Redis淘汰机制
前言
正好最近工作上把C和C++捡回来一些,顺便跟着源码看看Redis的过期策略与内存淘汰机制。整理了下几篇文章,转载from:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/8aa619933ebb
https://blog.csdn.net/asdfsadfasdfsa/article/details/88339060
https://www.jb51.net/article/147115.htm
1、Redis过期策略
Redis过期策略包括三种,定时过期,惰性过期以及定期过期:
- 定时过期:每个设置过期时间的key都需要创建一个定时器,到过期时间就会立即清除。该策略可以立即清除过期的数据,对内存很友好;但是会占用大量的CPU资源去处理过期的数据,从而影响缓存的响应时间和吞吐量。
- 惰性过期:只有当访问一个key时,才会判断该key是否已过期,过期则清除。该策略可以最大化地节省CPU资源,却对内存非常不友好。极端情况可能出现大量的过期key没有再次被访问,从而不会被清除,占用大量内存。
- 定期过期:每隔一定的时间,会扫描一定数量的数据库的expires字典中一定数量的key,并清除其中已过期的key。该策略是前两者的一个折中方案。通过调整定时扫描的时间间隔和每次扫描的限定耗时,可以在不同情况下使得CPU和内存资源达到最优的平衡效果。
(expires字典会保存所有设置了过期时间的key的过期时间数据,其中,key是指向键空间中的某个键的指针,value是该键的毫秒精度的UNIX时间戳表示的过期时间。键空间是指该Redis集群中保存的所有键。)
这里首先看下redis内部的存储结构:
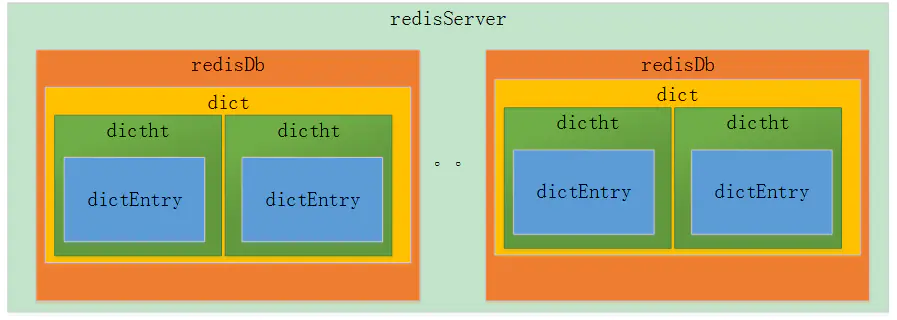 redis的存储结构从外层往内层依次是redisDb、dict、dictht、dictEntry,前面的就不关注了,我们从 dictEntry开始看:
redis的存储结构从外层往内层依次是redisDb、dict、dictht、dictEntry,前面的就不关注了,我们从 dictEntry开始看:
/*
* 哈希表
*
* 每个字典都使用两个哈希表,从而实现渐进式 rehash 。
*/
typedef struct dictht {
// 哈希表数组
dictEntry **table;
// 哈希表大小
unsigned long size;
// 哈希表大小掩码,用于计算索引值
// 总是等于 size - 1
unsigned long sizemask;
// 该哈希表已有节点的数量
unsigned long used;
} dictht;dictEntry **table可以理解为hash的桶,通过挂链法解决冲突,而桶中的元素就是redis的基本存储单元:
/*
* 哈希表节点
*/
typedef struct set {
// 键
void *key;
// 值
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
} v;
// 指向下个哈希表节点,形成链表
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;这里是不是很像hashmap,数据加链表的结构,事实上原理也差不多,在set时,根据key定位到对应的桶,然后挂接在头部,jdk1.8后hashmap也是选择头插,这里数据的插入源码就不看了,跟hashmap还挺像的;
这里只看过期策略的实现,redis的过期事件存储在db->expires的对象当中,redis 会将每个设置了过期时间的 key 放入到一个独立的字典中,以后会定时遍历这个字典来删除到期的 key。除了定时遍历之外,它还会使用惰性策略来删除过期的 key,所谓惰性策略就是在客户端访问这个 key 的时候,redis 对 key 的过期时间进行检查,如果过期了就立即删除。定时删除是集中处理,惰性删除是零散处理。
代码段 小部件
这里的setExpire方法只是设置了过期时间,具体的过期策略如下:
1.1 惰性删除
//db.c
/* 判断键key是否已过期,如果过期将其从数据库中删除 */
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* 获取键的过期时间*/
mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
mstime_t now;
/* 该键没有设置过期时间 */
if (when < 0) return 0; /* No expire for this key */
/* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */
if (server.loading) return 0;
/* 获取当前时间,lua脚本相关 */
now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime();
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return now > when;
/* 当前时间小于过期时间,该键没有过期,不需要删除 */
if (now <= when) return 0;
/* 执行到这里,说明这个键已过期,需要删除 */
/* 过期键数量加一 */
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
propagateExpire(db,key);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",key,db->id);
/* 从数据字典和时间字典中删除(即从数据库中删除,因为该键在两个字典中,所以需要删除两个) */
return dbDelete(db,key);
}
惰性删除即只在读这个键时判断是否过期,很明显,这种方式可能会有大量的过期key未删除。
1.2 周期删除
//server.c
/* 随机选择若干键节点判断其是否过期,如果过期将其删除 */
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
...
