲解),里面又创建了GifDrawableTransformation来包裹这两个参数
GifBitmapWrapperTransformation(Transformation bitmapTransformation,
TransformationifDrawable> gifDataTransformation) {
this.bitmapTransformation = bitmapTransformation;
this.gifDataTransformation = gifDataTransformation;
} 然后调用了glide.buildImageViewTarget(view, transcodeClass)
<R> Target<R> buildImageViewTarget(ImageView imageView, Class<R> transcodedClass) {
return imageViewTargetFactory.buildTarget(imageView, transcodedClass);
}这里的transcodedClass传入的是 GlideDrawable
public Target buildTarget(ImageView view, Class clazz) {
if (GlideDrawable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (Target) new GlideDrawableImageViewTarget(view);
} else if (Bitmap.class.equals(clazz)) {
return (Target) new BitmapImageViewTarget(view);
} else if (Drawable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (Target) new DrawableImageViewTarget(view);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unhandled class: " + clazz
+ ", try .as*(Class).transcode(ResourceTranscoder)");
}
} 根据clazz的类型不同,构建不同的ImageViewTarget
public GlideDrawableImageViewTarget(ImageView view) {
this(view, GlideDrawable.LOOP_FOREVER);
}
public GlideDrawableImageViewTarget(ImageView view, int maxLoopCount) {
super(view);
this.maxLoopCount = maxLoopCount;
}
无论哪种类型的ImageViewTarget都调用了父类ImageViewTarget的构造方法
public ImageViewTarget(ImageView view) {
super(view);
}
public ViewTarget(T view) {
if (view == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("View must not be null!");
}
this.view = view;
sizeDeterminer = new SizeDeterminer(view);
}
public SizeDeterminer(View view) {
this.view = view;
}然后这个GlideDrawableImageViewTarget会被传入到into方法中
public > Y into(Y target) {
Util.assertMainThread();
if (target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must pass in a non null Target");
}
if (!isModelSet) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must first set a model (try #load())");
}
Request previous = target.getRequest();
if (previous != null) {
previous.clear();
requestTracker.removeRequest(previous);
previous.recycle();
}
Request request = buildRequest(target);
target.setRequest(request);
lifecycle.addListener(target);
requestTracker.runRequest(request);
return target;
} 判断之前针对这个imageView创建的GlideDrawableImageViewTarget是否已经创建了Request ,如果已经存在则进行清空,并从requestTracker中移除,如果之前从创建过,就首先调用buildRequest方法创建Request
private Request buildRequest(Target target) {
if (priority == null) {
priority = Priority.NORMAL;
}
return buildRequestRecursive(target, null);
} 这里有Request 优先级的设置
private Request obtainRequest(Target target, float sizeMultiplier, Priority priority,
RequestCoordinator requestCoordinator) {
return GenericRequest.obtain(
loadProvider,
model,
signature,
context,
priority,
target,
sizeMultiplier,
placeholderDrawable,
placeholderId,
errorPlaceholder,
errorId,
fallbackDrawable,
fallbackResource,
requestListener,
requestCoordinator,
glide.getEngine(),
transformation,
transcodeClass,
isCacheable,
animationFactory,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
diskCacheStrategy);
}
进入到obtain方法中
GenericRequest request = (GenericRequest) REQUEST_POOL.poll();
if (request == null) {
request = new GenericRequest();
}
request.init(loadProvider,
model,
signature,
context,
priority,
target,
sizeMultiplier,
placeholderDrawable,
placeholderResourceId,
errorDrawable,
errorResourceId,
fallbackDrawable,
fallbackResourceId,
requestListener,
requestCoordinator,
engine,
transformation,
transcodeClass,
isMemoryCacheable,
animationFactory,
overrideWidth,
overrideHeight,
diskCacheStrategy);
return request; 首先从REQUEST_POOL这个队列中拿出一个request,如果不存在,则新建一个,request的构造函数是空实现,其相关参数是在其init方法进行初始化的
{
this.loadProvider = loadProvider;
this.model = model;
this.signature = signature;
this.fallbackDrawable = fallbackDrawable;
this.fallbackResourceId = fallbackResourceId;
this.context = context.getApplicationContext();
this.priority = priority;
this.target = target;
this.sizeMultiplier = sizeMultiplier;
this.placeholderDrawable = placeholderDrawable;
this.placeholderResourceId = placeholderResourceId;
this.errorDrawable = errorDrawable;
this.errorResourceId = errorResourceId;
this.requestListener = requestListener;
this.requestCoordinator = requestCoordinator;
this.engine = engine;
this.transformation = transformation;
this.transcodeClass = transcodeClass;
this.isMemoryCacheable = isMemoryCacheable;
this.animationFactory = animationFactory;
this.overrideWidth = overrideWidth;
this.overrideHeight = overrideHeight;
this.diskCacheStrategy = diskCacheStrategy;
status = Status.PENDING;
// We allow null models by just setting an error drawable. Null models will always have empty providers, we
// simply skip our sanity checks in that unusual case.
