spring单元测试集锦
参考资料
java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException
Java高并发,如何解决,什么方式解决
使用 Spring 进行单元测试
普通查询性能测试
本测试目的在于摸清单纯的数据库查询的性能以及并发数量。
测试代码为java代码调用存储过程然后成功返回查询数据
存储过程:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION "sp_common_region_getRegionPath"("id" int4)
RETURNS varchar
AS $BODY$
declare tmpId integer;
declare needGoing boolean;
declare loopIndex integer;
declare selected_result record;
declare json_result varchar;
declare tmp_array json[];
declare real_array json[];
declare tmp_json_obj json;
declare arr_length integer;
begin
tmpId:=id;
needGoing:=true;
loopIndex:=0;
tmp_array:=array[]::json[];
real_array:=array[]::json[];
perform * from common_region cr where cr.id=tmpId;
<>
while needGoing loop
if FOUND then
needGoing:=true;
<>
for selected_result in select * from common_region cr where cr.id=tmpId loop
select row_to_json(cr) into tmp_json_obj from common_region cr where cr.id=tmpId;
-- raise notice 'tmp_json_obj is:%',tmp_json_obj;
tmp_array:=array_prepend(tmp_json_obj,tmp_array);
tmpId:=selected_result.parent_id;
loopIndex:=loopIndex+1;
end loop labelLoop4Lv2;
else
needGoing:=false;
raise notice '注意,这里没有发现任何记录。';
if loopIndex=0 then
return '';
else
exit labelLoop4Lv1;
end if ;
end if;
end loop labelLoop4Lv1;
return array_to_json(tmp_array);
end;
$BODY$
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql' VOLATILE
;
java端调用代码:
@Service
public class RegionService {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public List getPath(Integer id){
int theParamIndex=0;
List paths=new ArrayList<>();
paths=jdbcTemplate.execute(new CallableStatementCreator() {
@Override
public CallableStatement createCallableStatement(Connection con) throws SQLException {
String sql="{ call \"sp_common_region_getRegionPath\"(?,null)}";
sql="{ call \"sp_common_region_getRegionPath\"(?)}";
CallableStatement st=con.prepareCall(sql);
int paraIndex=1;
st.setInt(paraIndex,id);
return st;
}
},new CallableStatementCallback>(){
@Override
public List doInCallableStatement(CallableStatement cs) throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
