CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的应用场景
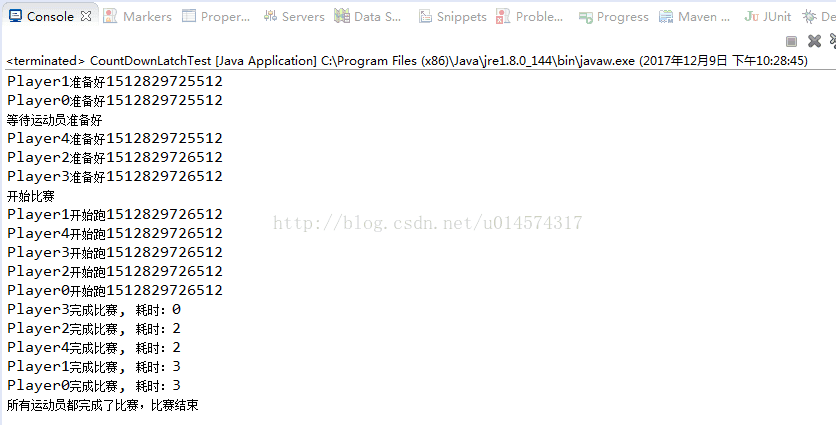
模拟运动员100米赛跑的场景。我们定义两个CountDownLatch对象,初始化为5,分别代表起跑前5个运动员准备就绪,定义一个CountDownLatch对象,初始化为1,代表裁判鸣枪之后,大家才能一起跑,另外一个CountDownLatch代表五个运动员均达到终点,比赛才结束,效果如截图所示。
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class CountDownLatchTest {
private static final int N = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
testCountDownLatch();
}
private static void testCountDownLatch() {
CountDownLatch latchStart = new CountDownLatch(N);
CountDownLatch latchOver = new CountDownLatch(N);
CountDownLatch startSignal = new CountDownLatch(1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
new Thread(new Player(i, latchStart, latchOver, startSignal)).start();
}
System.out.println("等待运动员准备好");
try {
latchStart.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("开始比赛");
startSignal.countDown();
try {
latchOver.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("所有运动员都完成了比赛,比赛结束");
}
}
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Player implements Runnable {
private CountDownLatch latchStart;
private CountDownLatch latchOver;
private CountDownLatch startSignal;
private int id;
private static Random sRandom = new Random();
public Player(int id, CountDownLatch latchStart, CountDownLatch lacthOver, CountDownLatch startSignal) {
this.id = id;
this.latchStart = latchStart;
this.latchOver = lacthOver;
this.startSignal = startSignal;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sRandom.nextInt(2));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Player" + id + "准备好" + System.currentTimeMillis());
this.latchStart.countDown();
try {
this.startSignal.await();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Player" + id + "开始跑" + System.currentTimeMillis());
long duration = sRandom.nextInt(5);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(duration);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Player" + id + "完成比赛, 耗时:" + duration);
this.latchOver.countDown();
}
}
我们定义两个CyclicBarrier对象,初始化为5,分别代表起跑前5个运动员准备就绪,因为CyclicBarrier是让所有线程达到同一个屏障,所以不像CountDownLatch里面要再统一起跑时间,另外一个CyclicBarrier代表五个运动员均达到终点,比赛才结束,效果如截图所示。
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
public class CyclicBarrierTest {
private static final int N = 5;
public static final void main(String[] args) {
testCyclicBarrier();
}
private static void testCyclicBarrier() {
CyclicBarrier barrierPrepare = new CyclicBarrier(N, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("所有运动员准备完毕,开始比赛");
}
});
CyclicBarrier barrierOver = new CyclicBarrier(N, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("所有运动员比赛都完成了,结束比赛");
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
new Thread(new Player(i, barrierPrepare, barrierOver)).start();
}
}
}
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Player implements Runnable {
private CyclicBarrier barrierPrepared;
private CyclicBarrier barrierOver;
private int id;
private static Random sRandom = new Random();
public Player(int id, CyclicBarrier barrierPrepared, CyclicBarrier barrierOver) {
this.barrierPrepared = barrierPrepared;
this.barrierOver = barrierOver;
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sRandom.nextInt(3));
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("运动员" + id + "准备比赛");
try {
barrierPrepared.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("远动员" + id + "开始比赛" + System.currentTimeMillis());
int duration = sRandom.nextInt(5);
try {
Thread.sleep(duration);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("运动员" + id + "完成比赛,比赛时长:" + duration);
try {
barrierOver.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}