if (model != null) {
check("ModelLoader", loadProvider.getModelLoader(), "try .using(ModelLoader)");
check("Transcoder", loadProvider.getTranscoder(), "try .as*(Class).transcode(ResourceTranscoder)");
check("Transformation", transformation, "try .transform(UnitTransformation.get())");
if (diskCacheStrategy.cacheSource()) {
check("SourceEncoder", loadProvider.getSourceEncoder(),
"try .sourceEncoder(Encoder) or .diskCacheStrategy(NONE/RESULT)");
} else {
check("SourceDecoder", loadProvider.getSourceDecoder(),
"try .decoder/.imageDecoder/.videoDecoder(ResourceDecoder) or .diskCacheStrategy(ALL/SOURCE)");
}
if (diskCacheStrategy.cacheSource() || diskCacheStrategy.cacheResult()) {
// TODO if(resourceClass.isAssignableFrom(InputStream.class) it is possible to wrap sourceDecoder
// and use it instead of cacheDecoder: new FileToStreamDecoder(sourceDecoder)
// in that case this shouldn't throw
check("CacheDecoder", loadProvider.getCacheDecoder(),
"try .cacheDecoder(ResouceDecoder) or .diskCacheStrategy(NONE)");
}
if (diskCacheStrategy.cacheResult()) {
check("Encoder", loadProvider.getEncoder(),
"try .encode(ResourceEncoder) or .diskCacheStrategy(NONE/SOURCE)");
}
}
} 对request进行赋值,然后各种check校验,根据DiskCacheStrategy中策略的不同,一共4种策略,默认DiskCacheStrategy的策略是RESULT
public enum DiskCacheStrategy {
/** Caches with both {@link #SOURCE} and {@link #RESULT}. */
ALL(true, true),
/** Saves no data to cache. */
NONE(false, false),
/** Saves just the original data to cache. */
SOURCE(true, false),
/** Saves the media item after all transformations to cache. */
RESULT(false, true);
private final boolean cacheSource;
private final boolean cacheResult;
DiskCacheStrategy(boolean cacheSource, boolean cacheResult) {
this.cacheSource = cacheSource;
this.cacheResult = cacheResult;
}
/**
* Returns true if this request should cache the original unmodified data.
*/
public boolean cacheSource() {
return cacheSource;
}
/**
* Returns true if this request should cache the final transformed result.
*/
public boolean cacheResult() {
return cacheResult;
}
}
回到GenericRequestBuilder 的into方法中
Request request = buildRequest(target);
target.setRequest(request);
lifecycle.addListener(target);
requestTracker.runRequest(request);将这个request 设置进GlideDrawableImageViewTarget中
public void setRequest(Request request) {
setTag(request);
}
private void setTag(Object tag) {
if (tagId == null) {
isTagUsedAtLeastOnce = true;
view.setTag(tag);
} else {
view.setTag(tagId, tag);
}
}其实就是将imageView和request 通过setTag方法进行绑定
然后将GlideDrawableImageViewTarget添加到lifecycle中,接着调用requestTracker.runRequest(request),执行这个request
public void runRequest(Request request) {
requests.add(request);
if (!isPaused) {
request.begin();
} else {
pendingRequests.add(request);
}
}首先将request添加到requests中
private final Set<Request> requests = Collections.newSetFromMap(new WeakHashMap<Request, Boolean>());然后执行request的begin方法
public void begin() {
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
if (model == null) {
onException(null);
return;
}
status = Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE;
if (Util.isValidDimensions(overrideWidth, overrideHeight)) {
onSizeReady(overrideWidth, overrideHeight);
} else {
target.getSize(this);
}
if (!isComplete() && !isFailed() && canNotifyStatusChanged()) {
target.onLoadStarted(getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logV("finished run method in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime));
}
}
onSizeReady方法中调用了Engine的load方法,首先创建了一个EngineKey
EngineKey key = keyFactory.buildKey(id, signature, width, height, loadProvider.getCacheDecoder(),
loadProvider.getSourceDecoder(), transformation, loadProvider.getEncoder(),
transcoder, loadProvider.getSourceEncoder());通过这个key去查找缓存是否存在
EngineResource cached = loadFromCache(key, isMemoryCacheable);
private EngineResource loadFromCache(Key key, boolean isMemoryCacheable) {
if (!isMemoryCacheable) {
return null;
}
EngineResource cached = getEngineResourceFromCache(key);
if (cached != null) {
cached.acquire();
activeResources.put(key, new ResourceWeakReference(key, cached, getReferenceQueue()));
}
return cached;
}通过getEngineResourceFromCache方法获取EngineResource
private EngineResource getEngineResourceFromCache(Key key) {
Resource cached = cache.remove(key);
final EngineResource result;
if (cached == null) {
result = null;
} else if (cached instanceof EngineResource) {
// Save an object allocation if we've cached an EngineResource (the typical case).