while (num--) {
dictEntry *de;
long long ttl;
/* 在时间字典中随机选择一个键节点 */
if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
/* 获取键节点的值,即过期时间 */
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)-now;
/* 判断是否过期,如果过期,删除 */
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
if (ttl > 0) {
/* We want the average TTL of keys yet not expired. */
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
}
...
}
通过随机选取节点的方式来清理内存,如果过期,则删除,这里的删除方式跟惰性删除中调用字典删除API的方式不同,其代码如下:
//server.c
/*
* 判断键节点是否过期,如果过期将其从数据库中删除
* db : 数据库
* de : 键节点
* now : 当前时间
*/
int activeExpireCycleTryExpire(redisDb *db, dictEntry *de, long long now) {
/* 获取键的过期时间 */
long long t = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
/* 判断是否过期 */
if (now > t) {
/* 从键节点中取出键 */
sds key = dictGetKey(de);
/* 因为Redis中键默认都是sds存储的,所以这里需要将其转化为robj*格式以满足函数传参 */
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(key,sdslen(key));
propagateExpire(db,keyobj);
/* 将键和其对应的值从数据库中删除 */
dbDelete(db,keyobj);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",keyobj,db->id);
/* 键的引用计数减一,因为是刚创建的,所以引用计数就是1,这里会将keyobj对象删除 */
decrRefCount(keyobj);
/* 过期键个数加一 */
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
1.3 定时删除
通过设置定时器来完成定时删除,在设置键的过期时间的同时,创建一个定时器( timer ). 让定时器在键的过期时间来临时,立即执行对键的删除操作,时间一到就调用回调函数删除键值对~~~
2、Redis内存淘汰过程
processCommand是Redis内存数据淘汰的核心实现:
int processCommand(redisClient *c) {
/* Handle the maxmemory directive.
*
* First we try to free some memory if possible (if there are volatile
* keys in the dataset). If there are not the only thing we can do
* is returning an error. */
// 如果设置了最大内存,那么检查内存是否超过限制,并做相应的操作
if (server.maxmemory) {
// 如果内存已超过限制,那么尝试通过删除过期键来释放内存
int retval = freeMemoryIfNeeded();
// 如果即将要执行的命令可能占用大量内存(REDIS_CMD_DENYOOM)
// 并且前面的内存释放失败的话
// 那么向客户端返回内存错误
if ((c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_DENYOOM) && retval == REDIS_ERR) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.oomerr);
return REDIS_OK;
}
}这里重点看freeMemoryIfNeeded()方法:
int freeMemoryIfNeeded(void) {
/* Compute how much memory we need to free. */
// 计算需要释放多少字节的内存
mem_tofree = mem_used - server.maxmemory;
// 初始化已释放内存的字节数为 0
mem_freed = 0;
// 根据 maxmemory 策略,
// 遍历字典,释放内存并记录被释放内存的字节数
while (mem_freed < mem_tofree) {
int j, k, keys_freed = 0;
// 遍历所有字典
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
long bestval = 0; /* just to prevent warning */
sds bestkey = NULL;
dictEntry *de;
redisDb *db = server.db+j;
dict *dict;
if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU ||
server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM)
{
// 如果策略是 allkeys-lru 或者 allkeys-random
// 那么淘汰的目标为所有数据库键
dict = server.db[j].dict;
} else {
// 如果策略是 volatile-lru 、 volatile-random 或者 volatile-ttl
// 那么淘汰的目标为带过期时间的数据库键
dict = server.db[j].expires;
}
// 跳过空字典
if (dictSize(dict) == 0) continue;
/* volatile-random and allkeys-random policy */
// 如果使用的是随机策略,那么从目标字典中随机选出键
if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM ||
server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM)
{
de = dictGetRandomKey(dict);
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
}
/* volatile-lru and allkeys-lru policy */
// 如果使用的是 LRU 策略,
// 那么从一集 sample 键中选出 IDLE 时间最长的那个键
else if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU ||
server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU)
{
struct evictionPoolEntry *pool = db->eviction_pool;
while(bestkey == NULL) {
evictionPoolPopulate(dict, db->dict, db->eviction_pool);
/* Go backward from best to worst element to evict. */
