图像处理常用函数汇总篇(opencv、numpy)持续更新中~
0 目录
1 opencv
1.1 cv2.minAreaRect
1.2 cv2.boxPoints
2 numpy
2.1 np.random.randint()
1 Opencv 篇
1.1 cv2.minAreaRect
函数原型
cv2.minAreaRect(Points) 生成最小外接矩形
其中points是点集,数据类型为ndarray,array((x1,y1),(x2,y2),…,(xn,yn))
而minAreaRect就是求出在上述点集下的最小面积矩形
eg:
返回对象rect
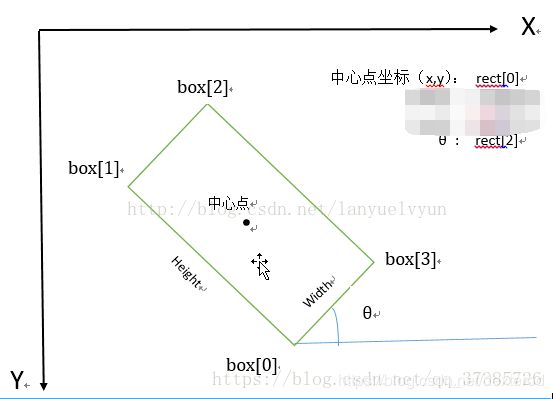
其中 rect(0) = 中心点坐标 (x_c, y_c) , rect(1) = 矩形宽高 (w, h), rect(2) = 角度 theta
实例
可以用作坐标变换(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4) -> (x_c, y_c, w, h, theta)
boxes = []
coordinate = np.array([[167., 203., 96., 132., 132., 96., 203., 167., 1.]])
for rect in coordinate:
box = np.int0(rect[:-1])
box = box.reshape([4, 2])
rect1 = cv2.minAreaRect(box)
print(rect1)
# rect1 = ((149.50001525878906, 149.50001525878906), (50.91169357299805, 100.40917205810547), -45.0)
1.2 cv2.boxPoints
根据minAreaRect的返回值,返回外接矩形的四个顶点坐标。
借用1.1.2的图,即返回box[0],box[1],box[2],box[3]四个点的坐标。
实例:
可以用作坐标变换(x_c, y_c, w, h, theta) -> (x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4)
boxes = []
coordinate = (x_c, y_c, w, h, theta)
for rect in coordinate:
box = cv2.boxPoints(((rect[0], rect[1]), (rect[2], rect[3]), rect[4]))
box = np.reshape(box, [-1, ])
boxes.append([box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3], box[4], box[5], box[6], box[7]])
2 Numpy 篇
2.1 np.random.randint( )
numpy.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype=‘l’)
low (inclusive) to high (exclusive)的随机整数。
如果默认high=None,则取[0, low)
low: 从分布中提取的最小的整数
high: 分布中提取的最大值
size: int or tuple of ints, optional
输出形态,例如(m,n,k),默认为None,表示给出单值
实例
np.random.randint(5, size=(2, 4))
array([[4, 0, 2, 1],
[3, 2, 2, 0]])
color = (np.random.randint(255), np.random.randint(255), np.random.randint(255))