Android:代码撸彩妆 2(大眼,瘦脸,大长腿)
序言
本篇文章是代码撸彩妆的第二篇, 主要介绍在Android上怎么进行图片的局部变形,并实现抖音上比较火的大眼,瘦脸,大长腿特效.
在开始之前我们先来回顾上一篇的主要内容.
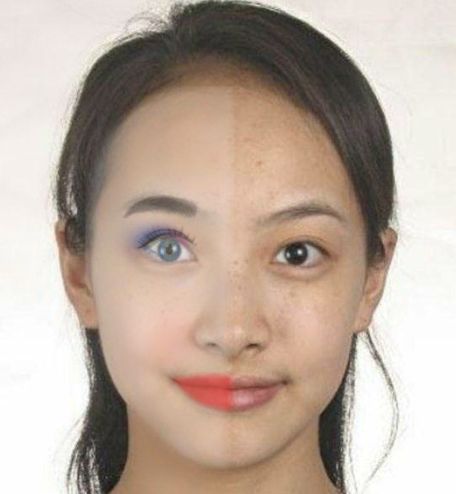
使用代码画一半的效果如下

public enum Region {
FOUNDATION("粉底"),
BLUSH("腮红"),
LIP("唇彩"),
BROW("眉毛"),
EYE_LASH("睫毛"),
EYE_CONTACT("美瞳"),
EYE_DOUBLE("双眼皮"),
EYE_LINE("眼线"),
EYE_SHADOW("眼影");
private String name;
Region(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
使用代码画出各种效果. 上一篇的文章地址 Android:让你的“女神”逆袭,代码撸彩妆(画妆)
上一篇和本篇的代码所在地址一致,都已经托管到github,如果你喜欢,欢迎给一个star,谢谢 https://github.com/DingProg/Makeup
现在开始我们今天的主题,人体(图像)的局部变形,如果要直接看效果的话,可以点击目录快速滑到效果区域.
大眼
效果
实现
图片局部缩放原理
我们知道,图片的放大缩小,是比较容易的事,相应的库已经封装好了,可以直接使用(我们并不需要关注图形放大缩小的插值处理等). 但是图片的局部放大缩小,并没有直接封装好,比如Android里面的bitmap,并没有直接局部处理放大缩小的API.
那我们先来看一下什么是图形的局部缩放?
局部的缩放,我们可以想象成中心点被缩放的比例比较小,而边缘的地方被缩放的比例很小,或者边界区域几乎没有变化,这样就可以达到一种平滑的效果。如果直接只对选中的圆形区域,变化的话,那边缘就变成了断裂式的缩放.
借用1993年的一篇博士论文 Interactive Image Warping 对局部图片进行缩放
代码实现
既然要让眼睛放大,那么我们就把对应的近圆心的点的值️赋给远心点。
按照论文里所提到的思路,进行部分修改,实现如下.