result = (EngineResource) cached;
} else {
result = new EngineResource(cached, true /*isCacheable*/);
}
return result;
}先从cache中寻找资源,如果找到则将其从cache中移除并放入activeResources中,,activeResources是一个Map
if (cached != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(cached);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from cache", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}
然后如果资源在缓存中找到后会放入cb.onResourceReady(cached)进行回调,cb是ResourceCallback
如果loadFromCache找不到则调用loadFromActiveResources
private EngineResource loadFromActiveResources(Key key, boolean isMemoryCacheable) {
if (!isMemoryCacheable) {
return null;
}
EngineResource active = null;
WeakReference> activeRef = activeResources.get(key);
if (activeRef != null) {
active = activeRef.get();
if (active != null) {
active.acquire();
} else {
activeResources.remove(key);
}
}
return active;
} 其实就是从activeResources中获取EngineResource,如果能获取到EngineResource,则放入cb.onResourceReady进行回调
EngineResource active = loadFromActiveResources(key, isMemoryCacheable);
if (active != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(active);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from active resources", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}cache是LruResourceCache对象,作为资源的LRU缓存;activeResources是以弱引用为值的Map,用于缓存使用中的资源。比一般内存缓存额外多一级缓存的意义在于,当内存不足时清理cache中的资源时,不会对使用中的Bitmap造成影响。
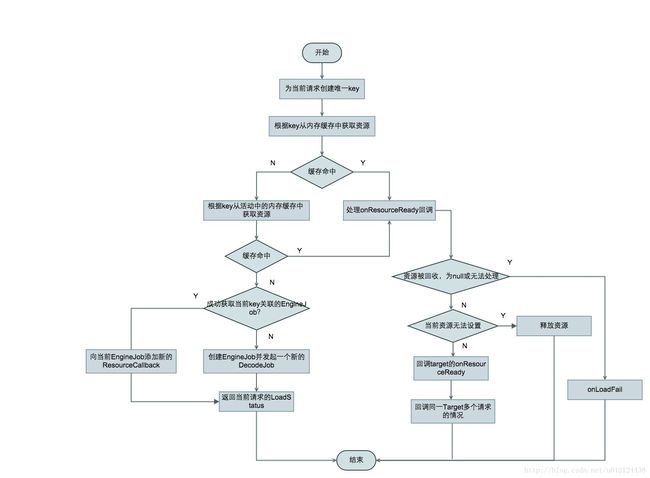
以上两个缓存中都找不到的话,就会从jobs通过key获取EngineJob,如果EngineJob存在的话,则用其构造LoadStatus进行返回
EngineJob current = jobs.get(key);
if (current != null) {
current.addCallback(cb);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Added to existing load", startTime, key);
}
return new LoadStatus(cb, current);
}
否则,则创建EngineJob对象并调用其start方法,同时也创建了DecodeJob,将EngineJob和DecodeJob构造一个EngineRunnable
EngineJob engineJob = engineJobFactory.build(key, isMemoryCacheable);
DecodeJob<T, Z, R> decodeJob = new DecodeJob<T, Z, R>(key, width, height, fetcher, loadProvider, transformation,
transcoder, diskCacheProvider, diskCacheStrategy, priority);
EngineRunnable runnable = new EngineRunnable(engineJob, decodeJob, priority);
jobs.put(key, engineJob);
engineJob.addCallback(cb);
engineJob.start(runnable);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Started new load", startTime, key);
}
return new LoadStatus(cb, engineJob);EngineJob的start方法执行EngineRunnable
public void start(EngineRunnable engineRunnable) {
this.engineRunnable = engineRunnable;
future = diskCacheService.submit(engineRunnable);
}diskCacheService的类型是ThreadPoolExecutor的子类FifoPriorityThreadPoolExecutor,也就是说将engineRunnable放入线程池中执行。
然后自然会执行到EngineRunnable的run方法
@Override
public void run() {
if (isCancelled) {
return;
}
Exception exception = null;
Resource> resource = null;
try {
resource = decode();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Exception decoding", e);
}
exception = e;
}
if (isCancelled) {
if (resource != null) {
resource.recycle();
}
return;
}
if (resource == null) {
onLoadFailed(exception);
} else {
onLoadComplete(resource);
}
}
在EngineRunnable的run方法中进行编码,执行decode方法
private Resource decode() throws Exception {
if (isDecodingFromCache()) {
return decodeFromCache();
} else {
return decodeFromSource();
}
}根据缓存策略调用decodeFromCache或者decodeFromSource
private Resource decodeFromSource() throws Exception {
return decodeJob.decodeFromSource();
}
先看decodeFromSource,调用DecodeJob的decodeFromSource方法。
public Resource decodeFromSource() throws Exception {
Resource decoded = decodeSource();
return transformEncodeAndTranscode(decoded);
} 先看decodeSource里面的逻辑
private Resource decodeSource() throws Exception {
Resource decoded = null;
try {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
final A data = fetcher.loadData(priority);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Fetched data", startTime);
}
if (isCancelled) {
return null;
}
decoded = decodeFromSourceData(data);
} finally {
fetcher.cleanup();
}
return decoded;
