一、简介
Spring Boot简化了Spring应用的开发,采用约定大于配置的思想,去繁从简,很方便就能构建一个独立的、产品级别的应用。
1.传统J2EE开发的缺点
开发笨重、配置繁多复杂、开发效率低下、部署流程复杂、第三方技术集成难度大。
2.SpringBoot的优点
- 快速重建独立运行的Spring项目以及与主流框架集成。
- 使用嵌入式的Servlet容器,应用无需打成WAR包
- starters自动依赖与版本控制
- 大量的自动配置、简化开发,也可以修改其默认值
- 无需配置XML,无代码生成
- 准生产环境的运行时应用监控
- 与云计算的天然继承
3.SpringBoot helloworld说明
1.starters
- SpringBoot为我们提供了简化企业级开发绝大多数场景的starters pom(启动器),只要引入了相应场景的starters pom,相关技术的绝大部分配置将会消除(字段配置),从而简化我们的开发。业务中我们就会使用到SpringBoot为我们字段配置的Bean。
- 这些starters几乎涵盖了javaee所有常用场景,SpringBoot对这些场景依赖的jar也做了严格的测试和版本控制。
- spring-boot-dependencies里面定义了jar包的版本。
2.入口类和@SpringBootApplication
- 程序从main方法开始运行。
- 使用SpringApplication.run()加载主程序类
- 主程序类需标注@SpringBootApplication
- @EnableAutoConfiguration是核心注解
- @Import导入所有的自动配置场景
- @AutoConfigurationPackage定义默认的包扫描规则。
- 程序启动扫描主程序类所在的包以及下面所有子包的组件
3.自动配置
自动配置xxxAutoConfiguration
- SpringBoot中存现大量的这些类,这些类的作用就是帮我们进行自动装配
- 它会将这个场景需要的所有组件都注册到容器中,并配置好
- 他们在类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories文件中
- spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar中包含了所有场景的字段配置类代码
- 这些自动配置类是SpringBoot进行自动装配的关键。
二、SpringBoot配置
1.配置文件
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件。配置文件名是固定的。
-application.properties或者application.yml- 配置文件放在src/main/resources目录或者类路径/config下。
全局配置文件的作用是对一些默认配置进行修改
2.配置文件值注入
- @Value和@ConfigurationProperties为属性注入值进行对比
| 对比点 | @ConfigurationProperties | @Value |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件中的属性 | 一个个指定 |
| 松散绑定(松散语法) | 支持 | 不支持 |
| SpEL | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR303数据校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂类型封装 | 支持 | 不支持 |
属性名匹配规则
-person.firstName 使用标准方式
-person.first-name 使用-
-person.first_name 使用_
-PERSON_FIRST_NAME 推荐系统属性使用这种写法@PropertySource
加载指定的配置文件ConfigurationProperties
-与@Bean结合为属性赋值
-与@PropertySource(只能用于properties文件)结合读取指定文件。ConfigurationProperties Validation
-支持JSR303进行配置文件值校验。
@Component
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:person.properties"})
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person")
@Validated
public class Person{
@Email
@Value("${person.email}")
private String email;
}- ImportResource读取外部配置文件
3.配置文件占位符
RandomValuePropertySource
配置文件中可以使用随机数
-${random.value}
-${random.int}
-${random.long}
-${random.int(10)}
-${random.int[1024,65536]}- 属性配置占用符
-可以在配置文件中引用前面配置过的属性(Y优先级前面配置过的这里都可以使用)。
-${app.name:默认值}来指定找不到属性时的默认值。
app.name=MyApp
app.description=${app.name} is a SpringBoot Application4.profile
profile是Spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活指定参数的方式快速切换环境。
#### 1.多profile文件形式
格式:application-{profile}.properties/yml
application-dev.properties、application-prod.properties2.多profile文档块模式
spring.profiles.active=prod #激活指定配置
spring.profiles=prod
server.port=80
# default表示未指定时的默认配置
spring.profiles=default
server.port=8080
3.激活方式
- 命令行:--spring.profiles.active=dev
- 配置文件:spring.profiles.active=dev
- jvm参数:-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
5.配置文件加载位置
SpringBoot启动会扫描一下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为SpringBoot的默认配置文件。
- file:./config/
- file:./
- classpath:/config/
-classpath:/
-以上是按照优先级从高到低的顺序,所有位置的文件都会被加载,高优先级配置内容会覆盖低优先级配置内容。
-可以通过配置spring.config.location来改变默认配置。
6.外部配置加载顺序
- 命令行参数
- 来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
- Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
- 操作系统环境变量
- RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
- jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
- jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
- jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
- jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
- @Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource。
- 通过SpringApplication.setDefaultproperties指定的默认属性。
7.自动配置原理
1.SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能@EnableAutoConfiguration
2.@EnableAutoConfiguration作用
- 利用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件。
- 将类路径小META-INF/spring.factories里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中。
3.@Conditional派生注解
| @Conditional扩展注解 | 作用(判断是否满足当期指定条件) |
|---|---|