/**
* 眼睛放大算法
* @param bitmap 原来的bitmap
* @param centerPoint 放大中心点
* @param radius 放大半径
* @param sizeLevel 放大力度 [0,4]
* @return 放大眼睛后的图片
*/
public static Bitmap magnifyEye(Bitmap bitmap, Point centerPoint, int radius, float sizeLevel) {
TimeAopUtils.start();
Bitmap dstBitmap = bitmap.copy(Bitmap.Config.RGB_565, true);
int left = centerPoint.x - radius < 0 ? 0 : centerPoint.x - radius;
int top = centerPoint.y - radius < 0 ? 0 : centerPoint.y - radius;
int right = centerPoint.x + radius > bitmap.getWidth() ? bitmap.getWidth() - 1 : centerPoint.x + radius;
int bottom = centerPoint.y + radius > bitmap.getHeight() ? bitmap.getHeight() - 1 : centerPoint.y + radius;
int powRadius = radius * radius;
int offsetX, offsetY, powDistance, powOffsetX, powOffsetY;
int disX, disY;
//当为负数时,为缩小
float strength = (5 + sizeLevel * 2) / 10;
for (int i = top; i <= bottom; i++) {
offsetY = i - centerPoint.y;
for (int j = left; j <= right; j++) {
offsetX = j - centerPoint.x;
powOffsetX = offsetX * offsetX;
powOffsetY = offsetY * offsetY;
powDistance = powOffsetX + powOffsetY;
if (powDistance <= powRadius) {
double distance = Math.sqrt(powDistance);
double sinA = offsetX / distance;
double cosA = offsetY / distance;
double scaleFactor = distance / radius - 1;
scaleFactor = (1 - scaleFactor * scaleFactor * (distance / radius) * strength);
distance = distance * scaleFactor;
disY = (int) (distance * cosA + centerPoint.y + 0.5);
disY = checkY(disY, bitmap);
disX = (int) (distance * sinA + centerPoint.x + 0.5);
disX = checkX(disX, bitmap);
//中心点不做处理
if (!(j == centerPoint.x && i == centerPoint.y)) {
dstBitmap.setPixel(j, i, bitmap.getPixel(disX, disY));
}
}
}
}
TimeAopUtils.end("eye","magnifyEye");
return dstBitmap;
}
private static int checkY(int disY, Bitmap bitmap) {
if (disY < 0) {
disY = 0;
} else if (disY >= bitmap.getHeight()) {
disY = bitmap.getHeight() - 1;
}
return disY;
}
private static int checkX(int disX, Bitmap bitmap) {
if (disX < 0) {
disX = 0;
} else if (disX >= bitmap.getWidth()) {
disX = bitmap.getWidth() - 1;
}
return disX;
}
其中里面计算缩放前后后的点,使用的是如下图所示的计算规则计算.

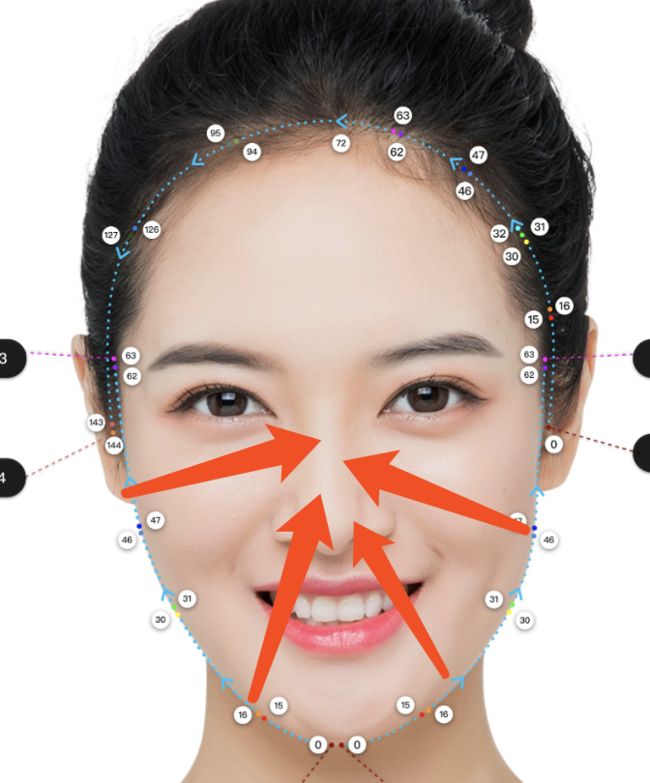
有了这个方法,我们借助人脸识别的结果,把眼睛中心部分传入进去就可以实现自动大眼的效果了.
Bitmap magnifyEye = MagnifyEyeUtils.magnifyEye(bitmap,
Objects.requireNonNull(FacePoint.getLeftEyeCenter(faceJson)),
FacePoint.getLeftEyeRadius(faceJson) * 3, 3);
略有不足
- 代码所示部分没有使用插值 (代码直接使用了值替代,而不是使用 两个点,三个点,进行插值计算),如果放大的比例很大,可能会出现模糊的效果
- Android Bitmap直接获取像素,效率低,正确的方式应该是一次全部获取对应的像素,然后在数组上进行操作(考虑内容,就直接采用了每次去读取/设置),操作完之后,在设置回去。
瘦脸
效果
手动模式
自动模式
实现
大眼效果,使用了bitmap直接去操作像素点,效率有点低,所以在实现瘦脸和打长腿时,采用了另外的实现方式实现.