}
先通过DataFetcher访问网络获得文件流,接口DataFetcher的实现类根据配置而不同,我们看看HttpUrlFetcher的loadData方法的实现
@Override
public InputStream loadData(Priority priority) throws Exception {
return loadDataWithRedirects(glideUrl.toURL(), 0 /*redirects*/, null /*lastUrl*/, glideUrl.getHeaders());
}其实内部就是建立网络链接,获取InputStream
private InputStream loadDataWithRedirects(URL url, int redirects, URL lastUrl, Map headers)
throws IOException {
if (redirects >= MAXIMUM_REDIRECTS) {
throw new IOException("Too many (> " + MAXIMUM_REDIRECTS + ") redirects!");
} else {
// Comparing the URLs using .equals performs additional network I/O and is generally broken.
// See http://michaelscharf.blogspot.com/2006/11/javaneturlequals-and-hashcode-make.html.
try {
if (lastUrl != null && url.toURI().equals(lastUrl.toURI())) {
throw new IOException("In re-direct loop");
}
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
// Do nothing, this is best effort.
}
}
urlConnection = connectionFactory.build(url);
for (Map.Entry headerEntry : headers.entrySet()) {
urlConnection.addRequestProperty(headerEntry.getKey(), headerEntry.getValue());
}
urlConnection.setConnectTimeout(2500);
urlConnection.setReadTimeout(2500);
urlConnection.setUseCaches(false);
urlConnection.setDoInput(true);
// Connect explicitly to avoid errors in decoders if connection fails.
urlConnection.connect();
if (isCancelled) {
return null;
}
final int statusCode = urlConnection.getResponseCode();
if (statusCode / 100 == 2) {
return getStreamForSuccessfulRequest(urlConnection);
} else if (statusCode / 100 == 3) {
String redirectUrlString = urlConnection.getHeaderField("Location");
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(redirectUrlString)) {
throw new IOException("Received empty or null redirect url");
}
URL redirectUrl = new URL(url, redirectUrlString);
return loadDataWithRedirects(redirectUrl, redirects + 1, url, headers);
} else {
if (statusCode == -1) {
throw new IOException("Unable to retrieve response code from HttpUrlConnection.");
}
throw new IOException("Request failed " + statusCode + ": " + urlConnection.getResponseMessage());
}
}
之后会将InputStream 传入decodeFromSourceData方法中
private Resource<T> cacheAndDecodeSourceData(A data) throws IOException {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
SourceWriter<A> writer = new SourceWriter<A>(loadProvider.getSourceEncoder(), data);
diskCacheProvider.getDiskCache().put(resultKey.getOriginalKey(), writer);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Wrote source to cache", startTime);
}
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource<T> result = loadFromCache(resultKey.getOriginalKey());
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE) && result != null) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Decoded source from cache", startTime);
}
return result;
}先将SourceWriter放入diskCacheProvider的DiskCache中,然后调用loadFromCache
private Resource loadFromCache(Key key) throws IOException {
File cacheFile = diskCacheProvider.getDiskCache().get(key);
if (cacheFile == null) {
return null;
}
Resource result = null;
try {
result = loadProvider.getCacheDecoder().decode(cacheFile, width, height);
} finally {
if (result == null) {
diskCacheProvider.getDiskCache().delete(key);
}
}
return result;
} 根据需要将文件流写入磁盘缓存,再对文件流进行编码
public Resource decode(InputStream source, int width, int height) {
Bitmap bitmap = downsampler.decode(source, bitmapPool, width, height, decodeFormat);
return BitmapResource.obtain(bitmap, bitmapPool);
} ublic Bitmap decode(InputStream is, BitmapPool pool, int outWidth, int outHeight, DecodeFormat decodeFormat) {
final ByteArrayPool byteArrayPool = ByteArrayPool.get();
final byte[] bytesForOptions = byteArrayPool.getBytes();
final byte[] bytesForStream = byteArrayPool.getBytes();
final BitmapFactory.Options options = getDefaultOptions();
// Use to fix the mark limit to avoid allocating buffers that fit entire images.