| @ConditionalOnJava | 系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 满足SpEL表达式指定 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 系统中有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass | 容器中没有指定类 |
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate | 容器中只有一个指定的Bean,或者这个Bean是首选Bean |
| @ConditionalOnProperty | 系统中指定的属性是否有指定的值 |
| @ConditionalOnResource | 类路径下是否存在指定资源文件 |
| @ConditionalOnWebApplication | 当前是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | 当前不是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnJndi | JNDI存在指定项 |
- 作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效。
三、SpringBoot与日志
1.日志框架
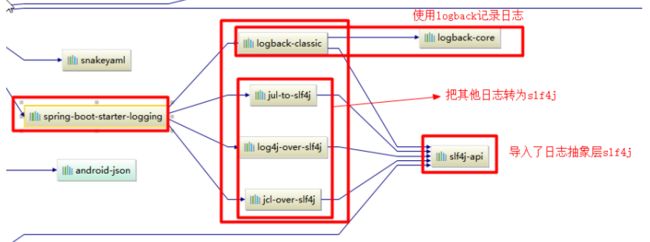
市场上存在非常多的日志框架,JUL(java.util.logging)、JCL(Apache Commons Logging)、Log4J、Log4J2、Logback、SLF4j、jboss-logging等。
- SpringBoot早框架内部使用JCL。spring-boot-starter-logging采用了slf4j+logback的形式,SpringBoot也能自动配置(jul、log4j2、logback)并简化配置。
| 日志门面 | 日志实现 |
|---|---|
| JCL、SLF4J、jboss-logging | log4j、JUL、Log4j2、Logback |
| 日志系统 | 配置文件 |
|---|---|
| Logback | logback-spring.xml、logback-spring.groovy、logback.xml或logback.groovy |
| Log4j2 | log4j2-spring.xml、log4j2.xml |
| JUL | logging.properties |
- 总结:
1.SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录。
2.SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j。
3.如果要引入其他日志框架,要排除Spring框架的commons-logging依赖。
四、Web开发
1.SpringBoot对静态资源的映射规则
- 所有/webjars/**,都去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 下面找资源。
- "/**" 访问当前项目的任何资源,都去(静态资源的文件夹)找映射。
- 欢迎页;静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面,被"/**" 映射。
- 所有的 **/favicon.ico都是在静态资源文件下找。
2.SpringMVC自动配置
1.SpringMVC auto-configuration
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的默认配置(WebMvcAutoConfiguration)如下:
- 包含了ContentNegotiatingViewResolver和BeanNameViewResolver。
- 自动配置了ViewResolver
- ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:组合所有的视图解析器
- 支持静态资源,包括支持Wenjars
- 静态首页访问
- 支持favicon.ico
- 自动注册了Converter、GenericConverter、Formatter。
- Converter:转换器。
- Formatter:格式化器- 支持HttpMessageConverters
- HttpMessageConverter:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应。
- HttpMessageConverters:从容器中确定,获取所有的HttpMessageConverter;
- HttpMessageConverter:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应。
- 自动注入MessageCodesResolver,定义错误码生成规则。
- 自动使用ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer。
2.扩展SpringMVC
编写一个配置类(@Configuration),是WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型,不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/desperado").setViewName("success");
}
}原理
- WebMvcAutoConfiguration是SpringMVC的自动配置类。
- 在做其他自动配置时会导入。
- 容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer都会一起被注册。
- 我们自定义的配置类也会被调用。
3.全面接管SpringMVC
如果想要使SpringMVC的自动配置失效,只需要在我们自定义的配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc注解即可。
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/desperado").setViewName("success");
}
}原理
- @EnableWebMvc的注解
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguation.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc{}- DelegatingWebMvcConfiguation
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguation extend WebMvcConfigurationSupport{}- WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class,DispatcherServlet.class,
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter.class})
//容器中没有这个组件,这个自动配置类才会生效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class})
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration{}- @EnableWebMvc会将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来。
- 导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能。
4.修改默认配置
- SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,显卡容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean 、@Component),如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才会进行自动配置;如果某些组件可以有多个,将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来。
- 在SpringBoot中有许多的xxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置
- 在SpringBoot中有许多的xxxCustomizer帮助我们进行定制配置
5.默认访问首页
使用自定义WebMvcConfigurationAdapter进行配置
//使用WebMvcConfigurationAdapter可以扩展SpringMVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
//浏览器发送/desperado 请求来到success
registry.addViewController("/desperado").setViewName("success");
}
//所有的webMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起起作用