for (k = REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (pool[k].key == NULL) continue;
de = dictFind(dict,pool[k].key);
/* Remove the entry from the pool. */
sdsfree(pool[k].key);
/* Shift all elements on its right to left. */
memmove(pool+k,pool+k+1,
sizeof(pool[0])*(REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-k-1));
/* Clear the element on the right which is empty
* since we shifted one position to the left. */
pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key = NULL;
pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].idle = 0;
/* If the key exists, is our pick. Otherwise it is
* a ghost and we need to try the next element. */
if (de) {
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
break;
} else {
/* Ghost... */
continue;
}
}
}
}
/* volatile-ttl */
// 策略为 volatile-ttl ,从一集 sample 键中选出过期时间距离当前时间最接近的键
else if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
for (k = 0; k < server.maxmemory_samples; k++) {
sds thiskey;
long thisval;
de = dictGetRandomKey(dict);
thiskey = dictGetKey(de);
thisval = (long) dictGetVal(de);
/* Expire sooner (minor expire unix timestamp) is better
* candidate for deletion */
if (bestkey == NULL || thisval < bestval) {
bestkey = thiskey;
bestval = thisval;
}
}
}
/* Finally remove the selected key. */
// 删除被选中的键
if (bestkey) {
long long delta;
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(bestkey,sdslen(bestkey));
propagateExpire(db,keyobj);
/* We compute the amount of memory freed by dbDelete() alone.
* It is possible that actually the memory needed to propagate
* the DEL in AOF and replication link is greater than the one
* we are freeing removing the key, but we can't account for
* that otherwise we would never exit the loop.
*
* AOF and Output buffer memory will be freed eventually so
* we only care about memory used by the key space. */
// 计算删除键所释放的内存数量
delta = (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
dbDelete(db,keyobj);
delta -= (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
mem_freed += delta;
// 对淘汰键的计数器增一
server.stat_evictedkeys++;
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_EVICTED, "evicted",
keyobj, db->id);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
keys_freed++;
/* When the memory to free starts to be big enough, we may
* start spending so much time here that is impossible to
* deliver data to the slaves fast enough, so we force the
* transmission here inside the loop. */
if (slaves) flushSlavesOutputBuffers();
}
}
if (!keys_freed) return REDIS_ERR; /* nothing to free... */
}
return REDIS_OK;
}2.1 随机淘汰
随机淘汰的场景下获取待删除key的策略,随机找hash桶再次hash指定位置的dictEntry即可。
就是在场景REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM和REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU情况下的待淘汰的key。
/*
* 随机返回字典中任意一个节点。
*
* 可用于实现随机化算法。
*
* 如果字典为空,返回 NULL 。
*
* T = O(N)
*/
dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d)
{
dictEntry *he, *orighe;
unsigned int h;
int listlen, listele;
// 字典为空
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;
// 进行单步 rehash
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 如果正在 rehash ,那么将 1 号哈希表也作为随机查找的目标
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) {
// T = O(N)
do {
h = random() % (d->ht[0].size+d->ht[1].size);
he = (h >= d->ht[0].size) ? d->ht[1].table[h - d->ht[0].size] :
d->ht[0].table[h];
} while(he == NULL);
// 否则,只从 0 号哈希表中查找节点
} else {
// T = O(N)
do {
h = random() & d->ht[0].sizemask;
he = d->ht[0].table[h];
} while(he == NULL);
}
/* Now we found a non empty bucket, but it is a linked
* list and we need to get a random element from the list.