RecyclableBufferedInputStream bufferedStream = new RecyclableBufferedInputStream(
is, bytesForStream);
// Use to retrieve exceptions thrown while reading.
// TODO(#126): when the framework no longer returns partially decoded Bitmaps or provides a way to determine
// if a Bitmap is partially decoded, consider removing.
ExceptionCatchingInputStream exceptionStream =
ExceptionCatchingInputStream.obtain(bufferedStream);
// Use to read data.
// Ensures that we can always reset after reading an image header so that we can still attempt to decode the
// full image even when the header decode fails and/or overflows our read buffer. See #283.
MarkEnforcingInputStream invalidatingStream = new MarkEnforcingInputStream(exceptionStream);
try {
exceptionStream.mark(MARK_POSITION);
int orientation = 0;
try {
orientation = new ImageHeaderParser(exceptionStream).getOrientation();
} catch (IOException e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.WARN)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Cannot determine the image orientation from header", e);
}
} finally {
try {
exceptionStream.reset();
} catch (IOException e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.WARN)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Cannot reset the input stream", e);
}
}
}
options.inTempStorage = bytesForOptions;
final int[] inDimens = getDimensions(invalidatingStream, bufferedStream, options);
final int inWidth = inDimens[0];
final int inHeight = inDimens[1];
final int degreesToRotate = TransformationUtils.getExifOrientationDegrees(orientation);
final int sampleSize = getRoundedSampleSize(degreesToRotate, inWidth, inHeight, outWidth, outHeight);
final Bitmap downsampled =
downsampleWithSize(invalidatingStream, bufferedStream, options, pool, inWidth, inHeight, sampleSize,
decodeFormat);
// BitmapFactory swallows exceptions during decodes and in some cases when inBitmap is non null, may catch
// and log a stack trace but still return a non null bitmap. To avoid displaying partially decoded bitmaps,
// we catch exceptions reading from the stream in our ExceptionCatchingInputStream and throw them here.
final Exception streamException = exceptionStream.getException();
if (streamException != null) {
throw new RuntimeException(streamException);
}
Bitmap rotated = null;
if (downsampled != null) {
rotated = TransformationUtils.rotateImageExif(downsampled, pool, orientation);
if (!downsampled.equals(rotated) && !pool.put(downsampled)) {
downsampled.recycle();
}
}
return rotated;
} finally {
byteArrayPool.releaseBytes(bytesForOptions);
byteArrayPool.releaseBytes(bytesForStream);
exceptionStream.release();
releaseOptions(options);
}
}编码过程中通过设置采样率缩放图片,降低内存占用,提高加载性能。
private Bitmap downsampleWithSize(MarkEnforcingInputStream is, RecyclableBufferedInputStream bufferedStream,
BitmapFactory.Options options, BitmapPool pool, int inWidth, int inHeight, int sampleSize,
DecodeFormat decodeFormat) {
// Prior to KitKat, the inBitmap size must exactly match the size of the bitmap we're decoding.
Bitmap.Config config = getConfig(is, decodeFormat);
options.inSampleSize = sampleSize;
options.inPreferredConfig = config;
if ((options.inSampleSize == 1 || Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT <= Build.VERSION.SDK_INT) && shouldUsePool(is)) {
int targetWidth = (int) Math.ceil(inWidth / (double) sampleSize);
int targetHeight = (int) Math.ceil(inHeight / (double) sampleSize);
// BitmapFactory will clear out the Bitmap before writing to it, so getDirty is safe.
setInBitmap(options, pool.getDirty(targetWidth, targetHeight, config));
}
return decodeStream(is, bufferedStream, options);
}
private static Bitmap decodeStream(MarkEnforcingInputStream is, RecyclableBufferedInputStream bufferedStream,
BitmapFactory.Options options) {
if (options.inJustDecodeBounds) {
// This is large, but jpeg headers are not size bounded so we need something large enough to minimize
// the possibility of not being able to fit enough of the header in the buffer to get the image size so
// that we don't fail to load images. The BufferedInputStream will create a new buffer of 2x the
// original size each time we use up the buffer space without passing the mark so this is a maximum
// bound on the buffer size, not a default. Most of the time we won't go past our pre-allocated 16kb.
is.mark(MARK_POSITION);
} else {
// Once we've read the image header, we no longer need to allow the buffer to expand in size. To avoid
// unnecessary allocations reading image data, we fix the mark limit so that it is no larger than our
// current buffer size here. See issue #225.