@Bean //将组件注册到容器
public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
//配置默认路径的页面
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login");
}
};
return adapter;
}
}6.国际化
1.编写国际化配置文件
编写不同语言的配置文件,比如login.properties、login_en_US.properties、login_zh_CN.properties等。
- SpringBoot自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件。
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
private static final Resource[] NO_RESOURCES = new Resource[0];
public MessageSourceAutoConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.messages"
)
public MessageSourceProperties messageSourceProperties() {
return new MessageSourceProperties();
}
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource(MessageSourceProperties properties) {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getBasename())) {
//设置国际化资源文件的基础名(去掉语言国家代码)
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(properties.getBasename())));
}
if (properties.getEncoding() != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(properties.getEncoding().name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(properties.isFallbackToSystemLocale());
Duration cacheDuration = properties.getCacheDuration();
if (cacheDuration != null) {
messageSource.setCacheMillis(cacheDuration.toMillis());
}
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(properties.isAlwaysUseMessageFormat());
messageSource.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(properties.isUseCodeAsDefaultMessage());
return messageSource;
}原理
根据请求头带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国际化。
五、错误处理机制
1.默认的错误处理机制
- 浏览器,默认返回一个默认的错误页面。
- 其他客户端,默认响应一个json数据。
原理
- 在DefaultErrorAttributes中获取错误页面的信息
public class DefaultErrorAttributes implements ErrorAttributes {
//获取错误页面的信息
public Map getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
errorAttributes.put("path", request.path());
Throwable error = this.getError(request);
HttpStatus errorStatus = this.determineHttpStatus(error);
errorAttributes.put("status", errorStatus.value());
errorAttributes.put("error", errorStatus.getReasonPhrase());
errorAttributes.put("message", this.determineMessage(error));
this.handleException(errorAttributes, this.determineException(error), includeStackTrace);
return errorAttributes;
}
} - 在BasicErrorController中处理/error请求
@Controller
@RequestMapping({"${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}"})
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
//产生html类型的数据,浏览器发送的请求来打这个方法处理
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//去哪个页面作为错误页面。包含页面地址和页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
//产生json数据,其他客户端来到这个方法处理
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}
} - ErrorPageCustomizer进行错误配置
public class ErrorProperties {
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
private boolean includeException;
private ErrorProperties.IncludeStacktrace includeStacktrace;
private final ErrorProperties.Whitelabel whitelabel;
}- ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration生成错误页面
public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {
private static class StaticView implements View {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.StaticView.class);
private StaticView() {
}
public void render(Map model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
String message = this.getMessage(model);
logger.error(message);
} else {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
Date timestamp = (Date)model.get("timestamp");
Object message = model.get("message");
Object trace = model.get("trace");
if (response.getContentType() == null) {
response.setContentType(this.getContentType());
}
builder.append("Whitelabel Error Page
").append("This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
").append("").append(timestamp).append("").append("There was an unexpected error (type=").append(this.htmlEscape(model.get("error"))).append(", status=").append(this.htmlEscape(model.get("status"))).append(").");
if (message != null) {
builder.append("").append(this.htmlEscape(message)).append("");
}
if (trace != null) {
builder.append("").append(this.htmlEscape(trace)).append("");
}
builder.append("");
