一、背景
公司业务某些页面加载很慢,简单通过日志并不能确认到底是哪些接口慢导致的,最近又在研究influxdb,于是计划通过influxdb+telegraf+grafana实现一套nginx监控,用来分析接口的耗时。
二、安装
我的开发机是centos7,以下安装命令都是在centos上的操作,其他操作系统请参考官方文档。
2.1、influxdb
wget https://dl.influxdata.com/influxdb/releases/influxdb-1.8.0.x86_64.rpm sudo yum localinstall influxdb-1.8.0.x86_64.rpm sudo systemctl start influxdb
这里因为我们只是测试验证,所以使用默认配置即可,如果现网环境,还是建议至少设置用户、密码等信息,默认influxdb的配置文件在/etc/influxdb/infludb.conf。
安装启动之后,可以直接在终端输入influx来尝试登陆下看看。
2.2、telegraf
wget https://dl.influxdata.com/telegraf/releases/telegraf-1.14.1-1.x86_64.rpm sudo yum localinstall telegraf-1.14.1-1.x86_64.rpm sudo systemctl start telegraf
这里telegraf也先使用默认的配置启动起来,后续配置在下一节详细讨论。
2.3、grafana
1 wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana-6.7.2-1.x86_64.rpm 2 sudo yum localinstall grafana-6.7.2-1.x86_64.rpm 3 sudo systemctl start grafana-server
grafana也是使用默认的配置,启动之后就可以通过http://your-ip:3000来访问grafana了。
三、配置
3.1、nginx log_format配置
本次监控的思路是通过telegraf抓取nginx的日志,并将信息导入到influxdb中,然后通过grafana将耗时数据展示出来,所以第一步我们需要先配置nginx的日志,以下是我使用的log_format:
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" $http_x_forwarded_for $host ' '"$upstream_addr" $upstream_status $request_time ' '$upstream_response_time "$cookie_uin" "$cookie_luin" "$cookie_username"';
虽然其中许多对于这里的监控不是必须的,但是由于要和现网保持一致,所以如果要跟随这篇文档来配置监控的话,建议也使用这个配置,因为这个日志的配置还会影响到telegraf日志解析的配置,这个地方有点麻烦,所以建议使用同样的配置,避免遇到奇葩的问题,待整个流程跑通了之后,可以再去熟悉telegraf日志解析的格式,进而根据需要调整自己的log_format。
3.2、telegraf input插件配置
这里使用了logparser插件来抓取日志,并使用grok格式来解析日志,一下是配置文件:
1 # Stream and parse log file(s). 2 [[inputs.logparser]] 3 ## Log files to parse. 4 ## These accept standard unix glob matching rules, but with the addition of 5 ## ** as a "super asterisk". ie: 6 ## /var/log/**.log -> recursively find all .log files in /var/log 7 ## /var/log/*/*.log -> find all .log files with a parent dir in /var/log 8 ## /var/log/apache.log -> only tail the apache log file 9 files = ["/var/log/nginx/access.log"] 10 11 ## Read files that currently exist from the beginning. Files that are created 12 ## while telegraf is running (and that match the "files" globs) will always 13 ## be read from the beginning. 14 from_beginning = false 15 16 ## Method used to watch for file updates. Can be either "inotify" or "poll". 17 # watch_method = "inotify" 18 19 ## Parse logstash-style "grok" patterns: 20 [inputs.logparser.grok] 21 ## This is a list of patterns to check the given log file(s) for. 22 ## Note that adding patterns here increases processing time. The most 23 ## efficient configuration is to have one pattern per logparser. 