Cavans的drawBitmapMesh方法
// Canvas
/**
* Draw the bitmap through the mesh, where mesh vertices are evenly distributed across the
* bitmap. There are meshWidth+1 vertices across, and meshHeight+1 vertices down. The verts
* array is accessed in row-major order, so that the first meshWidth+1 vertices are distributed
* across the top of the bitmap from left to right. A more general version of this method is
* drawVertices().
*
* Prior to API level {@value Build.VERSION_CODES#P} vertOffset and colorOffset were ignored,
* effectively treating them as zeros. In API level {@value Build.VERSION_CODES#P} and above
* these parameters will be respected.
*
* @param bitmap The bitmap to draw using the mesh
* @param meshWidth The number of columns in the mesh. Nothing is drawn if this is 0
* @param meshHeight The number of rows in the mesh. Nothing is drawn if this is 0
* @param verts Array of x,y pairs, specifying where the mesh should be drawn. There must be at
* least (meshWidth+1) * (meshHeight+1) * 2 + vertOffset values in the array
* @param vertOffset Number of verts elements to skip before drawing
* @param colors May be null. Specifies a color at each vertex, which is interpolated across the
* cell, and whose values are multiplied by the corresponding bitmap colors. If not
* null, there must be at least (meshWidth+1) * (meshHeight+1) + colorOffset values
* in the array.
* @param colorOffset Number of color elements to skip before drawing
* @param paint May be null. The paint used to draw the bitmap
*/
public void drawBitmapMesh(@NonNull Bitmap bitmap, int meshWidth, int meshHeight,
@NonNull float[] verts, int vertOffset, @Nullable int[] colors, int colorOffset,
@Nullable Paint paint) {
super.drawBitmapMesh(bitmap, meshWidth, meshHeight, verts, vertOffset, colors, colorOffset,
paint);
}
这个方法,大概说的是,将图片使用网格的方式先进行分割,然后操作这些网格,就可以让图片达到扭曲的效果.
代码实现
Gif中拖动就可以进行自动瘦脸功能,这是一个自定义的View,在View上通过手势操作,去改变那个网格,然后在调用重绘.
第一步,初始化图片,把图片放在View的中心
private void zoomBitmap(Bitmap bitmap, int width, int height) {
if(bitmap == null) return;
int dw = bitmap.getWidth();
int dh = bitmap.getHeight();
float scale = 1.0f;
// 图片的宽度大于控件的宽度,图片的高度小于空间的高度,我们将其缩小
if (dw > width && dh < height) {
scale = width * 1.0f / dw;
}
// 图片的宽度小于控件的宽度,图片的高度大于空间的高度,我们将其缩小
if (dh > height && dw < width) {
scale = height * 1.0f / dh;
}
// 缩小值
if (dw > width && dh > height) {
scale = Math.min(width * 1.0f / dw, height * 1.0f / dh);
}
// 放大值
if (dw < width && dh < height) {
scale = Math.min(width * 1.0f / dw, height * 1.0f / dh);
}
//缩小
if (dw == width && dh > height) {
scale = height * 1.0f / dh;
}
dx = width / 2 - (int) (dw * scale + 0.5f) / 2;
dy = height / 2 - (int) (dh * scale + 0.5f) / 2;
mScale = scale;
restoreVerts();
}
接着初始化网格
//将图像分成多少格
private int WIDTH = 200;
private int HEIGHT = 200;
//交点坐标的个数
private int COUNT = (WIDTH + 1) * (HEIGHT + 1);
//用于保存COUNT的坐标
//x0, y0, x1, y1......