List res=new ArrayList<>();
cs.execute();
ResultSet rs=(ResultSet)cs.getResultSet();
if (rs.next()){
String json_str=rs.getString(1);
if(ValidateUtils.isEmpty(json_str)){
return res;
}
res=JSONObject.parseArray(json_str,Region.class);
}
rs.close();
cs.getConnection().setAutoCommit(true);
return res;
}
});
return paths;
}
}
/**
* @author MR white
* @version 2.00
*/
public class Region {
public Long id=0L;
public void setId(Long id){
this.id=id;
}
public Long getId(){
return this.id;
}
public Long parent_id=0L;
public void setParent_id(Long parent_id){
this.parent_id=parent_id;
}
public Long getParent_id(){
return this.parent_id;
}
public String name="";
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public Integer level=0;
public void setLevel(Integer level){
this.level=level;
}
public Integer getLevel(){
return this.level;
}
public String code="";
public void setCode(String code){
this.code=code;
}
public String getCode(){
return this.code;
}
public String pingyin="";
public void setPingyin(String pingyin){
this.pingyin=pingyin;
}
public String getPingyin(){
return this.pingyin;
}
public String name_en="";
public void setName_en(String name_en){
this.name_en=name_en;
}
public String getName_en(){
return this.name_en;
}
public void setNULL(){
this.id=null;
this.parent_id=null;
this.name=null;
this.level=null;
this.code=null;
this.pingyin=null;
this.name_en=null;
}
public void resetDefaultVal(){
this.id=0L;
this.parent_id=0L;
this.name="";
this.level=0;
this.code="";
this.pingyin="";
this.name_en="";
}
}
java端测试代码:
public class RegionTester extends BaseTest {
@Autowired
private RegionService regionService;
@Test
public void singleThreadGetPath(){
List list=regionService.getPath(5600);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(list));
}
@Test
public synchronized void multiThreadGetPath() throws InterruptedException {
runMultiThreadTest(250, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Double rnd = (Math.random() * 10000);
int rndId = rnd.intValue() % 5000;
List list = regionService.getPath(rndId);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(list));
