Js全栈开发之koa2中间件分离与数据层搭建
koa2中间件分离与数据层搭建
接着上一篇《Js全栈开发之koa2视图层搭建》来继续学习koa2,上一篇着重汇总讲解了使用模板和静态包拆分出视图层的一些具体步骤,而没有讲解模型层,本篇将总结数据库的访问及模型层的搭建,以及从koa2项目中拆分出中间件的具体步骤。这里的模型层采用的ORM框架是Sequelize,数据库为MySQL。
文章目录
- koa2中间件分离与数据层搭建
- 1. 提取中间件层
- 1.2 项目结构
- 1.3 midsend中间件
- 1.4 中间件层拆分
- 1.5 app.js入口处理
- 2. ORM框架Sequelize使用
- 2.1 npm安装Sequelize
- 2.2 orm数据层结构
- 2.3 dbConn.js数据库连接脚本
- 2.4 models/customer.js模型
- 2.5 syncTable.js数据同步脚本
- 2.6 api/customer.js数据操作方法
- 2.7 控制器层customer.js方法
- 2.8 路由层中间件
1. 提取中间件层
为方便维护,将中间件层从app.js入口文件中提取出来。新增middleware中间件目录,增加midsend发送json串的中间件。
1.2 项目结构
├── controller/
│ ├── home.js
├── service/
│ ├── home.js
├── middleware/
│ ├── midsend/
│ ├──── index.js
│ ├── index.js
├── views/
│ ├── common/
│ ├──── header.html
│ ├──── footer.html
│ ├──── layout.html
│ ├──── layout-home.html
│ ├── home/
│ ├──── index.html
│ ├──── login.html
│ ├──── success.html
├── public/
│ ├── home/
│ ├──── main.css
├── app.js
├── router.js
├── package.json
1.3 midsend中间件
index.js 将响应返回类型改为json格式的字符串,且将对象json序列化
module.exports = () => {
function render(json) {
this.set("Content-Type", "application/json")
this.body = JSON.stringify(json)
}
return async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.send = render.bind(ctx)
await next()
}
}
使用misend
await ctx.send({
status: 'success',
data:[
{
name : 'dahlin',
age:'18'
},{
name : 'leon',
age:'22'
}
,{
name : 'ada',
age:'16'
}
]
})
1.4 中间件层拆分
index.js 将中间件引入的部分代码从app.js中拆分出来
const path = require('path')
const bodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser')
const nunjucks = require('koa-nunjucks-2')
const staticFiles = require('koa-static')
const miSend = require('./midsend')
module.exports = (app) => {
app.use(staticFiles(path.resolve(__dirname, "../public")))
app.use(nunjucks({
ext: 'html',
path: path.join(__dirname, '../views'),
nunjucksConfig: {
trimBlocks: true
}
}));
app.use(bodyParser())
app.use(miSend())
// 最后拦截异常信息
app.use(async (ctx,next) =>{
try {
await next();
} catch (ex) {
var jsonData={
status:-1,
message:ex.message
}
await ctx.send(jsonData);
}
})
}
1.5 app.js入口处理
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
const router = require('./router')
const middleware = require('./middleware')
middleware(app)
router(app)
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running at http://localhost:3000')
})
其他部分代码参见上一篇博文。
2. ORM框架Sequelize使用
使用安装Sequelize前,需要安装mysql驱动包和Sequelize框架
2.1 npm安装Sequelize
npm install mysql2 -save
npm install sequelize -save
2.2 orm数据层结构
增加db数据目录及子目录api和models。api目录里存放的是操作数据库的增删改查方法,models中存放的是数据库的表模型脚本,用于生成表同步表,同步数据库数据用。dbConn.js是数据库连接方法,syncTable.js是同步数据库脚本。
├── controller/
│ ├── home.js
│ ├── customer.js
├── db/
│ ├── api/
│ ├──── customer.js
│ ├── models/
│ ├──── customer.js
│ ├── dbConn.js
│ ├── syncTable.js
├── service/
│ ├── home.js
├── middleware/
│ ├── midsend/
│ ├──── index.js
│ ├── index.js
├── views/
│ ├── common/
│ ├──── header.html
│ ├──── footer.html
│ ├──── layout.html
│ ├──── layout-home.html
│ ├── home/
│ ├──── index.html
│ ├──── login.html
│ ├──── success.html
├── public/
│ ├── home/
│ ├──── main.css
├── app.js
├── router.js
├── package.json
2.3 dbConn.js数据库连接脚本
var Sequelize = require('sequelize');
// 数据库配置文件
var sqlConfig = {
host: "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx",
user: "root",
password: "xxxxx*",
database: "koa2learn"
};
var sequelize = new Sequelize(sqlConfig.database, sqlConfig.user, sqlConfig.password, {
host: sqlConfig.host,
dialect: 'mysql',
pool: {
max: 10,
min: 0,
idle: 10000
}
});
module.exports = sequelize;
2.4 models/customer.js模型
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
const sequenlizeObj = require('../dbConn.js');
const Customer = sequenlizeObj.define('customer',{
id:{
type: Sequelize.BIGINT(11),
primaryKey: true,
allowNull: false,
unique: true,
autoIncrement: true
},
name:{
type:Sequelize.STRING(20),
allowNull:false
},
sex:{
type: Sequelize.ENUM(['男','女']),
