Logistic回归思想:根据现有数据对分类边界线建立回归公式,一次进行分类。寻找最佳拟合参数,使用的是最优化算法。
Sigmoid函数具体的计算公式如下:
import numpy as np
#Logistic回归梯度上升优化算法
def loadDataSet():
dataMat=[]
labelMat=[]
fr=open('testSet.txt')
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr=line.strip().split()
# 为了方便计算,我们将 X0 的值设为 1.0 ,也就是在每一行的开头添加一个 1.0 作为 X0
dataMat.append([1.0,float(lineArr[0]),float(lineArr[1])])
labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2]))
return dataMat,labelMat
#定义sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-inX))
#输入数据特征与数据的类别标签
#返回最佳回归系数(weights)
def gradAscent(dataMatIn,classLabels):
# 转换为numpy型
dataMatrix=np.mat(dataMatIn)
# 转化为矩阵[[0,1,0,1,0,1.....]],并转制[[0],[1],[0].....]
# transpose() 行列转置函数,将行向量转化为列向量
labelMat=np.mat(classLabels).transpose()
# m->数据量,样本数 n->特征数
m,n=np.shape(dataMatrix)
# 步长
alpha=0.001
# 迭代次数
maxCycles=500
# 初始化权值向量,每个维度均为1.0
weights=np.ones((n,1))
for k in range(maxCycles):
# 回归系数与数据向量相乘带入Sigmoid函数中,得到h,注意h是向量
h=sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights)
# 误差为标记值(labelMat)-预测值(h)
error=(labelMat-h)
weights=weights+alpha*dataMatrix.transpose()*error
return weights
#输出函数:
import logRegres
dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet()
print(logRegres.gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat))
输出:
[[ 4.12414349]
[ 0.48007329]
[-0.6168482 ]]
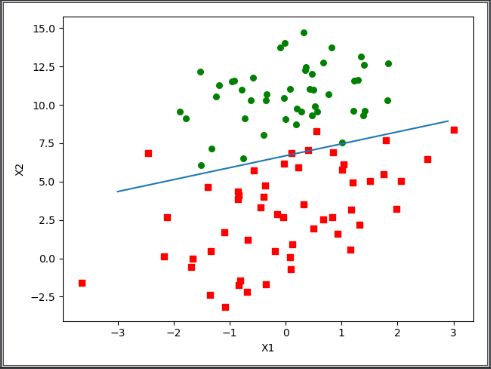
分析数据:画出决策边界
#画出数据集和Logistic回归最佳拟合直线的函数
def plotBestFit(weights):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 得数据矩阵,标签向量
dataMat,labelMat=loadDataSet()
# 将dataMat转换为array
dataArr=np.array(dataMat)
# 得dataArr行数
n=np.shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1=[]
ycord1=[]
xcord2=[]
ycord2=[]
for i in range(n):
# 标签为1
if int(labelMat[i]==1):
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1])
ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2])
# 标签为0
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1])
ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2])
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(111)
# red square红方块
ax.scatter(xcord1,ycord1,s=30,c='red',marker='s')
# 绿圆点
ax.scatter(xcord2,ycord2,s=30,c='green')
# 在[-3.0,3.0]区间里以0.1的步长取数,得列表
x=np.arange(-3.0,3.0,0.1)
# 直线方程:weights[0] + weights[1] * x + weights[2] * 2 = 0
y=(-weights[0]-weights[1]*x)/weights[2]
ax.plot(x,y)
plt.xlabel('X1')
plt.ylabel('X2')
plt.show()
#输出结果:
weights=logRegres.gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat)
print(logRegres.plotBestFit(weights.getA()))
输出:
训练算法:随机梯度上升
#随机梯度上升算法
#输入:无,输出:优化后的权重向量
def stocGradAscent0(dataMatrix,classLabels):
# 得dataMatrix的行数、列数
m,n=np.shape(dataMatrix)
# 步长
alpha=0.01
# n阶权重向量
weights=np.ones(n)
for i in range(m):
h=sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[i]*weights))
error=classLabels[i]-h
weights=weights+alpha*error*dataMatrix[i]
return weights
#输出结果
weights=logRegres.stocGradAscent0(array(dataArr),labelMat)
print(logRegres.plotBestFit(weights))
输出:
改进的随机梯度上升算法
#改进的随机梯度上升算法
def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix,classLables,numIter=150):
m,n=np.shape(dataMatrix)
weights=np.ones(n)
for j in range(numIter):
dataIndex=list(range(m))
for i in range(m):
# 使得步长随着迭代的进行而逐渐减小
alpha=4/(1.0+j+i)+0.01
# 随机取第randIndex行的dataMatrix
import random
randIndex=int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))
h=sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weights))
error=classLables[randIndex]-h
weights=weights+alpha*error*dataMatrix[randIndex]
# 删除第randIndex行,不参与迭代
del(dataIndex[randIndex])
return weights
输出:
机器学习第五章示例:从疝气病症预测病马的死亡率
准备数据
数据缺失可选的做法:
测试算法:用Logistic回归进行分类
#Logistic回归分类函数
#功能:预测类别标签
#输入:特征向量,回归系数,输出:预测的类别标签
def classifyVector(inX,weights):
prob=sigmoid(sum(inX*weights))
if prob>0.5:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
def colicTest():
frTrain=open('horseColicTraining.txt')
frTest=open('horseColicTest.txt')
trainingSet=[]
trainingLabels=[]
for line in frTrain.readlines():
# strip()表示删除空白符,split()表示分割
currLine=line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr=[]
for i in range(21):
# 将这个属性放入lineArr
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
# 属性集
trainingSet.append(lineArr)
# 标签集
trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21]))
trainWeights=stocGradAscent1(np.array(trainingSet),trainingLabels,500)
errorCount=0
numTestVec=0.0
for line in frTest.readlines():
numTestVec+=1.0
# strip()表示删除空白符,split()表示分割
currLine=line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr=[]
for i in range(21):
# 将这个属性放入lineArr
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
# 预测标签和验证标签不一致
if int(classifyVector(np.array(lineArr),trainWeights)!=int(currLine[21])):
errorCount+=1
errorRate=(float(errorCount)/numTestVec)
print("the error rate of this test is :%f" % errorRate)
return errorRate
def multiTest():
numTests=10
errorSum=0.0
for k in range(numTests):
errorSum += colicTest()
print("after %d iterations the average error rate is : %f" % (numTests,errorSum/float(numTests)))
输出:
the error rate of this test is :0.298507
the error rate of this test is :0.358209
the error rate of this test is :0.328358
the error rate of this test is :0.447761
the error rate of this test is :0.373134
the error rate of this test is :0.313433
the error rate of this test is :0.388060
the error rate of this test is :0.343284
the error rate of this test is :0.358209
the error rate of this test is :0.432836
after 10 iterations the average error rate is : 0.364179
小结
Logistic回归的目的是寻找一个非线性函数Sigmoid的最佳拟合参数,求解过程可以由最优化算法来完成。