response.getWriter().append(builder.toString());
}
}
private String htmlEscape(Object input) {
return input != null ? HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(input.toString()) : null;
}
private String getMessage(Map model) {
Object path = model.get("path");
String message = "Cannot render error page for request [" + path + "]";
if (model.get("message") != null) {
message = message + " and exception [" + model.get("message") + "]";
}
message = message + " as the response has already been committed.";
message = message + " As a result, the response may have the wrong status code.";
return message;
}
public String getContentType() {
return "text/html";
}
}
5.DefaultErrorViewResolver解析页面
public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered {
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = this.resolve((String)SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map model) {
//默认去找一个页, error/404
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
//模板引擎可以解析这个页面地址就要模板引擎解析
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
//模板引擎可用的情况下返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址
//模板引擎不可以,就在静态资源文件夹下找对应的页面
return provider != null ? new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model) : this.resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
} 2.错误页面的优先级(自定义错误页面)
- 在模板引擎的情况下,error/状态码(将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的error文件夹下),发生此状态码的错误就会来到对应的页面;
- 没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到错误页面),就在静态资源文件夹下找。
- 以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面。
3.如何定制错误的json数据
- 自定义异常处理&返回定制json数据(没有自适应效果)
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
public Map handleException(Exception e){
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code","错误信息");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
return map;
}
} 2.转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理。
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
//传入我们自己的错误状态码,否则就不会进入定制错误页面的解析流程
request.setAttribute("java.servlet.error.status_code","500");
map.put("code","错误信息");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
//转发到/error
return "forward:/error";
}
} 4.将定制的数据发送出去
出现错误之后,回来到/error请求,会被BasicErrorController处理,响应出去可以获取的数据是由getErrorAttributes得到的。
- 编写一个ErrorController的实现类(或者是编写AbstractErrorController的子类),放到容器中。
- 页面上能用的数据,或者是json返回能用的数据都是通过errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes得到;容器中DefaultErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes()默认进行数据处理.
//给容器中加入自定义的ErrorAttributes
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
//获取ErrorAttributes的map
Map map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
//加入自己属性字段
map.put("name","desperado");
return map;
}
} 六、配置嵌入式Servlet容器
SpringBoot默认使用Tomcat作为内嵌的Servlet容器
1.修改Servlet容器的配置
在配置文件application文件中修改和server有关的配置。
server.port=8081
server.context_path=/crud
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=utf-82. 定制Servlet容器的相关配置
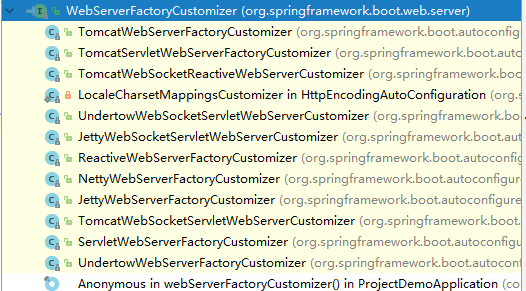
编写一个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer(2.x中使用WebServerFactoryCustomizer),来修改Servlet容器的配置。
@Bean
public WebServerFactoryCustomizer webServerFactoryCustomizer(){
return new WebServerFactoryCustomizer(){
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory factory) {
factory.setPort(8081);
}
};
} 3.注册Servlet三大组件
由于SpringBoot是默认以jar包的方式启动内嵌的Servlet容器来启动SpringBoot的web应用,没有web.xml文件。所以注册Servlet、Filter、Listener的方式也不同
1. 注入Servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean =
new ServletRegistrationBean<>(new MyServlet(), "/myServlet");
return registrationBean;
} 2. 注入Filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
registrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter());
registrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/hello","/myServlet"));
return registrationBean;
} 3. 注入Listener
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener(){
ServletListenerRegistrationBean registrationBean =
new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<>(new MyListener());
return registrationBean;
} 4.替换为其他嵌入式Servlet容器
替换为其他的Servlet非常简单,只需要在pom中引入其依赖,然后排除tomcat的依赖即可.