}
});
}
}
注意,basetest是经过定制的,为了能够同时运行多个线程而得到结果,加了一点东西,代码如下:
package main;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:spring-mvc.xml","classpath:spring-mybatis.xml"})
@ContextConfiguration(locations={
"classpath*:applicationContext.xml",
"classpath*:spring/spring-mvc.xml"}
)
public class BaseTest {
Date beginDate;
Long begin=null;
Long end=null;
Date endDate=null;
@Before
public void init() {
//--初始化spring上下文
System.out.println("初始化spring上下文中......");
//在运行测试之前的业务代码
beginDate = new Date();
begin = beginDate.getTime();
System.out.println("任务开始时间:" + beginDate);
}
@After
public void after() {
//在测试完成之后的业务代码
endDate = new Date();
end = endDate.getTime();
System.out.println("任务结束时间:" + endDate + "");
System.out.println("任务话费时间:" + (end - begin) + "毫秒");
}
public void runMultiThreadTest(int runThreadCount,Runnable runnable){
{
final int threadSize=runThreadCount;
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadSize);
final AtomicInteger lockCount=new AtomicInteger(threadSize);
final AtomicInteger successCount=new AtomicInteger(0);
try {
for (int i = 0; i < threadSize; i++) {
final int theThreadNumber = i;
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
runnable.run();
successCount.incrementAndGet();
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
lockCount.decrementAndGet();
}
}
});
}
while(true){
synchronized (this){
if(lockCount.intValue()>0){
;
}
else{
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println("共运行线程"+threadSize+"个,成功运行线程:"+successCount.get()+"个");
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
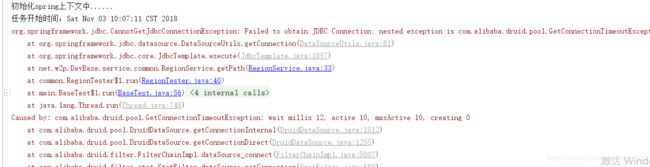
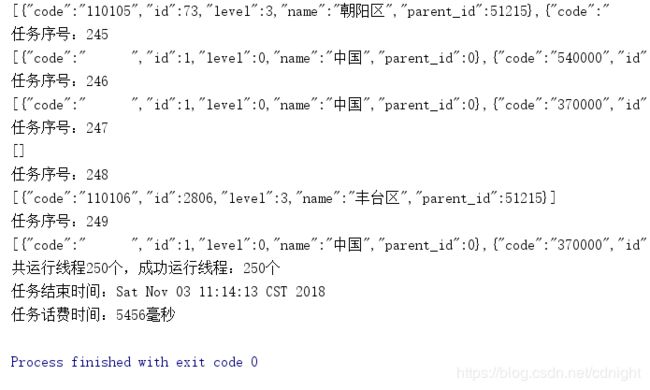
单线程的测试就算了。。测不出什么东西。现在直接运行多线程的测试方法,然后可以看到。。
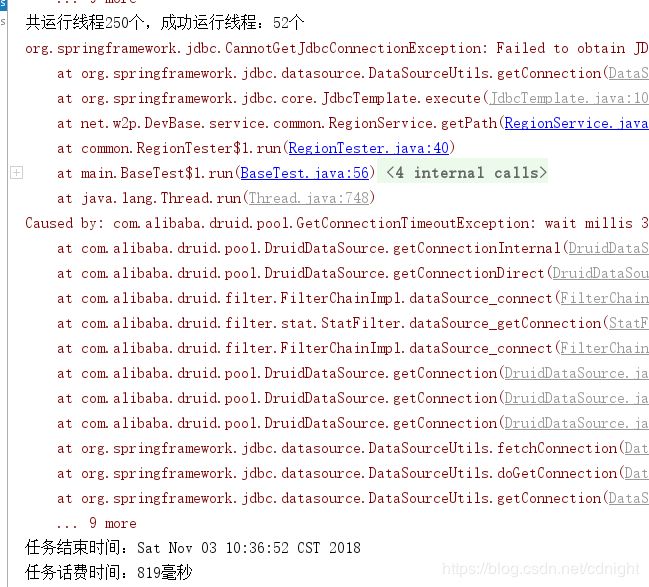
一堆报错。
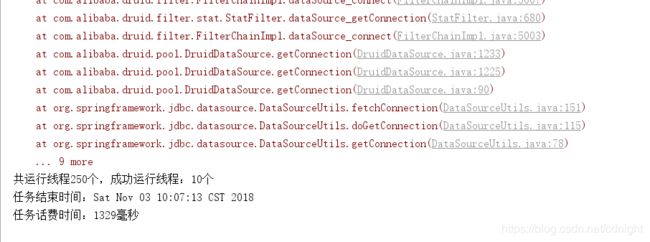
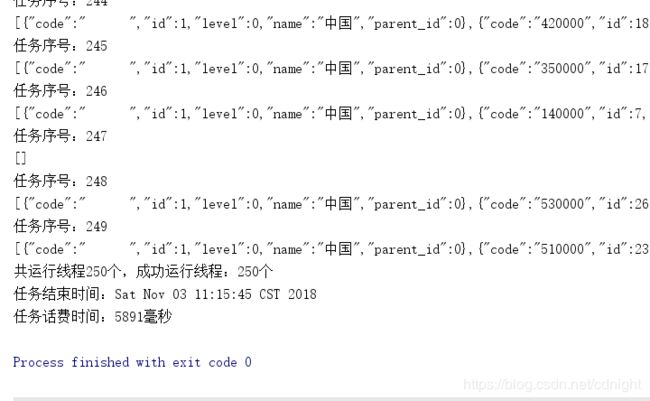
可以看到。。成功的线程就只有10个。。而我们的并发数量是250,可见250这个并发也是很恐怖的—不过引起这个的原因是druid的数据库连接池的最大数量设定为10,下面我们设定一下并发为50然后再看看结果:
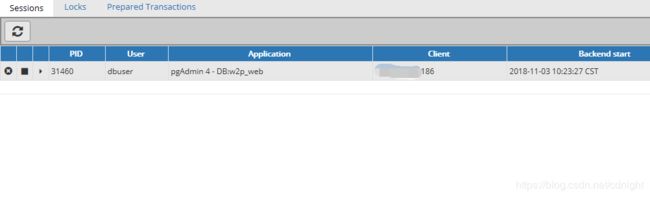
启动时候留意一下pgadmin4,查看一下数据库连接,可以发现,
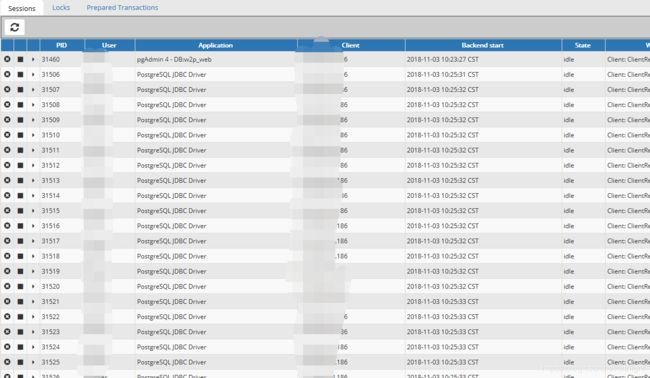
除了第一个是pgadmin拿来连接之外,其他的在数据库连接池初始化的时候就已经事先获得连接了。