24 ## Other common built-in patterns are: 25 ## %{COMMON_LOG_FORMAT} (plain apache & nginx access logs) 26 ## %{COMBINED_LOG_FORMAT} (access logs + referrer & agent) 27 # patterns = ["%{COMMON_LOG_FORMAT}"] 28 patterns = ["%{NGINX_ACCESS_LOG}"] 29 30 ## Name of the outputted measurement name. 31 measurement = "nginx_access_log" 32 33 ## Full path(s) to custom pattern files. 34 custom_pattern_files = [] 35 36 ## Custom patterns can also be defined here. Put one pattern per line. 37 custom_patterns = ''' 38 NGINX_ACCESS_LOG %{IP:remote_addr} - (-|%{WORD:remote_user}) \[%{HTTPDATE:time_local}\] %{QS:request} %{NUMBER:status:int} %{NUMBER:body_bytes_sent:int} %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent} %{IPORHOST:xforwardedfor} %{IPORHOST:host} %{QS:upstream_addr} (-|%{NUMBER:upstream_status:int}) %{BASE10NUM:request_time:float} (-|%{BASE10NUM:upstream_response_time:float}) %{QS:cookie_uin} %{QS:cookie_luin} 39 ''' 40 41 ## Timezone allows you to provide an override for timestamps that 42 ## don't already include an offset 43 ## e.g. 04/06/2016 12:41:45 data one two 5.43µs 44 ## 45 ## Default: "" which renders UTC 46 ## Options are as follows: 47 ## 1. Local -- interpret based on machine localtime 48 ## 2. "Canada/Eastern" -- Unix TZ values like those found in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones 49 ## 3. UTC -- or blank/unspecified, will return timestamp in UTC 50 # timezone = "Canada/Eastern" 51 52 ## When set to "disable", timestamp will not incremented if there is a 53 ## duplicate. 54 # unique_timestamp = "auto"
其中最核心的地方是NGINX_ACCESS_LOG的配置,它决定了如何去解析nginx的日志,这里使用到了grok的语法,更多关于grok的信息见参考资料。
修改之后记得使用systemctl restart telegraf命令使改动生效。
3.3、grafana的配置
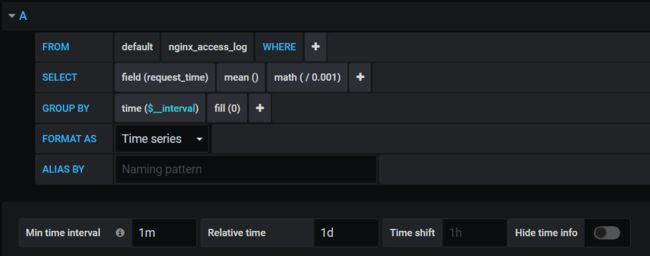
grafana需要先配置influxdb数据源,具体操作可以看下grafana的文档,这里说一下如何配置从influxdb查询数据并将数据展示出来,这里主要用到了日志中解析出来的request_time。
四、效果
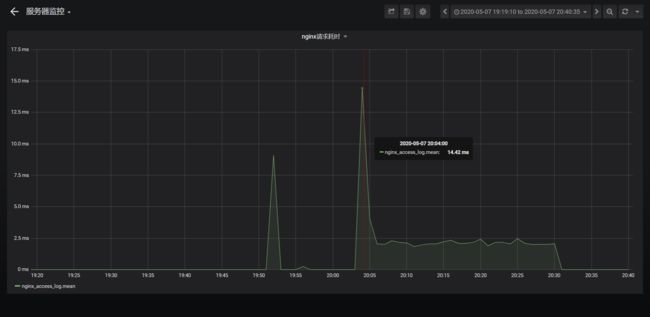
这里可以看到,很清晰明了的把nginx的调用耗时展示了出来,但是到这里并没有结束,因为并没有达到我们的目的:定位哪些接口查询较慢,目前仅仅实现了一个全局的视图,能够知道目前有没有接口很慢,但是不知道哪个接口慢(除非直接查influxdb),我思考了一下,这是因为其实grafana只是用来展示metric的,metric更多的是关注统计,而哪个接口慢更多的是需要关注个体,这里是grafana很难实现的(除非一个接口一个query,那配置起来就太麻烦了),所以要解决我们的问题其实是需要引入全链路追踪系统的,这个目前还在调研中,待部署上线了再写篇文章介绍一下全链路追踪。
五、参考资料
1、grok patterns:http://grokdebug.herokuapp.com/patterns#
2、grok debug:http://grokdebug.herokuapp.com/
3、telegraf文档:https://docs.influxdata.com/telegraf/v1.14/
4、grok input data format:https://docs.influxdata.com/telegraf/v1.14/data_formats/input/grok/