bufferedStream.fixMarkLimit();
}
final Bitmap result = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is, null, options);
try {
if (options.inJustDecodeBounds) {
is.reset();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.ERROR)) {
Log.e(TAG, "Exception loading inDecodeBounds=" + options.inJustDecodeBounds
+ " sample=" + options.inSampleSize, e);
}
}
return result;
}
这样返回的InpuStream就通过downsampleWithSize方法变为了Bitmap,如果设置了degreesToRotate(旋转的角度),就调用rotateImageExif设置
Bitmap rotated = null;
if (downsampled != null) {
rotated = TransformationUtils.rotateImageExif(downsampled, pool, orientation);
if (!downsampled.equals(rotated) && !pool.put(downsampled)) {
downsampled.recycle();
}
}public static Bitmap rotateImageExif(Bitmap toOrient, BitmapPool pool, int exifOrientation) {
final Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
initializeMatrixForRotation(exifOrientation, matrix);
if (matrix.isIdentity()) {
return toOrient;
}
// From Bitmap.createBitmap.
final RectF newRect = new RectF(0, 0, toOrient.getWidth(), toOrient.getHeight());
matrix.mapRect(newRect);
final int newWidth = Math.round(newRect.width());
final int newHeight = Math.round(newRect.height());
Bitmap.Config config = getSafeConfig(toOrient);
Bitmap result = pool.get(newWidth, newHeight, config);
if (result == null) {
result = Bitmap.createBitmap(newWidth, newHeight, config);
}
matrix.postTranslate(-newRect.left, -newRect.top);
final Canvas canvas = new Canvas(result);
final Paint paint = new Paint(PAINT_FLAGS);
canvas.drawBitmap(toOrient, matrix, paint);
return result;
}回到decodeFromSource方法
public Resource decodeFromSource() throws Exception {
Resource decoded = decodeSource();
return transformEncodeAndTranscode(decoded);
} private Resource<Z> transformEncodeAndTranscode(Resource<T> decoded) {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource<T> transformed = transform(decoded);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Transformed resource from source", startTime);
}
writeTransformedToCache(transformed);
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource<Z> result = transcode(transformed);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Transcoded transformed from source", startTime);
}
return result;
}
transform方法调用了Transformation的transform方法
private Resource transform(Resource decoded) {
if (decoded == null) {
return null;
}
Resource transformed = transformation.transform(decoded, width, height);
if (!decoded.equals(transformed)) {
decoded.recycle();
}
return transformed;
}
Transformation是接口;BitmapTransformation实现了该接口但留下了另一个抽象方法transform;CenterCrop和FitCenter两个类继承了BitmapTransformation并实现了抽象方法transform。
public final Resource transform(Resource resource, int outWidth, int outHeight) {
if (!Util.isValidDimensions(outWidth, outHeight)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot apply transformation on width: " + outWidth + " or height: "
+ outHeight + " less than or equal to zero and not Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL");
}
Bitmap toTransform = resource.get();
int targetWidth = outWidth == Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL ? toTransform.getWidth() : outWidth;
int targetHeight = outHeight == Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL ? toTransform.getHeight() : outHeight;
Bitmap transformed = transform(bitmapPool, toTransform, targetWidth, targetHeight);
final Resource result;
if (toTransform.equals(transformed)) {
result = resource;
} else {
result = BitmapResource.obtain(transformed, bitmapPool);
}
return result;
}
接下来看一下CenterCrop的transform方法
protected Bitmap transform(BitmapPool pool, Bitmap toTransform, int outWidth, int outHeight) {
final Bitmap toReuse = pool.get(outWidth, outHeight, toTransform.getConfig() != null
? toTransform.getConfig() : Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Bitmap transformed = TransformationUtils.centerCrop(toReuse, toTransform, outWidth, outHeight);
if (toReuse != null && toReuse != transformed && !pool.put(toReuse)) {
toReuse.recycle();
}
return transformed;
}由BitmapPool提供一个Bitmap作为下一步的Canvas载体。BitmapPool的实现类是LruBitmapPool,顾名思义是一个基于LRU方式的Bitmap缓存池,用于Bitmap的复用。
接下来是TransformationUtils的centerCrop方法
public static Bitmap centerCrop(Bitmap recycled, Bitmap toCrop, int width, int height) {
if (toCrop == null) {
return null;
} else if (toCrop.getWidth() == width && toCrop.getHeight() == height) {
return toCrop;
}
// From ImageView/Bitmap.createScaledBitmap.
final float scale;
float dx = 0, dy = 0;
Matrix m = new Matrix();
if (toCrop.getWidth() * height > width * toCrop.getHeight()) {
scale = (float) height / (float) toCrop.getHeight();
dx = (width - toCrop.getWidth() * scale) * 0.5f;
} else {
scale = (float) width / (float) toCrop.getWidth();
dy = (height - toCrop.getHeight() * scale) * 0.5f;
}
m.setScale(scale, scale);
m.postTranslate((int) (dx + 0.5f), (int) (dy + 0.5f));
final Bitmap result;
if (recycled != null) {
result = recycled;
} else {
result = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, getSafeConfig(toCrop));
}
// We don't add or remove alpha, so keep the alpha setting of the Bitmap we were given.
