Spring 中 LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy 代理类的源码解析
Spring LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy 代理类的源码解析
1、该类的实现思路
(1)、代理了目标数据源 dataSource 的所有方法,其中在 invoke 方法,Spring使用了排除法;
(2)、只有 dataSource 获取到Connection之后,在执行 java.sql.Connection#prepareStatement(java.lang.String) 时候,Spring 才会主动去数据库链接池中获取 Connection ,这样做的好处就是提高数据库链接的使用率和效率;
(3)、据此我们可以看到 Spring 的良苦用心,LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy 经常会被用在一些分库分表、多数据源事务的应用当中;
(4)、多数据源的事务管理解决方案,很多采用了同时开启所有数据源事务、同时提交的策略,例如:阿里的 cobar 解决方案等;
(5)、如果我们的数据源是使用了 LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy 则在执行 Connection#prepareStatement 之前,spring 是不会向数据库连接池获取数据库链接的
2、源代码分析
public class LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy extends DelegatingDataSource {
// 省略属性 getter/setter 方法
/**
* Create a new LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy.
* @see #setTargetDataSource
*/
public LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy() {
}
/**
* Create a new LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy.
* @param targetDataSource the target DataSource
*/
public LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy(DataSource targetDataSource) {
setTargetDataSource(targetDataSource);
afterPropertiesSet();
}
// 该方法会在Spring Bean 加载初始化的时候执行,功能和 bean 标签的属性 init-method 一样
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
super.afterPropertiesSet();
// Determine default auto-commit and transaction isolation
// via a Connection from the target DataSource, if possible.
if (this.defaultAutoCommit == null || this.defaultTransactionIsolation == null) {
try {
Connection con = getTargetDataSource().getConnection();
try {
checkDefaultConnectionProperties(con);
}
finally {
con.close();
}
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
logger.warn("Could not retrieve default auto-commit and transaction isolation settings", ex);
}
}
}
/**
* Check the default connection properties (auto-commit, transaction isolation),
* keeping them to be able to expose them correctly without fetching an actual
* JDBC Connection from the target DataSource.
* This will be invoked once on startup, but also for each retrieval of a
* target Connection. If the check failed on startup (because the database was
* down), we'll lazily retrieve those settings.
* @param con the Connection to use for checking
* @throws SQLException if thrown by Connection methods
*/
protected synchronized void checkDefaultConnectionProperties(Connection con) throws SQLException {
if (this.defaultAutoCommit == null) {
this.defaultAutoCommit = con.getAutoCommit();
}
if (this.defaultTransactionIsolation == null) {
this.defaultTransactionIsolation = con.getTransactionIsolation();
}
}
// 以下三个方法都是通过代理模式返回一个目标 targetDataSource 的代理类
// 其中 LazyConnectionInvocationHandler 实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,重点关注 invoke 方法的实现逻辑
/**
* Return a Connection handle that lazily fetches an actual JDBC Connection
* when asked for a Statement (or PreparedStatement or CallableStatement).
* The returned Connection handle implements the ConnectionProxy interface,
* allowing to retrieve the underlying target Connection.
* @return a lazy Connection handle
* @see ConnectionProxy#getTargetConnection()
*/
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
ConnectionProxy.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] {ConnectionProxy.class},
new LazyConnectionInvocationHandler());
}
/**
* Return a Connection handle that lazily fetches an actual JDBC Connection
* when asked for a Statement (or PreparedStatement or CallableStatement).
* The returned Connection handle implements the ConnectionProxy interface,
* allowing to retrieve the underlying target Connection.
* @param username the per-Connection username
* @param password the per-Connection password
* @return a lazy Connection handle
* @see ConnectionProxy#getTargetConnection()
*/
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
ConnectionProxy.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] {ConnectionProxy.class},
new LazyConnectionInvocationHandler(username, password));
}
/**
* Invocation handler that defers fetching an actual JDBC Connection
* until first creation of a Statement.
*/
// 代理类的实现代理了 ConnectionProxy 的实现类
private class LazyConnectionInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private String username;
private String password;
private Boolean readOnly = Boolean.FALSE;
private Integer transactionIsolation;
private Boolean autoCommit;
private boolean closed = false;
private Connection target;
public LazyConnectionInvocationHandler() {
this.autoCommit = defaultAutoCommit();
this.transactionIsolation = defaultTransactionIsolation();
}
public LazyConnectionInvocationHandler(String username, String password) {
this();
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// Invocation on ConnectionProxy interface coming in...
// 以下的这些 if …… else 的判断,主要就是通过排除法锁定prepareStatement 方法
// 只要 method.getName 不为:prepareStatement 则spring都使用了硬编码做了模拟方法实现,可以仔细分析一下源代码
if (method.getName().equals("equals")) {
// We must avoid fetching a target Connection for "equals".