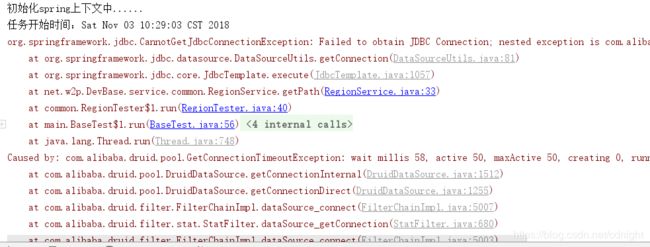
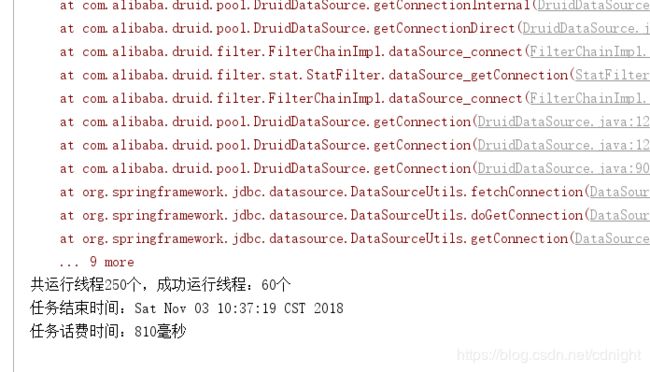
而代码运行结果为:
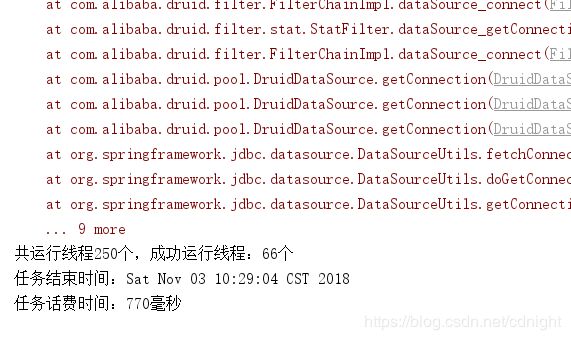
还是会报错,拿不到连接,不过并发成功数量已经升到66个了,而不是50个----按照逻辑成功的应该是50的,最多。。不过,每个线程获取连接的时候估计会先等几毫米,假如这时候一个任务查询成功释放连接的话,那么也会获得连接从而运行程序的。
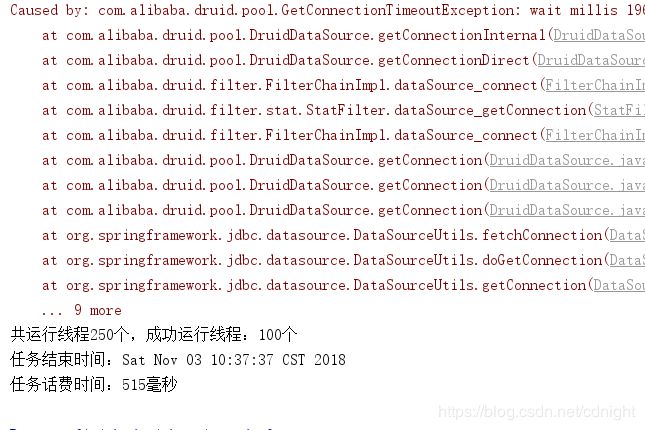
可见程序结束之后连接都释放了。
接下来进行多次测试,务求获得比较准确的性能概况。
并发太高的话无论如何一些请求都是会出错的,这样不行。
无论如何,客户端发起的请求都必须完成,无论是250同时来的请求还是1000个,单鉴于单机的硬件都是有限的,无法无限提升连接数量,所以,下面提出尝试一种解决方案,就是用阻塞队列进行处理。
阻塞队列执行任务性能测试
好了,并发数量太大的话多线程的执行都成问题了,现在改为阻塞队列来试试,下面要改改baseTest的代码,添加阻塞队列的测试方法。
package main;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:spring-mvc.xml","classpath:spring-mybatis.xml"})
@ContextConfiguration(locations={
"classpath*:applicationContext.xml",
"classpath*:spring/spring-mvc.xml"}
)
public class BaseTest {
Date beginDate;
Long begin=null;
Long end=null;
Date endDate=null;
@Before
public void init() {
//--初始化spring上下文
System.out.println("初始化spring上下文中......");
//在运行测试之前的业务代码
beginDate = new Date();
begin = beginDate.getTime();
System.out.println("任务开始时间:" + beginDate);
}
@After
public void after() {
//在测试完成之后的业务代码
endDate = new Date();
end = endDate.getTime();
System.out.println("任务结束时间:" + endDate + "");
System.out.println("任务话费时间:" + (end - begin) + "毫秒");
}
/***用于测试最大并发***/
public void runMultiThreadTest(int runThreadCount,Runnable runnable){
{
final int threadSize=runThreadCount;
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadSize);
final AtomicInteger lockCount=new AtomicInteger(threadSize);
final AtomicInteger successCount=new AtomicInteger(0);
try {
for (int i = 0; i < threadSize; i++) {
final int theThreadNumber = i;
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
runnable.run();
successCount.incrementAndGet();
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
lockCount.decrementAndGet();
}
}
});
}
while(true){
synchronized (this){
if(lockCount.intValue()>0){
;
}
else{
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println("共运行线程"+threadSize+"个,成功运行线程:"+successCount.get()+"个");
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/***用于测试任务阻塞的任务队列执行下的性能***/