TransformationUtils.setAlpha(toCrop, result);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(result);
Paint paint = new Paint(PAINT_FLAGS);
canvas.drawBitmap(toCrop, m, paint);
return result;
}在TransformationUtils的centerCrop方法中,根据目标尺寸调整矩阵并绘制结果。
FitCenter类的逻辑与centerCrop类相似,回到DecodeJob的transformEncodeAndTranscode方法
接下来调用writeTransformedToCache将转换结果写入磁盘缓存,
private void writeTransformedToCache(Resource transformed) {
if (transformed == null || !diskCacheStrategy.cacheResult()) {
return;
}
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
SourceWriter> writer = new SourceWriter>(loadProvider.getEncoder(), transformed);
diskCacheProvider.getDiskCache().put(resultKey, writer);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Wrote transformed from source to cache", startTime);
}
} 再调用transcode方法进行转码
private Resource transcode(Resource transformed) {
if (transformed == null) {
return null;
}
return transcoder.transcode(transformed);
}
transcode方法中的transcoder的实际类型是GlideBitmapDrawableTranscoder
public Resource transcode(Resource toTranscode) {
GlideBitmapDrawable drawable = new GlideBitmapDrawable(resources, toTranscode.get());
return new GlideBitmapDrawableResource(drawable, bitmapPool);
} GlideBitmapDrawableTranscoder的transcode方法将Bitmap资源进行封装
public GlideBitmapDrawableResource(GlideBitmapDrawable drawable, BitmapPool bitmapPool) {
super(drawable);
this.bitmapPool = bitmapPool;
}到这里就结束了decodeFromSource的流程。
接下来看decodeFromCache
private Resource> decodeFromCache() throws Exception {
Resource> result = null;
try {
result = decodeJob.decodeResultFromCache();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "Exception decoding result from cache: " + e);
}
}
if (result == null) {
result = decodeJob.decodeSourceFromCache();
}
return result;
}先调用DecodeJob的decodeResultFromCache方法获取,获取失败则调用DecodeJob的decodeSourceFromCache方法
public Resource<Z> decodeResultFromCache() throws Exception {
if (!diskCacheStrategy.cacheResult()) {
return null;
}
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource<T> transformed = loadFromCache(resultKey);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Decoded transformed from cache", startTime);
}
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource<Z> result = transcode(transformed);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Transcoded transformed from cache", startTime);
}
return result;
}decodeResultFromCache方法从磁盘缓存中获取对应Bitmap并将其转码
public Resource decodeSourceFromCache() throws Exception {
if (!diskCacheStrategy.cacheSource()) {
return null;
}
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource decoded = loadFromCache(resultKey.getOriginalKey());
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Decoded source from cache", startTime);
}
return transformEncodeAndTranscode(decoded);
} decodeSourceFromCache方法从磁盘缓存中获取对应Bitmap并将其转换(因为是原尺寸,需要调整大小)
EngineRunnable的decode是decodeFromCache和decodeFromSource二选一,decodeFromCache也获取失败的话会怎么样呢?
public void run() {
if (isCancelled) {
return;
}
Exception exception = null;
Resource> resource = null;
try {
resource = decode();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Exception decoding", e);
}
exception = e;
}
if (isCancelled) {
if (resource != null) {
resource.recycle();
}
return;
}
if (resource == null) {
onLoadFailed(exception);
} else {
onLoadComplete(resource);
}
}缓存中没有结果的情况下会调用onLoadFailed方法
private void onLoadFailed(Exception e) {
if (isDecodingFromCache()) {
stage = Stage.SOURCE;
manager.submitForSource(this);
} else {
manager.onException(e);
}
}
public void submitForSource(EngineRunnable runnable) {
future = sourceService.submit(runnable);
}
变更缓存策略重新放入线程池中执行,也就是从网络获取。这里的线程池是sourceService而不是上面的diskCacheService,
得到了处理结果,接下来调用EngineRunnable的onLoadComplete方法将结果传入
private void onLoadComplete(Resource resource) {
manager.onResourceReady(resource);
}onLoadComplete方法调用了EngineJob的onResourceReady方法
public void onResourceReady(final Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
MAIN_THREAD_HANDLER.obtainMessage(MSG_COMPLETE, this).sendToTarget();
}private static class MainThreadCallback implements Handler.Callback {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message message) {
if (MSG_COMPLETE == message.what || MSG_EXCEPTION == message.what) {
EngineJob job = (EngineJob) message.obj;
if (MSG_COMPLETE == message.what) {
job.handleResultOnMainThread();
} else {
job.handleExceptionOnMainThread();
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
}关键在handleResultOnMainThread中
private void handleResultOnMainThread() {
if (isCancelled) {
resource.recycle();
return;
} else if (cbs.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Received a resource without any callbacks to notify");
}
engineResource = engineResourceFactory.build(resource, isCacheable);
hasResource = true;
// Hold on to resource for duration of request so we don't recycle it in the middle of notifying if it
// synchronously released by one of the callbacks.
