【MATLAB】BP神经网络玩耍
【MATLAB】BP神经网络玩耍
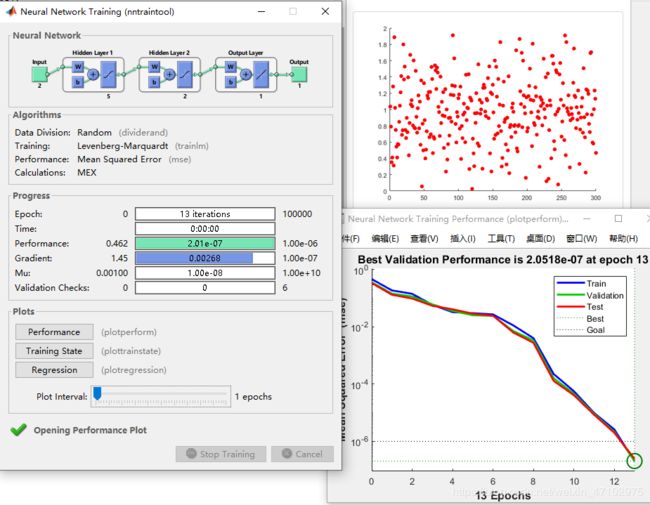
尝试训练一个简单的加法器
% 加法器
clear;
clc;
N = 300;
X=1:1:N;
Y1=zeros(2,N);
T = zeros(1,N);
for i = 1:N
Y1(:,i) = [rand , rand];
T(i) = Y1(1,i) + Y1(2,i) ;
%T(i) = rand;
end
net=newff(Y1,T,[5,2]);
net.trainParam.epochs=100000;
net.trainParam.goal=0.000001;
LP.lr=0.1;
net=train(net,Y1,T);%开始训练
% 创建测试集
for i = 1:N
Y1(:,i) = [rand , rand];
T(i) = Y1(1,i) + Y1(2,i) ;
%T(i) = rand;
end
Y2=sim(net,Y1);%获取实际输出
scatter(X,T,'fill');
hold on
scatter(X,Y2,'r','fill');
测试效果好
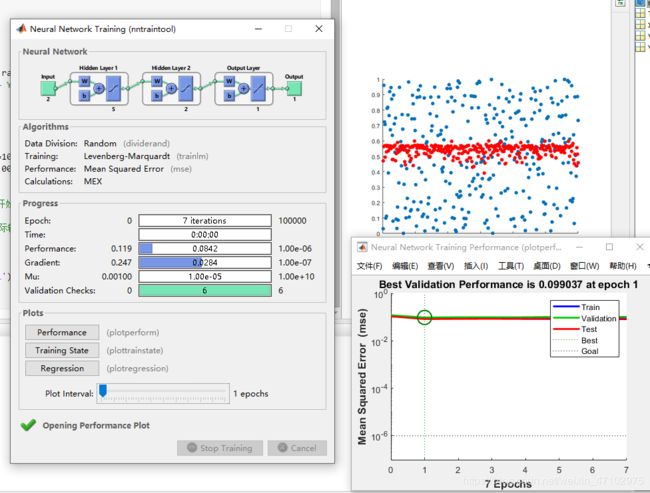
尝试诱骗神经网络
让训练集的输入和输出无关
% 骗子
clear;
clc;
N = 300;
X=1:1:N;
Y1=zeros(2,N);
T = zeros(1,N);
for i = 1:N
Y1(:,i) = [rand , rand];
% T(i) = Y1(1,i) + Y1(2,i) ;
T(i) = rand;
end
net=newff(Y1,T,[5,2]);
net.trainParam.epochs=100000;
net.trainParam.goal=0.000001;
LP.lr=0.1;
net=train(net,Y1,T);%开始训练
Y2=sim(net,Y1);% 这里换做训练集获取实际输出
scatter(X,T,'fill');
hold on
scatter(X,Y2,'r','fill');发现骗子数据无法进行学习。或许这体现了该算法的一定“智能”。
尝试手写数字识别
数据的来源与读取
这里使用经典的 MNIST 数据集:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
参照 https://blog.csdn.net/u010936286/article/details/80667138 读取数据
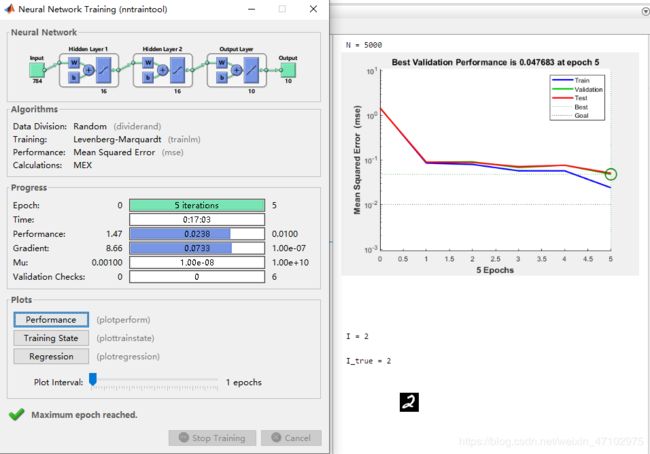
训练
因为电脑性能限制,故只选取少量数据进行训练。
参照 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1bx411M7Zx 选取16 16的隐含层
clear;
clc;
load('test_x.mat')
load('train_y.mat')
test_x = test_x';
train_y = train_y';
net=newff(test_x,train_y,[16,16]);
net.trainParam.epochs=100;
net.trainParam.goal=0.01;
LP.lr=0.1;
N = 5000 % 使用数据集的个数,最大60000
net=train(net,test_x(:,1:N),train_y(:,1:N));%开始训练检验
通过画图的形式简单地探索影响准确性的因素
s = 28291; % 0~60000随便选
t = test_x(:,s);
Y=sim(net,t);%获取实际输出
[~,I] = max(Y,[],1);
I = I-1
[~,I_true] = max(train_y(:,s),[],1);
I_true = I_true - 1
% 画图
s_image = zeros(28,28);
for i = 1:28
s_image(i,:) = t((i-1)*28+1:i*28);
end
imshow(s_image,[0,255])
- 识别正确的一个例子:
- 识别错误的一个例子: