图灵学院:java高并发之ConcurrentMap
简介
今天浅显的学习了下concurrentHashmap,是为了高并发而实现,内部采用分离锁的设计,有效地避开了热点访问。而对于每个分段,ConcurrentHashmap采用final和内存可见修饰符volatile关键字。
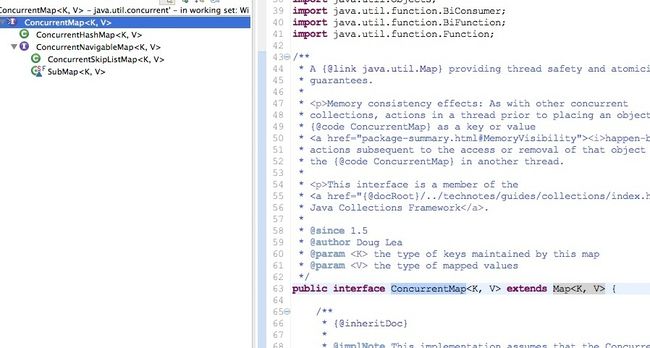
1:ConcurrentMap的继承和实现关系
ConcurrentMap接口继承Map接口,他的实现类有ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap接口继承ConcurrentHashMap 实现类是ConcurrentSkipListMap(jdk1.6新增)
详图如下:
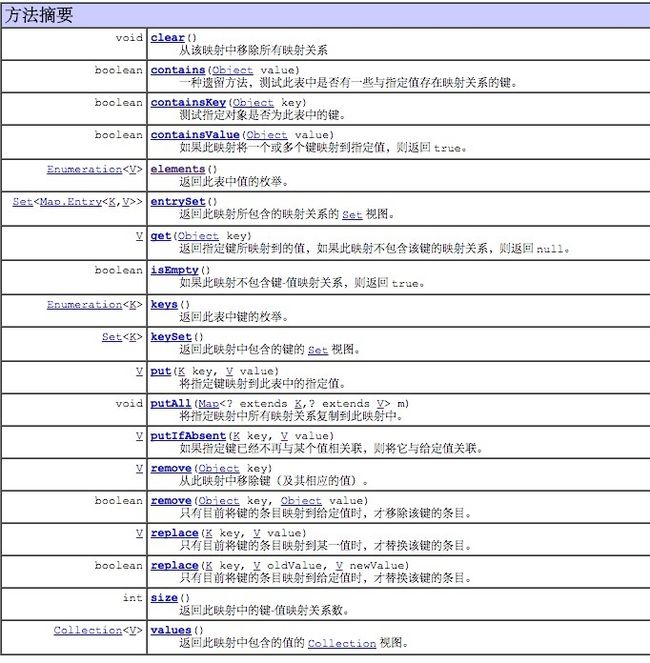
2:ConcurrentHashMap的主要方法(本文JDK1.8)
主要方法如下图:
1:put方法,此方法是同步的
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
//这里做了NPE判断 hashmap是没有NPE判断的
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
//这边加了一个循环,就是不断的尝试,因为在table的初始化和casTabAt用到了compareAndSwapInt、compareAndSwapObject
//因为如果其他线程正在修改tab,那么尝试就会失败,所以这边要加一个for循环,不断的尝试
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) { //put方法里面实现了synchronized同步,注意在jdk1.8之前一直使用的是lock锁
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);//转化为红黑树
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
2:clear方法
public void clear() {
long delta = 0L; // negative number of deletions
int i = 0;
Node[] tab = table;
while (tab != null && i < tab.length) {
int fh;
Node f = tabAt(tab, i);
if (f == null)
++i;
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) {
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
i = 0; // restart
}
else {
synchronized (f) {//同步
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node p = (fh >= 0 ? f :
(f instanceof TreeBin) ?
((TreeBin)f).first : null);
while (p != null) {
--delta;
p = p.next;
}
setTabAt(tab, i++, null);
}
}
}
}
if (delta != 0L)
addCount(delta, -1);
}
3:remove
public V remove(Object key) {
return replaceNode(key, null, null);
}
/**
* Implementation for the four public remove/replace methods:
* Replaces node value with v, conditional upon match of cv if
* non-null. If resulting value is null, delete.