private float[] verts = new float[COUNT * 2];
//用于保存原始的坐标
private float[] orig = new float[COUNT * 2];
private void restoreVerts() {
int index = 0;
float bmWidth = mBitmap.getWidth();
float bmHeight = mBitmap.getHeight();
for (int i = 0; i < HEIGHT + 1; i++) {
float fy = bmHeight * i / HEIGHT;
for (int j = 0; j < WIDTH + 1; j++) {
float fx = bmWidth * j / WIDTH;
//X轴坐标 放在偶数位
verts[index * 2] = fx;
orig[index * 2] = verts[index * 2];
//Y轴坐标 放在奇数位
verts[index * 2 + 1] = fy;
orig[index * 2 + 1] = verts[index * 2 + 1];
index += 1;
}
}
showCircle = false;
showDirection = false;
}
那最后一步把这个图片画上去
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if(mBitmap == null) return;
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(dx, dy);
canvas.scale(mScale, mScale);
if (isShowOrigin) {
canvas.drawBitmapMesh(mBitmap, WIDTH, HEIGHT, orig, 0, null, 0, null);
} else {
canvas.drawBitmapMesh(mBitmap, WIDTH, HEIGHT, verts, 0, null, 0, null);
}
canvas.restore();
if (showCircle && isEnableOperate) {
canvas.drawCircle(startX, startY, radius, circlePaint);
canvas.drawCircle(startX, startY, 5, directionPaint);
}
if (showDirection && isEnableOperate) {
canvas.drawLine(startX, startY, moveX, moveY, directionPaint);
}
}
那么接下来,就来操作网格,然后产生一些变形的效果了.
添加事件监听
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (!isEnableOperate) return true;
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
//绘制变形区域
startX = event.getX();
startY = event.getY();
showCircle = true;
invalidate();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//绘制变形方向
moveX = event.getX();
moveY = event.getY();
showDirection = true;
invalidate();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
showCircle = false;
showDirection = false;
//调用warp方法根据触摸屏事件的坐标点来扭曲verts数组
if(mBitmap != null && verts!= null && !mBitmap.isRecycled()) {
warp(startX, startY, event.getX(), event.getY());
}
if (onStepChangeListener != null) {
onStepChangeListener.onStepChange(false);
}
break;
}
return true;
}
这里重点,看我们的wrap方法,来操作网格的变形.先简述一下思路,我们刚才看到眼睛的放大,就是中心部分,操作幅度大,离的远的地方基本不操作.
来看一下代码
private void warp(float startX, float startY, float endX, float endY) {
startX = toX(startX);
startY = toY(startY);
endX = toX(endX);
endY = toY(endY);
//计算拖动距离
float ddPull = (endX - startX) * (endX - startX) + (endY - startY) * (endY - startY);
float dPull = (float) Math.sqrt(ddPull);
//dPull = screenWidth - dPull >= 0.0001f ? screenWidth - dPull : 0.0001f;
if (dPull < 2 * r) {
if (isSmllBody) {
dPull = 1.8f * r;
} else {
dPull = 2.5f * r;
}
}
int powR = r * r;
int index = 0;
int offset = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < HEIGHT + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < WIDTH + 1; j++) {
//边界区域不处理
if(i < offset || i > HEIGHT - offset || j < offset || j > WIDTH - offset){
index = index + 1;
continue;
}
//计算每个坐标点与触摸点之间的距离
float dx = verts[index * 2] - startX;
float dy = verts[index * 2 + 1] - startY;
float dd = dx * dx + dy * dy;
if (dd < powR) {
//变形系数,扭曲度
double e = (powR - dd) * (powR - dd) / ((powR - dd + dPull * dPull) * (powR - dd + dPull * dPull));
double pullX = e * (endX - startX);
double pullY = e * (endY - startY);
verts[index * 2] = (float) (verts[index * 2] + pullX);
verts[index * 2 + 1] = (float) (verts[index * 2 + 1] + pullY);
// check
if(verts[index * 2] < 0){
verts[index * 2] = 0;
}
if(verts[index * 2] > mBitmap.getWidth()){
verts[index * 2] = mBitmap.getWidth();
}
if(verts[index * 2 + 1] < 0){
verts[index * 2 +1] = 0;
}
if(verts[index * 2 + 1] > mBitmap.getHeight()){
verts[index * 2 + 1] = mBitmap.getHeight();
}
}
index = index + 1;
}
}
invalidate();
}
只要在操作半径内,对X和Y进行不同的变形即可.