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jetty
5. 嵌入式Servlet容器自动配置原理
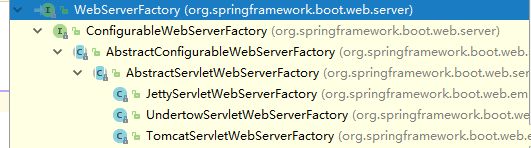
- EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration(2.x对应ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration):嵌入式容器的自动配置
@Configuration
class ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration {
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration() {
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ServletWebServerFactory.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
public static class EmbeddedUndertow {
public EmbeddedUndertow() {
}
@Bean
public UndertowServletWebServerFactory undertowServletWebServerFactory() {
return new UndertowServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class, WebAppContext.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ServletWebServerFactory.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
public static class EmbeddedJetty {
public EmbeddedJetty() {
}
@Bean
public JettyServletWebServerFactory JettyServletWebServerFactory() {
return new JettyServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
@Configuration
//判断当前是否引入了tomcat依赖
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class})
///判断当前容器没有用户自己定义ServletWebServerFactory:
//嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂;作用:创建嵌入式的Servlet容器
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ServletWebServerFactory.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
public static class EmbeddedTomcat {
public EmbeddedTomcat() {
}
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
}- 嵌入式Servlet容器工厂
- 嵌入式的Servlet容器
4.以tomcat为例
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory : this.createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
this.customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
this.configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
Iterator var5 = this.additionalTomcatConnectors.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
Connector additionalConnector = (Connector)var5.next();
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
this.prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return thisb.getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
- 容器中导入 WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
public class WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
//初始化之前
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//如果当前初始化的是一个WebServerFactory类型的组件
if (bean instanceof WebServerFactory) {
this.postProcessBeforeInitialization((WebServerFactory)bean);
}
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
private void postProcessBeforeInitialization(WebServerFactory webServerFactory) {
// 获取所有的定制器,调用每一个定制器的customize方法来给servlet容器进行属性赋值
((Callbacks)LambdaSafe.callbacks(WebServerFactoryCustomizer.class, this.getCustomizers(), webServerFactory, new Object[0]).withLogger(WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class)).invoke((customizer) -> {
customizer.customize(webServerFactory);
});
}
private Collection> getCustomizers() {
if (this.customizers == null) {
// 定制Servlet容器,给容器中可以添加一个WebServerFactoryCustomizer类型的组件
this.customizers = new ArrayList(this.getWebServerFactoryCustomizerBeans());
this.customizers.sort(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
this.customizers = Collections.unmodifiableList(this.customizers);
}
return this.customizers;
}
private Collection> getWebServerFactoryCustomizerBeans() {
//从容器中获取所有这个类型的组件:WebServerFactoryCustomizer
return this.beanFactory.getBeansOfType(WebServerFactoryCustomizer.class, false, false).values();
}
}
总结
- SpringBoot根据导入的依赖情况,给容器中添加相应的WebServerFactory【TomcatServletWebServerFactory】。
- 容器中某个组件要创建对象就会使用WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor后置处理器,只要是嵌入式的Servlet工厂,后置处理器就会进行处理。
- 后置处理器从容器中获取所有的WebServerFactoryCustomizer,调用定制器的定制方法
6.嵌入式Servlet容器启动过程
- SpringBoot启动运行run方法。
- 调用refreshContext(context);刷新IOC容器【创建IOC容器,并初始化容器,创建容器中的每一个组件】;如果是web应用创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,如果是reactive应用创建AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext,否则创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch(this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", var3);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}- 调用refresh(context);刷新上面创建好的IOC容器
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Object var1 = this.startupShutdownMonitor;
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//准备刷新的context
this.prepareRefresh();
//调用子类去刷新内部的实例工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//准备在这个context中要使用的实例工厂
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行后置处理。
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//在context中调用注册为bean的工厂处理器。
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册拦截bean创建的bean处理器。
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//初始化此context的消息源
this.initMessageSource();
//初始化此上下文的事件多播器。
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//在特定的context子类中初始化其他特殊bean。
this.onRefresh();
// 检查监听器bean并注册它们。
this.registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余(非延迟初始化)单例。
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//最后一步:发布相应的事件。
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
//摧毁已经创建的单例以避免占用资源。
this.destroyBeans();
//重置 ‘active’ 标志
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
//Propagate exception to caller.
throw var9;
} finally {
//从我们开始,重置Spring核心中的常见内省缓存
//可能不再需要单例bean的元数据了...