*/
final V replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv) {
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
(f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null)
break;
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
boolean validated = false;
synchronized (f) { //同步
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
validated = true;
for (Node e = f, pred = null;;) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
V ev = e.val;
if (cv == null || cv == ev ||
(ev != null && cv.equals(ev))) {
oldVal = ev;
if (value != null)
e.val = value;
else if (pred != null)
pred.next = e.next;
else
setTabAt(tab, i, e.next);
}
break;
}
pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null)
break;
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
validated = true;
TreeBin t = (TreeBin)f;
TreeNode r, p;
if ((r = t.root) != null &&
(p = r.findTreeNode(hash, key, null)) != null) {
V pv = p.val;
if (cv == null || cv == pv ||
(pv != null && cv.equals(pv))) {
oldVal = pv;
if (value != null)
p.val = value;
else if (t.removeTreeNode(p))
setTabAt(tab, i, untreeify(t.first));
}
}
}
}
}
if (validated) {
if (oldVal != null) {
if (value == null)
addCount(-1L, -1);
return oldVal;
}
break;
}
}
}
return null;
}
4:get
get方法并没有同步,因此也不会和put方法冲突,当多个线程同时操作该map时,有的线程get,有的线程put,因为我们并不确定put方法执行完了没(即是否写了内存),所以get不一定能够得到最新值(put还没写进去,叫最新值也不是很妥当)。但是,一旦put操作执行完,那么get一定可以感知到最新值
public V get(Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
5:size方法也没有同步,存在和get方法同样的问题
public int size() {
long n = sumCount();
return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :
(int)n);
}
3:ConcurrentHashMap的特点和结构
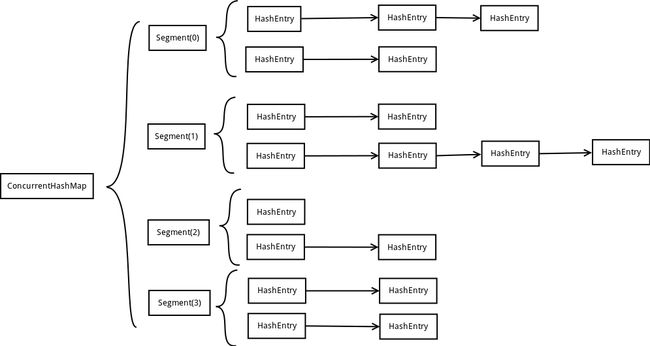
a:ConcurrentHashMap是一个线程安全的HashTable,它的主要功能是提供了一组和HashTable功能相同但是线程安全的方法。ConcurrentHashMap可以做到读取数据不加锁,并且其内部的结构可以让其在进行写操作的时候能够将锁的粒度保持地尽量地小,不用对整个ConcurrentHashMap加锁。
b:ConcurrentHashMap为了提高本身的并发能力,在内部采用了一个叫做Segment的结构,一个Segment其实就是一个类Hash Table的结构,Segment内部维护了一个链表数组.
我们用下面这一幅图来看下ConcurrentHashMap的内部结构(网上流传的)
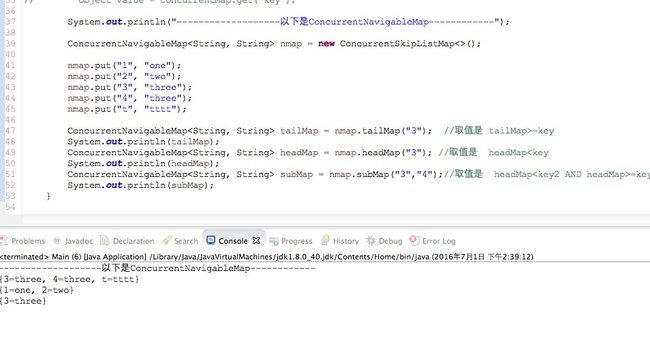
4:ConcurrentNavigableMap(jdk1.6以后新增的)
ConcurrentNavigableMap 是一个支持并发访问的 java.util.NavigableMap,它还能让它的子 map 具备并发访问的能力。所谓的 "子 map" 指的是诸如 headMap(),subMap(),tailMap() 之类的方法返回的 map。
NavigableMap 中的方法不再赘述,本小节我们来看一下 ConcurrentNavigableMap 添加的方法。
1:headMap()
headMap(T toKey) 方法返回一个包含了小于给定 toKey 的 key 的子 map。
2:tailMap()
tailMap(T fromKey) 方法返回一个包含了不小于给定 fromKey 的 key 的子 map。
3:subMap()
subMap() 方法返回原始 map 中,键介于 from(包含) 和 to (不包含) 之间的子 map
一张图看懂(关于这些方法更多信息参考官方 Java 文档)