public void runMultiThreadByBlockQueue(int threadCount,TaskProducer producer,TaskConsumer consumer){
final LinkedBlockingQueue queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(threadCount);
final int threadSize=threadCount;
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadSize);
final AtomicInteger lockCount=new AtomicInteger(threadSize);
final AtomicInteger successCount=new AtomicInteger(0);
try {
/***线程池同时产生任务队列***/
for (int i = 0; i < threadSize; i++) {
final int theThreadNumber = i;
TaskOutLine tmpOutLine=new TaskOutLine();
tmpOutLine.taskIndex=theThreadNumber;
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
tmpOutLine.taskData=producer.produce();
queue.put(tmpOutLine);
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
}
}
});
}
/***另起一个线程用于消费队列**/
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (lockCount.get()>0){
try{
TaskOutLine currentObj=queue.take();
consumer.consume(currentObj);
successCount.incrementAndGet();
}
catch (Exception ed){
}
finally {
lockCount.decrementAndGet();
}
}
}
}).start();
while(true){
synchronized (this){
if(lockCount.intValue()>0){
;
}
else{
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println("共运行线程"+threadSize+"个,成功运行线程:"+successCount.get()+"个");
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
}
public interface TaskProducer{
public Object produce();
}
public interface TaskConsumer{
public void consume(TaskOutLine taskOutLine);
}
public class TaskOutLine{
public int taskIndex=0;
public Object taskData=new Object();
public int getTaskIndex() {
return taskIndex;
}
public void setTaskIndex(int taskIndex) {
this.taskIndex = taskIndex;
}
public Object getTaskData() {
return taskData;
}
public void setTaskData(Object taskData) {
this.taskData = taskData;
}
}
}
然后在测试文件添加代码:
@Test
public synchronized void multiThreadGetPathByQueue() throws InterruptedException {
runMultiThreadByBlockQueue(250, new TaskProducer() {
@Override
public Object produce() {
Double rnd = (Math.random() * 10000);
Integer rndId = rnd.intValue() % 5000;
return rndId;
}
}, new TaskConsumer() {
@Override
public void consume(TaskOutLine outLine) {
TaskOutLine resOutLine=outLine;
