集合TreeMap原理刨解JDK1.8(7)
HashMap对象没有顺序,TreeMap实现是排序平衡二叉树,大致是红黑树,树可以排序。根据根节点比较左小右大的特点,注意的是按键排序,值不排序。
对象只要实现comparable可以排序,重写compareTo(Object obj) 实现排序。类不能实现可以使用Compartor这个比较器必须实现compare(String o1, String o2)方法
构造方法
1.第一个默认TreeMap类,比较自定义对象要实现Comparabe接口比较器,重写compareTo方法
2.第二个比较TreeMap参数要接收Compartor比较器对象。重写Compartor接口中compare方法,比较灵活
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
TreeMap的简单使用,按键字母正排序,String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER实现比较器忽视大小写,像String内部有比较器。
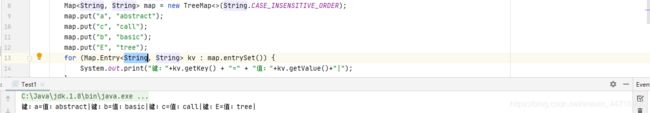
倒过来排序,实现Comparator比较器就可以,compare()返回int类型,方法参数o1是第一个对象,o2第二个对象交换对象。默认去重复,如果想不去重复,比较器可以改
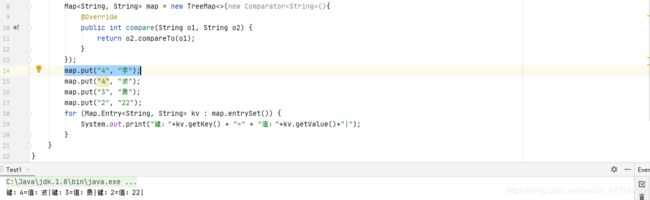
更简单的用法,调用Collections静态方法排序
//正序
Map<String, String> map = new TreeMap<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
//倒序
// Map map = new TreeMap<>(
// Collections.reverseOrder(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER));
map.put("4", "李");
map.put("4", "波");
map.put("3", "勇");
map.put("2", "22");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> kv : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.print("键:"+kv.getKey() + "=" + "值:"+kv.getValue()+"|");
}
重写比较器按时间排序,不是字符串排序
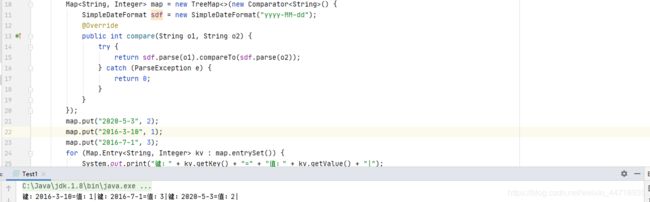
实现原理大致是
红黑树可看做平衡排序二叉树,
//比较器是构造方法传过来的,没传默认null
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//指向树的根节点,下面Entry
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* The number of structural modifications to the tree.
* 树的结构修改数
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
这静态内部类Entry由外部root对象引用。由根节点访问下面每一个节点Entry
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
//节点引用左边
Entry<K,V> left;
//节点引用右边
Entry<K,V> right;
//父节点
Entry<K,V> parent;
//节点颜色,默认根节点是黑色
boolean color = BLACK;
/**
* Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with
* {@code null} child links, and BLACK color.
*/
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
put()添加方法,首先添加前compare()检查key的类型和null。第一次添加判断是null创建Entry节点,指向root根节点
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
添加方法下面根据比较器comparator和Comparable来区分保存值,默认指向父节点,从父节点比较输入的key 和 引用key,小于根节点,将t节点设置左,大于根节点将t设置到右边。setValue()有重复的值,设置返回。循环结束t = null 。
//保存比较结果
int cmp;
//父节点
Entry<K,V> parent;
//比较器
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) { //实现比较器Comparator
do {
//开始t节点指向父节点
parent = t;
//从根节点比较键
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
//小于根节点,将t设置左边
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
//大于根节点,将t设置到右边
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
//比较有这个键返回设置值
return t.setValue(value);
//t null退出循环
} while (t != null);
}
else { //Comparable实现比较器
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
//compareTo比较
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//上面步骤找到父节点后,就是新建一个节点,k / v 根
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
//插入的值和根节点比较,要么是左节点要么是右节点
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//调整树的平衡
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
get()方法根据键获取值,通过p找到值value
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
containsValue()方法根据值获取通过for循环,找到返回true,valEquals比较里面是equals
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
if (valEquals(value, e.value))
return true;
return false;
}

remove()删除方法。底层deleteEntry()方法删除键,删除修改指向,给赋nul,l分为左和右以及根节点。
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p); //重要方法
return oldValue;
}