// Only consider equal when proxies are identical.
return (proxy == args[0]);
}
else if (method.getName().equals("hashCode")) {
// We must avoid fetching a target Connection for "hashCode",
// and we must return the same hash code even when the target
// Connection has been fetched: use hashCode of Connection proxy.
return System.identityHashCode(proxy);
}
else if (method.getName().equals("unwrap")) {
if (((Class) args[0]).isInstance(proxy)) {
return proxy;
}
}
else if (method.getName().equals("isWrapperFor")) {
if (((Class) args[0]).isInstance(proxy)) {
return true;
}
}
else if (method.getName().equals("getTargetConnection")) {
// Handle getTargetConnection method: return underlying connection.
return getTargetConnection(method);
}
// 当没有执行 prepareStatement 方法,则 hasTargetConnection() 的返回值恒为 false
// 但是该 if 逻辑内部恰好排除了 prepareStatement 方法的执行,
// 也就是说当 Connection 执行 prepareStatement 时会进入else 的处理逻辑
if (!hasTargetConnection()) {
// No physical target Connection kept yet ->
// resolve transaction demarcation methods without fetching
// a physical JDBC Connection until absolutely necessary.
if (method.getName().equals("toString")) {
return "Lazy Connection proxy for target DataSource [" + getTargetDataSource() + "]";
}
else if (method.getName().equals("isReadOnly")) {
return this.readOnly;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("setReadOnly")) {
this.readOnly = (Boolean) args[0];
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("getTransactionIsolation")) {
if (this.transactionIsolation != null) {
return this.transactionIsolation;
}
// Else fetch actual Connection and check there,
// because we didn't have a default specified.
}
else if (method.getName().equals("setTransactionIsolation")) {
this.transactionIsolation = (Integer) args[0];
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("getAutoCommit")) {
if (this.autoCommit != null) {
return this.autoCommit;
}
// Else fetch actual Connection and check there,
// because we didn't have a default specified.
}
else if (method.getName().equals("setAutoCommit")) {
this.autoCommit = (Boolean) args[0];
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("commit")) {
// Ignore: no statements created yet.
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("rollback")) {
// Ignore: no statements created yet.
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("getWarnings")) {
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("clearWarnings")) {
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("close")) {
// Ignore: no target connection yet.
this.closed = true;
return null;
}
else if (method.getName().equals("isClosed")) {
return this.closed;
}
else if (this.closed) {
// Connection proxy closed, without ever having fetched a
// physical JDBC Connection: throw corresponding SQLException.
throw new SQLException("Illegal operation: connection is closed");
}
}
// Target Connection already fetched,
// or target Connection necessary for current operation ->
// invoke method on target connection.
try {
// Connection 执行 prepareStatement 时会执行到此处,invoke方法执行的时候第一个参数调用的方法将会初始化:target
return method.invoke(getTargetConnection(method), args);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
/**
* Return whether the proxy currently holds a target Connection.
*/
private boolean hasTargetConnection() {
return (this.target != null);
}
/**
* Return the target Connection, fetching it and initializing it if necessary.
*/
private Connection getTargetConnection(Method operation) throws SQLException {
if (this.target == null) {
// No target Connection held -> fetch one.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Connecting to database for operation '" + operation.getName() + "'");
}
// 根据条件,最终会从目标数据源上获取到数据库的链接 Connection
// Fetch physical Connection from DataSource.
this.target = (this.username != null) ?
getTargetDataSource().getConnection(this.username, this.password) :
getTargetDataSource().getConnection();
// If we still lack default connection properties, check them now.
checkDefaultConnectionProperties(this.target);
// Apply kept transaction settings, if any.
if (this.readOnly) {
try {
this.target.setReadOnly(this.readOnly);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// "read-only not supported" -> ignore, it's just a hint anyway
logger.debug("Could not set JDBC Connection read-only", ex);
}
}
if (this.transactionIsolation != null &&
!this.transactionIsolation.equals(defaultTransactionIsolation())) {
this.target.setTransactionIsolation(this.transactionIsolation);
}
if (this.autoCommit != null && this.autoCommit != this.target.getAutoCommit()) {
this.target.setAutoCommit(this.autoCommit);
}
}
else {
// Target Connection already held -> return it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using existing database connection for operation '" + operation.getName() + "'");
}
}
return this.target;
}
}
}3、测试用例跟踪
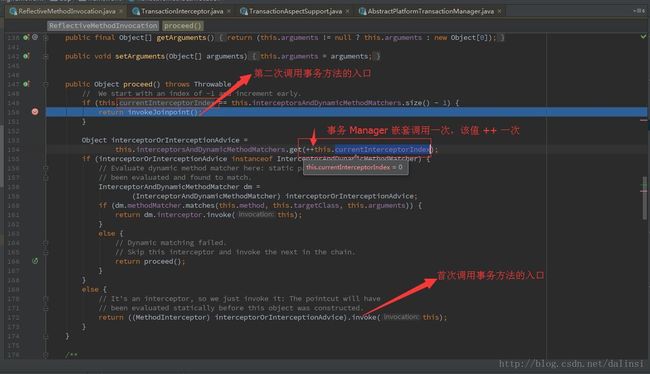
(1)、测试用例使用了Mybatis框架,跟踪源码可以发现Connection执行非 prepareStatement 方法,都将被代理类做一次排除、模拟实际的方法执行
(2)、只有Connection执行 prepareStatement 方法的之后才会执行到截图中的代码

(3)、两个事务处理类的事务方法嵌套调用过程(该点与本篇文章没有多大关系,是自己在尝试测试嵌套事务的调用过程)
4、本篇文章中源代码下载
本篇文章中分享的源代码可以去我的 gitHub 空间上下载,链接如下:
https://github.com/wangyingjie/jd-ssm-stu.git