engineResource.acquire();
listener.onEngineJobComplete(key, engineResource);
for (ResourceCallback cb : cbs) {
if (!isInIgnoredCallbacks(cb)) {
engineResource.acquire();
cb.onResourceReady(engineResource);
}
}
// Our request is complete, so we can release the resource.
engineResource.release();
}onResourceReady方法中向Handler传递消息并由MainThreadCallback处理消息 ,也就切换到了主线程。handleResultOnMainThread方法会调用GenericRequest的onResourceReady方法
public void onResourceReady(Resource resource) {
if (resource == null) {
onException(new Exception("Expected to receive a Resource with an object of " + transcodeClass
+ " inside, but instead got null."));
return;
}
Object received = resource.get();
if (received == null || !transcodeClass.isAssignableFrom(received.getClass())) {
releaseResource(resource);
onException(new Exception("Expected to receive an object of " + transcodeClass
+ " but instead got " + (received != null ? received.getClass() : "") + "{" + received + "}"
+ " inside Resource{" + resource + "}."
+ (received != null ? "" : " "
+ "To indicate failure return a null Resource object, "
+ "rather than a Resource object containing null data.")
));
return;
}
if (!canSetResource()) {
releaseResource(resource);
// We can't set the status to complete before asking canSetResource().
status = Status.COMPLETE;
return;
}
onResourceReady(resource, (R) received);
}private void onResourceReady(Resource resource, R result) {
// We must call isFirstReadyResource before setting status.
boolean isFirstResource = isFirstReadyResource();
status = Status.COMPLETE;
this.resource = resource;
if (requestListener == null || !requestListener.onResourceReady(result, model, target, loadedFromMemoryCache,
isFirstResource)) {
GlideAnimation animation = animationFactory.build(loadedFromMemoryCache, isFirstResource);
target.onResourceReady(result, animation);
}
notifyLoadSuccess();
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logV("Resource ready in " + LogTime.getElapsedMillis(startTime) + " size: "
+ (resource.getSize() * TO_MEGABYTE) + " fromCache: " + loadedFromMemoryCache);
}
}
onResourceReady方法调用GlideDrawableImageViewTarget的onResourceReady方法
public void onResourceReady(GlideDrawable resource, GlideAnimationsuper GlideDrawable> animation) {
if (!resource.isAnimated()) {
//TODO: Try to generalize this to other sizes/shapes.
// This is a dirty hack that tries to make loading square thumbnails and then square full images less costly
// by forcing both the smaller thumb and the larger version to have exactly the same intrinsic dimensions.
// If a drawable is replaced in an ImageView by another drawable with different intrinsic dimensions,
// the ImageView requests a layout. Scrolling rapidly while replacing thumbs with larger images triggers
// lots of these calls and causes significant amounts of jank.
float viewRatio = view.getWidth() / (float) view.getHeight();
float drawableRatio = resource.getIntrinsicWidth() / (float) resource.getIntrinsicHeight();
if (Math.abs(viewRatio - 1f) <= SQUARE_RATIO_MARGIN
&& Math.abs(drawableRatio - 1f) <= SQUARE_RATIO_MARGIN) {
resource = new SquaringDrawable(resource, view.getWidth());
}
}
super.onResourceReady(resource, animation);
this.resource = resource;
resource.setLoopCount(maxLoopCount);
resource.start();
}GlideDrawableImageViewTarget的onResourceReady方法调用其父类ImageViewTarget的onResourceReady方法
public void onResourceReady(Z resource, GlideAnimationsuper Z> glideAnimation) {
if (glideAnimation == null || !glideAnimation.animate(resource, this)) {
setResource(resource);
}
}ImageViewTarget的onResourceReady方法中调用的抽象方法setResource在子类GlideDrawableImageViewTarget中实现,该方法中调用了ImageView的setImageDrawable方法设置图像。至此,整个加载流程就完成了。
protected void setResource(GlideDrawable resource) {
view.setImageDrawable(resource);
}