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}- 调用onRefresh();web的IOC容器重写了onRefresh方法。
- Web IOC容器创建嵌入式的Servlet容器。
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = this.getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
this.getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException var4) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", var4);
}
}
this.initPropertySources();
}获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂: ServletWebServerFactory factory = this.getWebServerFactory();从IOC容器中获取ServletWebServerFactory组件;
使用容器工厂获取嵌入式的Servlet容器:his.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory : this.createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
this.customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
this.configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
Iterator var5 = this.additionalTomcatConnectors.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
Connector additionalConnector = (Connector)var5.next();
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
this.prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return this.getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}- 嵌入式的Servlet容器创建并启动Servlet容器。
9.先启动嵌入式的Servlet容器,再将IOC容器中剩余的没有创建出来的对象获取出来、IOC容器启动就会创建嵌入式的Servlet容器。
7.使用外置的Servlet容器
1. 嵌入式Servlet容器优缺点
优点:简单、便捷。
缺点:默认不支持JSP,优化定制比较复杂。
2.使用外部Servlet容器步骤
- 必须创建一个war项目。
- 将嵌入式的Tomcat指定为provided。
org.springframework.boot
spring‐boot‐starter‐tomcat
provided
- 必须编写一个SpringBootServletInitializer的子类,并调用configure方法。
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
//传入SpringBoot应用的主程序
return application.sources(SpringBoot04WebJspApplication.class);
}
}
- 启动服务器就可以了。
3.原理与规则
原理
启动服务器,服务器启动SpringBoot应用[SpringBootServletInitializer],启动IOC容器。
规则
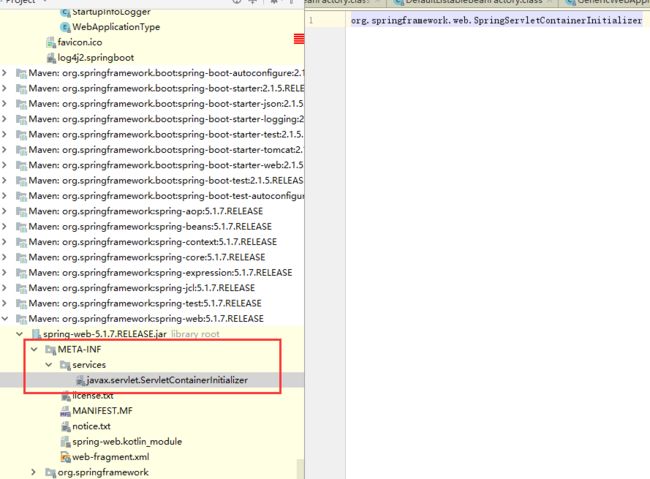
- 服务器启动会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包里面的ServletContainerInitializer实例。
- ServletContainerInitializer的实现放在jar包的META-INF/services文件下,有一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,内容就是ServletContainerInitializer实现类的全类名。
- 还可以使用@HandlerType,在启动应用时加载指定的类。
4. 启动流程
- 启动tomcat。
- 加载spring-web包下META-INF/services下面的javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件。
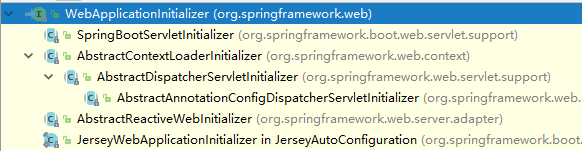
- SpringServletContainerInitializer将@HandlerType标注的所有这个类型的类都传入搭配onStartup方法的Set中,为这些WebApplicationInitializer类型的类创建实例。
@HandlesTypes({WebApplicationInitializer.class})
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
public SpringServletContainerInitializer() {
}
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
List initializers = new LinkedList();
Iterator var4;
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
var4 = webAppInitializerClasses.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Class waiClass = (Class)var4.next();
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass, new Class[0]).newInstance());
} catch (Throwable var7) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", var7);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
} else {
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
var4 = initializers.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
WebApplicationInitializer initializer = (WebApplicationInitializer)var4.next();
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
} - 每个WebApplicationInitializer到调用自己的onStartup()方法。
相当于SpringBootServletInitializer的类会被创建对象,并执行onStartup()方法。
SpringBootServletInitializer实例执行onStartup的时候会crateRootApplicationContext创建容器。
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 1.创建SpringApplicationBuilder
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = this.createSpringApplicationBuilder();
builder.main(this.getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = this.getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, (Object)null);
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent)});
}
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext)});
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.class);
// 2.调用configure方法,子类重新了这个方法,将SpringBoot的主程序类传入
builder = this.configure(builder);
builder.listeners(new ApplicationListener[]{new SpringBootServletInitializer.WebEnvironmentPropertySourceInitializer(servletContext)});
// 3.使用builder创建一个Spring应用
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getAllSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(this.getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(this.getClass()));
}
Assert.state(!application.getAllSources().isEmpty(), "No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
//确保错误页被注册
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class));
}
// 4. q启动Spring应用
return this.run(application);
}Spring的应用启动并且创建IOC容器。
先启动Servlet容器,再启动SpringBoot应用。