自动瘦脸实现
其实有了上面的拖动,要实现自动瘦脸就容易得多,我们对几个关键点进行模拟拖动即可。
实现代码如下
/**
* 瘦脸算法
*
* @param bitmap 原来的bitmap
* @return 之后的图片
*/
public static Bitmap smallFaceMesh(Bitmap bitmap, List<Point> leftFacePoint,List<Point> rightFacePoint,Point centerPoint, int level) {
//交点坐标的个数
int COUNT = (WIDTH + 1) * (HEIGHT + 1);
//用于保存COUNT的坐标
float[] verts = new float[COUNT * 2];
float bmWidth = bitmap.getWidth();
float bmHeight = bitmap.getHeight();
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < HEIGHT + 1; i++) {
float fy = bmHeight * i / HEIGHT;
for (int j = 0; j < WIDTH + 1; j++) {
float fx = bmWidth * j / WIDTH;
//X轴坐标 放在偶数位
verts[index * 2] = fx;
//Y轴坐标 放在奇数位
verts[index * 2 + 1] = fy;
index += 1;
}
}
int r = 180 + 15 * level;
warp(COUNT,verts,leftFacePoint.get(16).x,leftFacePoint.get(16).y,centerPoint.x,centerPoint.y,r);
warp(COUNT,verts,leftFacePoint.get(46).x,leftFacePoint.get(46).y,centerPoint.x,centerPoint.y,r);
warp(COUNT,verts,rightFacePoint.get(16).x,rightFacePoint.get(16).y,centerPoint.x,centerPoint.y,r);
warp(COUNT,verts,rightFacePoint.get(46).x,rightFacePoint.get(46).y,centerPoint.x,centerPoint.y,r);
Bitmap resultBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmap.getWidth(),bitmap.getHeight(), Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(resultBitmap);
Paint paint = new Paint();
canvas.drawBitmapMesh(bitmap,WIDTH, HEIGHT,verts,0,null,0,null);
return resultBitmap;
}
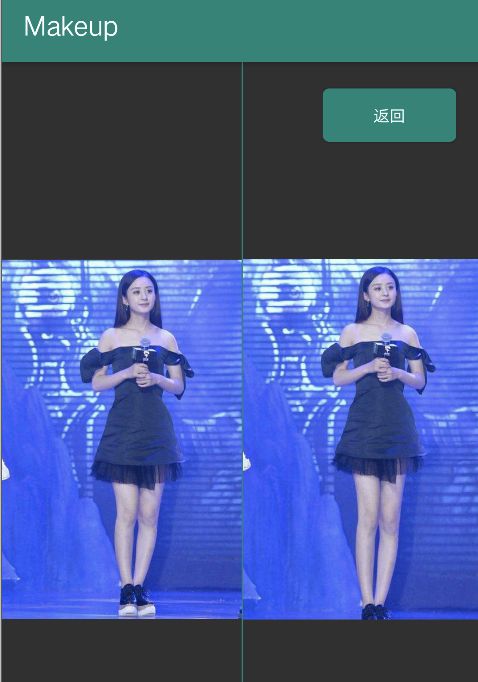
大长腿
看代码有些累吧,下面来看一个明星 美女,有人知道这是谁吗?问了两三个程序员朋友,要么不知道,要么说这是杨幂吗?哎,感叹程序员认识的明星就那么多吗?
效果
实现
上面的瘦脸操作需要对x和y两个地方进行操作,那大长腿就绘变得容易一些,仅仅操作Y方向即可.
