LeetCode 300.最长上升子序列
这道题目就是在一个数组中找到最长的上升子序列,且元素之间不必相邻,题目如下所示:
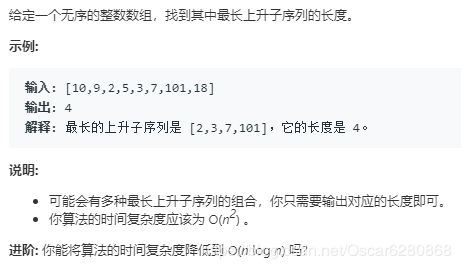
除了暴力解法,我们最优的解法还是用动态规划DP的方法来解答这个问题,那么解答的流程是怎么样的呢?我们来看下面这个流程图:
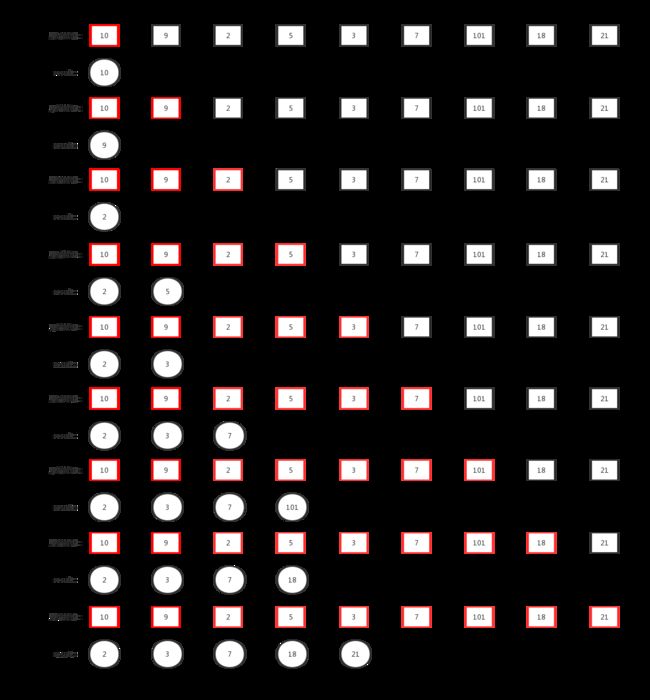
首先有一组 [ 10 , 9 , 2 , 5 , 3 , 7 , 101 , 18 , 21 ] [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18,21] [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18,21] 这样的一个数组,我们首先遍历这个数组,然后同时维护一个result数组:
- 把10放入result数组;
- 把9放入result数组,因为9比10小,那么9把10替换掉;
- 把2放入result数组,因为2比9小,那么2把9替换掉;
- 把5放入result数组,因为5大于2,那么把5放在2后面;
- 把3放入result数组,因为3小于5,那么3把5替换掉;
- 把7放入result数组,因为7大于3,那么把7放在3后面;
- 把101放入result数组,因为101大于7,那么把101放在7后面;
- 把18放入result数组,因为18小于101,那么18把101替换掉;
- 把21放入result数组,因为21大于18,那么21放在18后面;
- 遍历结束。
整个过程就如上所示,我们每一次将原始数组的元素拿到已排序的result结果数组中去, 然后将原始数组中的元素与result数组中的元素进行比较,如果比result数组中的元素小,那么就替换掉,如果比result数组中的元素大的话,那么就放在result数组后面,知道遍历结束。代码如下所示,其中 D P [ i ] DP[i] DP[i] 表示在第 i i i 个位置最长上升子序列的长度:
java:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0;
int res = 1;
int[] dp = new int[nums.length + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i){
dp[i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j){
if(nums[j] < nums[i]){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
python:
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
res = 1
if not nums:
return 0
dp = [1 for i in range(len(nums)+1)]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
for j in range(i):
if nums[j] < nums[i]:
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
return max(dp)
这就是用动态规划的思想来解决最长上升子序列的问题,代码中 D P [ i ] DP[i] DP[i] 就表示我们所维护的result数组,这样看来问题就比较容易解决了,希望能对大家对于动态规划的算法的理解有所提升,谢谢。