* The only sane way to do so is counting the elements and
* select a random index. */
// 目前 he 已经指向一个非空的节点链表
// 程序将从这个链表随机返回一个节点
listlen = 0;
orighe = he;
// 计算节点数量, T = O(1)
while(he) {
he = he->next;
listlen++;
}
// 取模,得出随机节点的索引
listele = random() % listlen;
he = orighe;
// 按索引查找节点
// T = O(1)
while(listele--) he = he->next;
// 返回随机节点
return he;
}2.2 LRU 策略
LRU 策略淘汰思路如下:
- dictGetRandomKeys随机获取指定数目的dictEntry。
- 将获取的的dictEntry进行下sort按照最近时间进行排序。
- 选择最近使用时间最久远的数据进行过期
- 每次过期的数据其实是采样的结果数据中的最近未被访问数据而非全局的。
void evictionPoolPopulate(dict *sampledict, dict *keydict, struct evictionPoolEntry *pool) {
int j, k, count;
dictEntry *_samples[EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE];
dictEntry **samples;
/* Try to use a static buffer: this function is a big hit...
* Note: it was actually measured that this helps. */
if (server.maxmemory_samples <= EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE) {
samples = _samples;
} else {
samples = zmalloc(sizeof(samples[0])*server.maxmemory_samples);
}
#if 1 /* Use bulk get by default. */
count = dictGetRandomKeys(sampledict,samples,server.maxmemory_samples);
#else
count = server.maxmemory_samples;
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) samples[j] = dictGetRandomKey(sampledict);
#endif
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
unsigned long long idle;
sds key;
robj *o;
dictEntry *de;
de = samples[j];
key = dictGetKey(de);
/* If the dictionary we are sampling from is not the main
* dictionary (but the expires one) we need to lookup the key
* again in the key dictionary to obtain the value object. */
if (sampledict != keydict) de = dictFind(keydict, key);
o = dictGetVal(de);
idle = estimateObjectIdleTime(o);
/* Insert the element inside the pool.
* First, find the first empty bucket or the first populated
* bucket that has an idle time smaller than our idle time. */
k = 0;
while (k < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE &&
pool[k].key &&
pool[k].idle < idle) k++;
if (k == 0 && pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key != NULL) {
/* Can't insert if the element is < the worst element we have
* and there are no empty buckets. */
continue;
} else if (k < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE && pool[k].key == NULL) {
/* Inserting into empty position. No setup needed before insert. */
} else {
/* Inserting in the middle. Now k points to the first element
* greater than the element to insert. */
if (pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-1].key == NULL) {
/* Free space on the right? Insert at k shifting
* all the elements from k to end to the right. */
memmove(pool+k+1,pool+k,
sizeof(pool[0])*(REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE-k-1));
} else {
/* No free space on right? Insert at k-1 */
k--;
/* Shift all elements on the left of k (included) to the
* left, so we discard the element with smaller idle time. */
sdsfree(pool[0].key);
memmove(pool,pool+1,sizeof(pool[0])*k);
}
}
pool[k].key = sdsdup(key);
pool[k].idle = idle;
}
if (samples != _samples) zfree(samples);
}通过random() & d->ht[j].sizemask方法随机获取从某个hash桶开始随机获取dictEntry。获取的待淘汰的数据通过count进行指定。
int dictGetRandomKeys(dict *d, dictEntry **des, int count) {
int j; /* internal hash table id, 0 or 1. */
int stored = 0;
if (dictSize(d) < count) count = dictSize(d);
while(stored < count) {
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
/* Pick a random point inside the hash table 0 or 1. */
unsigned int i = random() & d->ht[j].sizemask;
int size = d->ht[j].size;
/* Make sure to visit every bucket by iterating 'size' times. */
while(size--) {
dictEntry *he = d->ht[j].table[i];
while (he) {
/* Collect all the elements of the buckets found non
* empty while iterating. */
*des = he;
des++;
he = he->next;
stored++;
if (stored == count) return stored;
}
i = (i+1) & d->ht[j].sizemask;
}
/* If there is only one table and we iterated it all, we should
* already have 'count' elements. Assert this condition. */
assert(dictIsRehashing(d) != 0);
}
}
return stored; /* Never reached. */
}2.3 TTL时间淘汰
TTL时间淘汰策略跟随机策略很像,唯一的区别就是TTL时间淘汰基于采样结果进行选择然后选择距离过期时间最近的数据进行过期,所以他理论上结合了采样+TTL时间计算进行数据淘汰的。
for (k = 0; k < server.maxmemory_samples; k++) {
sds thiskey;
long thisval;
de = dictGetRandomKey(dict);
thiskey = dictGetKey(de);
thisval = (long) dictGetVal(de);
/* Expire sooner (minor expire unix timestamp) is better
* candidate for deletion */
if (bestkey == NULL || thisval < bestval) {
bestkey = thiskey;
bestval = thisval;
}
}