spring源码(一) springmvc启动过程,springmvc初始化过程
spring mvc配置
我们知道要想使用springmvc,一般需要配置如下
web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener来加载spring根配置文件。
<web-app>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:application-context.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
web-app>再加一个spring的根配置文件application-context.xml,可以什么内容都不写。大家有没有想过ContextLoaderListener的作用是什么,具体做了什么?如果先思考一下,带着问题再去看源码,更有益处!
当然为了能正常接收请求,还需要配置DispatcherServlet及对应的mvc配置文件,这里暂不配置,以专注springmvc初始化。
分析
很明显ContextLoaderListener是入口,首先看类继承层次图(intellij idea快捷键 ctrl+alt+shift+u)

ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener,这个接口的contextInitialized方法会在容器初始化时被调用。
ContextLoaderListener.java
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}contextInitialized 方法很简单,调用了ContextLoader 的initWebApplicationContext
ContextLoader.java
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}首先看注释,这个方法就是为给定的servlet context初始化spring application context,spring application context有两个来源,要么是使用构造方法传入的,要么通过web.xml中context-param指定contextClass、contextConfigLocation新创建的 ,一句话概括,这个方法是用来初始化spring application context的。方法返回值是WebApplicationContext,类继承层次图
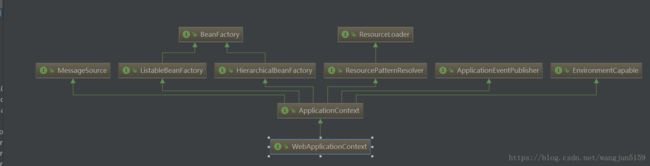
initWebApplicationContext()方法内部,首先判断ServletContext是否已经存在spring application context,如果存在则抛出错误。否则创建上下文this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);, 然后**配置并刷新**WebApplicationContextconfigureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext,然后将spring application context设置到servletcontext。简单来说
这里最重要的两个方法是createWebApplicationContext、configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext,坦白的说,createWebApplicationContext是创建了WebApplicationContext这个对象,在此基础上,configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext修改了WebApplicationContext的属性。
/**
* Instantiate the root WebApplicationContext for this loader, either the
* default context class or a custom context class if specified.
* This implementation expects custom contexts to implement the
* {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} interface.
* Can be overridden in subclasses.
*
In addition, {@link #customizeContext} gets called prior to refreshing the
* context, allowing subclasses to perform custom modifications to the context.
* @param sc current servlet context
* @return the root WebApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}看方法注释,使用默认的context class或者 自定义的context class实例化root webapplicationcontext。如果是自定义context class,那么它要实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口。
看代码,通过determineContextClass()返回context class,如果不是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,则抛出异常,也就是说,这个方法只能返回ConfigurableWebApplicationContext类型的ApplicaContext,为了一窥究竟,我们看determineContextClass()
protected Class determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}web.xml中没有配置context_class_param,所以只能是contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName()); 返回context class,继续跟踪
defaultStrategies
ContextLoader.java
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}ContextLoader.properties
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContextdefaultStrategies返回的是XmlWebApplicationContext这是通过ContextLoader.properties指定的,通过查看类层次图,XmlWebApplicationContext是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的子类
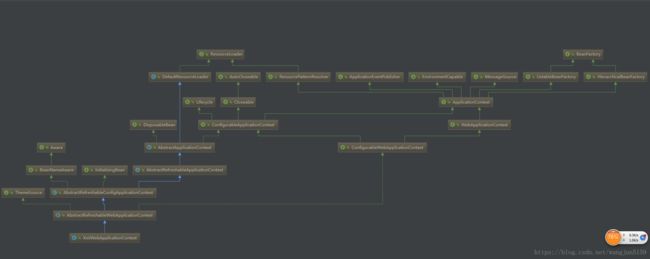
这里就清楚了,我们再继续看ContextLoader.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(),对ApplicationContext做了哪些修改。
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}代码里将contextConfigLocation设置到ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);初始化servlet context的property source,执行customizeContext()来执行自定义逻辑,最后执行refresh() 因为此时的wac是XmlWebApplicationContext,refresh()方法在父类AbstractApplicationContext中定义,所以执行AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
AbstractApplicationContext.java
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}大体上就是准备资源,然后创建BeanFactory、然后后处理BeanFactory(postProcessBeanFactory())、然后执行BeanFactory的后置处理器invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors、然后注册BeanPostProcessor……,这里不要犯迷糊,是先创建BeanFactory、然后执行BeanFactory的后置处理器,再注册BeanPostProcessor,然后在创建bean时,后置处理Bean。如果这个过程中失败,则确保已经创建的bean都毁灭。
总结
- spring mvc初始化,创建的ApplicationContext是
XmlWebApplicationContext,BeanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory,最重要的两个方法是createWebApplicationContext()、AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(),尤其是refresh()方法,下一步将此方法中的每个步骤搞明白。 - spring源码很优秀,整个springmvc初始化过程,逻辑很清晰;除此之外,在类层次结构设计上很庞大;
- 再说一点看源码的心得,看源码先大概流程,后细节,别一头扎进某个方法,看大概干了什么,梳理流程,然后再挖下去,这个过程中辅助类继承层次图(ctrl+alt+shift+u)至关重要,还有方法调用链使用ctrl+alt+h(intellij idea)也很实用。