Integer rndId=(Integer)resOutLine.taskData;
List list = regionService.getPath(rndId);
System.out.println("任务序号:"+outLine.taskIndex);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(list));
}
});
}
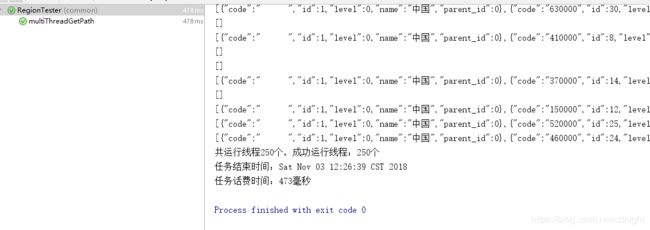
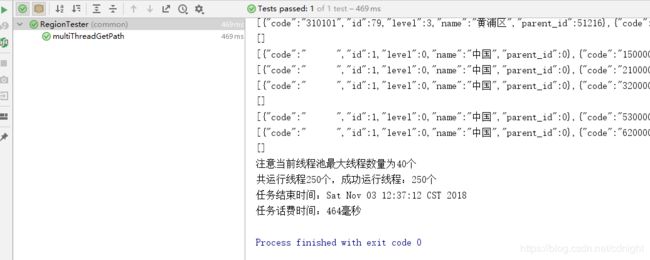
好了,多次执行看看性能如何:
可以看到,并发再多也是能够处理完毕的,就是耗费的时间有点多。
要5到6秒。按照第一种性能的测试来看。。50个并发的耗时是500ms到600ms,那么,一批一批完成250个任务的话,时间应该在2500ms到3000ms,所以阻塞队列可以处理完所有请求,防止并发过多而崩溃,但并不是性能的最优解。
下面将提出性能更好的方案。
任务分批提交
还记得线程池的设定吗?线程池可以设定最大线程执行数量的,也就是说,我们可以修改成为每次可以处理的最大并发数,那么修改一下代码:
baseTest
ount, int threadPoolSize, Runnable runnable){
{
final int threadSize= totalThreadCount;
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadPoolSize);
final AtomicInteger lockCount=new AtomicInteger(threadSize);
final AtomicInteger successCount=new AtomicInteger(0);
try {
for (int i = 0; i < threadSize; i++) {
final int theThreadNumber = i;
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
runnable.run();
successCount.incrementAndGet();
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
lockCount.decrementAndGet();
}
}
});
}
while(true){
synchronized (this){
if(lockCount.intValue()>0){
;
}
else{
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println("共运行线程"+threadSize+"个,成功运行线程:"+successCount.get()+"个");
}
catch (Exception ed){
ed.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
然后,调用例子是这样的:
@Test
public synchronized void multiThreadGetPath() throws InterruptedException {
runMultiThreadTest(250,25, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Double rnd = (Math.random() * 10000);
int rndId = rnd.intValue() % 5000;
List list = regionService.getPath(rndId);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(list));
}
});
}
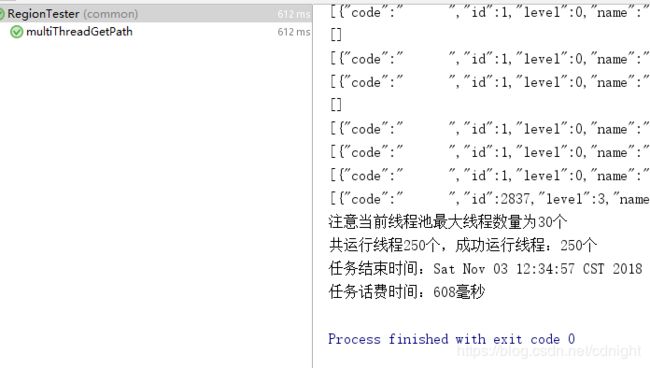
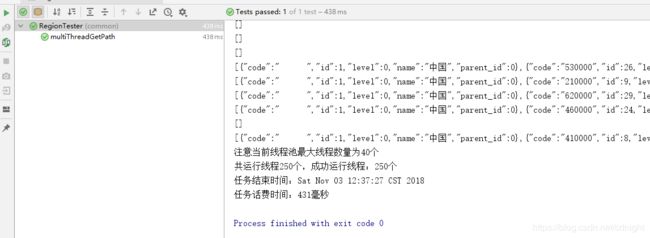
我们分别设定线程池的最大数量为25,30,40,观察一下效率变化。
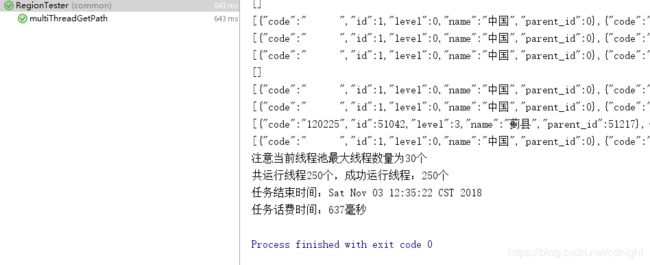
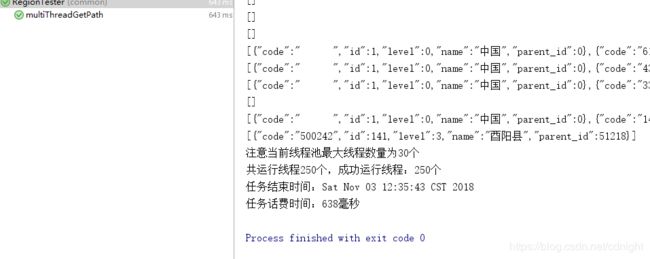
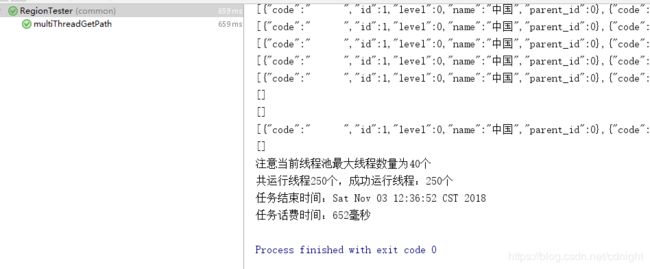
最大线程数量25:
最大线程数量30:
对了,在baseTest里面添加一下说明,例如:

这样就能得到最大线程数量了。
40的如下:
嗯。。。耗费时间=应用服务器耗时+数据库服务器耗时+数据传输耗时
即使应用服务器已经开多了线程不过时间看来没有多大的优化,估计已经到了数据库服务器的极限了。