allowNull:false
},
address:{
type:Sequelize.STRING(50)
},
phone:{
type:Sequelize.STRING(20),
allowNull:true
},
email:{
type: Sequelize.STRING(20),
allowNull:false
},
country:{
type:Sequelize.STRING(20)
},
city:{
type:Sequelize.STRING(30)
}
},{
timestamps:false,
tableName: 'customer'
});
module.exports = Customer;
2.5 syncTable.js数据同步脚本
const sequenlizeConn = require('./dbConn.js');
var customer = require('./models/customer.js');
sequenlizeConn.authenticate().then(() => {
console.log('Connection has been established successfully.');
// 同步表结构
customer.sync({
force: true // 强制同步,先删除表,然后新建
}).then(()=>{
// 添加一条基础数据
return customer.create({
name:'dahlin',
sex:'男',
email:'[email protected]',
phone:'13588888888',
country: '中国',
city:"北京",
address:'卢沟桥'
});
});
})
.catch(err => {
console.error('Unable to connect to the database:', err);
});
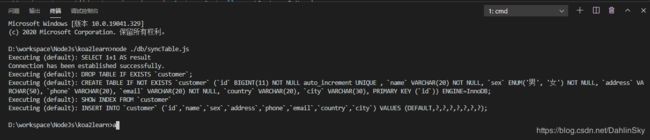
使用时需要在终端中执行node命令
node ./db/syncTable.js
2.6 api/customer.js数据操作方法
const Customer = require('../models/customer');
const { Op } = require('sequelize');
module.exports = {
getAllCustomers : async()=>{
return Customer.findAndCountAll({
attributes: ['id','name','sex','address','phone','email','country','city'],
order:[
['id', 'DESC']
]
});
},
getCustomerById : async(id)=>{
return Customer.findAll({
where: {
id: `${id}`
}
})
},
getCustomerByName: async(name)=>{
return Customer.findAll({
where: {
name: {
[Op.like]: `${name}`
}
}
})
},
updateCustomer: async(id,data)=> {
var item = await Customer.findAll({
where: {
id: `${id}`
}
});
if(item!=undefined){
return Customer.update(data, {where: {id: id}})
}else{
throw new Error('the customer is not exist!');
}
},
createCustomer: async(data)=>{
return Customer.create(data)
},
deleteCustomer: async(id)=>{
var item = await Customer.findAll({
where: {
id: `${id}`
}
});
if(item!=undefined){
return Customer.destroy({where: {id: id}})
}else{
throw new Error('the customer is not exist!');
}
}
}
2.7 控制器层customer.js方法
const customerModel = require('../db/api/customer');
module.exports = {
getAllCustomers: async(ctx, next) => {
const customerobjs = await customerModel.getAllCustomers();
var jsonData={
status:0,
data:customerobjs
}
await ctx.send(jsonData);
},
getCustomerById: async(ctx, next) => {
const customerobjs = await customerModel.getCustomerById(ctx.params.id);
var jsonData={
status:0,
data:customerobjs
}
await ctx.send(jsonData);
},
getCustomerByName: async(ctx, next) => {
const customerobjs = await customerModel.getCustomerByName(ctx.params.name);
var jsonData={
status:0,
data:customerobjs
}
await ctx.send(jsonData);
},
updateCustomer: async(ctx, next) => {
const customerobjs = await customerModel.updateCustomer(ctx.params.id,ctx.request.body)
var jsonData={
status:0,
data:customerobjs
}
ctx.send(jsonData);
},
createCustomer: async(ctx, next) => {
const customerobj =ctx.request.body;
const resultObj = await customerModel.createCustomer(customerobj);
var jsonData={
status:0,
data:resultObj
}
await ctx.send(jsonData);
},
deleteCustomer: async(ctx, next) => {
const customerobjs = await customerModel.deleteCustomer(ctx.params.id);
var jsonData={
status:0,
data:customerobjs
}
await ctx.send(jsonData);
}
}
2.8 路由层中间件
const router = require('koa-router')()
const HomeController = require('./controller/home')
const CustomerController = require('./controller/customer')
module.exports = (app) => {
// http://localhost:3000/customer/1
router.get('/customer/:id', CustomerController.getCustomerById)
// http://localhost:3000/customer/name/dahlin
router.get('/customer/name/:name', CustomerController.getCustomerByName)
// 增加数据方法
router.post('/customer', CustomerController.createCustomer)
// 修改数据方法
router.put('/customer/:id', CustomerController.updateCustomer)
// 删除数据方法
router.delete('/customer/:id', CustomerController.deleteCustomer)
app.use(router.routes())
.use(router.allowedMethods())
}
- 执行增加数据
- 执行查询所有数据
- 执行修改数据