第一张图,上面的覆盖层为一个自定义View,下层直接使用了瘦脸功能的那个View,把图片放在中心,只是不允许手势操作图片.
smallFaceView.setEnableOperate(false);
上层View核心代码
//AdjustLegView 绘制部分
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//line
canvas.drawRect(0, topLine, getWidth(), topLine + LINEHIGHT, paint);
//line
canvas.drawRect(0, bottomLine, getWidth(), bottomLine + LINEHIGHT, paint);
if (selectPos != -1) {
swap();
rect.set(0, topLine + LINEHIGHT, getWidth(), bottomLine);
canvas.drawRect(rect, bgPaint);
if(tipStr != null){
@SuppressLint("DrawAllocation") Rect textRect = new Rect();
textPaint.getTextBounds(tipStr,0,tipStr.length()-1,textRect);
canvas.drawText(tipStr,rect.left + (rect.width()/ 2 -textRect.width()/2),
rect.top + (rect.height()/ 2 -textRect.height()/2),textPaint);
}
}
}
手势交互部分
//AdjustLegView
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
float y = event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
selectPos = checkSelect(y);
lastY = y;
if(selectPos != -1 && listener != null){
listener.down();
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
if (selectPos == 1) {
// 最小 20 的偏移量
topLine += checkLimit(y - lastY);
invalidate();
}
if (selectPos == 2) {
bottomLine += checkLimit(y - lastY);
invalidate();
}
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
selectPos = -1;
invalidate();
if( listener != null){
listener.up(rect);
}
break;
}
return true;
}
private float checkLimit(float offset) {
if (selectPos == 1) {
if(topLine + offset > minLine && topLine + offset < maxLine){
return offset;
}
}
if (selectPos == 2) {
if(bottomLine + offset > minLine && bottomLine + offset < maxLine){
return offset;
}
}
return 0;
}
private int checkSelect(float y) {
selectPos = -1;
RectF rect = new RectF(0, y - OFFSETY, 0, y + OFFSETY);
float min = -1;
if (topLine >= rect.top && topLine <= rect.bottom) {
selectPos = 1;
min = rect.bottom - topLine;
}
if (bottomLine >= rect.top && bottomLine <= rect.bottom) {
if (min > bottomLine - rect.top || min == -1) {
selectPos = 2;
}
}
return selectPos;
}
大长腿
那么怎么把腿部拉长呢?直接看一下算法部分
private static void warpLeg(int COUNT, float verts[], float centerY,int totalHeight,float region,float strength) {
float r = region / 2; //缩放区域力度
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT * 2; i += 2) {
//计算每个坐标点与触摸点之间的距离
float dy = verts[i + 1] - centerY;
double e = (totalHeight - Math.abs(dy)) / totalHeight;
if(Math.abs(dy) < r){
//拉长比率
double pullY = e * dy * strength;
verts[i + 1] = (float) (verts[i + 1] + pullY);
}else if(Math.abs(dy) < 2 * r || dy > 0){
double pullY = e * e * dy * strength;
verts[i + 1] = (float) (verts[i + 1] + pullY);
}else if(Math.abs(dy) < 3 * r){
double pullY = e * e * dy * strength /2;
verts[i + 1] = (float) (verts[i + 1] + pullY);
}else {
double pullY = e * e * dy * strength /4;
verts[i + 1] = (float) (verts[i + 1] + pullY);
}
}
}
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(resultBitmap);
canvas.drawBitmapMesh(bitmap, WIDTH, HEIGHT, verts, 0, null, 0, null);
return resultBitmap;
依然使用的是drawBitmapMesh,算法部分,只对Y进行了操作,X部分不操作,并且距离越远,操作幅度越小. 尽量只拉长腿部,其他部分保持原有不动.
总结
本篇主要是介绍了,在Android上,使用原生API,怎么去实现一些酷炫的效果. 文中的所有代码都托管在github上,如果有需要,欢迎star, Github Makeup ,非常感谢.
本文大眼算法,廋脸算法仅来源网络,如有侵权,请联系作者立刻删除.大长腿算法,作者自己实践得出,可自行取用.
推荐阅读
Android:让你的“女神”逆袭,代码撸彩妆(画妆)
Flutter PIP(画中画)效果的实现
Android 绘制原理浅析【干货】