随机决策森林——OpenCV类CvRTrees使用实例
本文介绍:OpenCV机器学习库MLL中随机森林Random Trees的使用
参考文献:
1.Breiman, Leo (2001). "Random Forests". Machine Learning
2.Random Forests网站
不熟悉MLL的参考此文:OpenCV机器学习库MLL
OpenCV的机器学习算法都比较简单:train ——>predict
class CV_EXPORTS_W CvRTrees : public CvStatModel
{
public:
CV_WRAP CvRTrees();
virtual ~CvRTrees();
virtual bool train( const CvMat* trainData, int tflag,
const CvMat* responses, const CvMat* varIdx=0,
const CvMat* sampleIdx=0, const CvMat* varType=0,
const CvMat* missingDataMask=0,
CvRTParams params=CvRTParams() );
virtual bool train( CvMLData* data, CvRTParams params=CvRTParams() );
virtual float predict( const CvMat* sample, const CvMat* missing = 0 ) const;
virtual float predict_prob( const CvMat* sample, const CvMat* missing = 0 ) const;
CV_WRAP virtual bool train( const cv::Mat& trainData, int tflag,
const cv::Mat& responses, const cv::Mat& varIdx=cv::Mat(),
const cv::Mat& sampleIdx=cv::Mat(), const cv::Mat& varType=cv::Mat(),
const cv::Mat& missingDataMask=cv::Mat(),
CvRTParams params=CvRTParams() );
CV_WRAP virtual float predict( const cv::Mat& sample, const cv::Mat& missing = cv::Mat() ) const;
CV_WRAP virtual float predict_prob( const cv::Mat& sample, const cv::Mat& missing = cv::Mat() ) const;
CV_WRAP virtual cv::Mat getVarImportance();
CV_WRAP virtual void clear();
virtual const CvMat* get_var_importance();
virtual float get_proximity( const CvMat* sample1, const CvMat* sample2,
const CvMat* missing1 = 0, const CvMat* missing2 = 0 ) const;
virtual float calc_error( CvMLData* data, int type , std::vector* resp = 0 ); // type in {CV_TRAIN_ERROR, CV_TEST_ERROR}
virtual float get_train_error();
virtual void read( CvFileStorage* fs, CvFileNode* node );
virtual void write( CvFileStorage* fs, const char* name ) const;
CvMat* get_active_var_mask();
CvRNG* get_rng();
int get_tree_count() const;
CvForestTree* get_tree(int i) const;
protected:
virtual std::string getName() const;
virtual bool grow_forest( const CvTermCriteria term_crit );
// array of the trees of the forest
CvForestTree** trees;
CvDTreeTrainData* data;
int ntrees;
int nclasses;
double oob_error;
CvMat* var_importance;
int nsamples;
cv::RNG* rng;
CvMat* active_var_mask;
};
使用CvRTrees类,来对手写体数据作分类
// Example : random forest (tree) learning
// Author : Toby Breckon, [email protected]
// Copyright (c) 2011 School of Engineering, Cranfield University
// License : LGPL - http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html
#include // opencv general include file
#include // opencv machine learning include file
#include
using namespace cv; // OpenCV API is in the C++ "cv" namespace
/******************************************************************************/
// global definitions (for speed and ease of use)
//手写体数字识别
#define NUMBER_OF_TRAINING_SAMPLES 3823
#define ATTRIBUTES_PER_SAMPLE 64
#define NUMBER_OF_TESTING_SAMPLES 1797
#define NUMBER_OF_CLASSES 10
// N.B. classes are integer handwritten digits in range 0-9
/******************************************************************************/
// loads the sample database from file (which is a CSV text file)
int read_data_from_csv(const char* filename, Mat data, Mat classes,
int n_samples )
{
float tmp;
// if we can't read the input file then return 0
FILE* f = fopen( filename, "r" );
if( !f )
{
printf("ERROR: cannot read file %s\n", filename);
return 0; // all not OK
}
// for each sample in the file
for(int line = 0; line < n_samples; line++)
{
// for each attribute on the line in the file
for(int attribute = 0; attribute < (ATTRIBUTES_PER_SAMPLE + 1); attribute++)
{
if (attribute < 64)
{
// first 64 elements (0-63) in each line are the attributes
fscanf(f, "%f,", &tmp);
data.at(line, attribute) = tmp;
// printf("%f,", data.at(line, attribute));
}
else if (attribute == 64)
{
// attribute 65 is the class label {0 ... 9}
fscanf(f, "%f,", &tmp);
classes.at(line, 0) = tmp;
// printf("%f\n", classes.at(line, 0));
}
}
}
fclose(f);
return 1; // all OK
}
/******************************************************************************/
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
for (int i=0; i< argc; i++)
std::cout<(ATTRIBUTES_PER_SAMPLE, 0) = CV_VAR_CATEGORICAL;
double result; // value returned from a prediction
//加载训练数据集和测试数据集
if (read_data_from_csv(argv[1], training_data, training_classifications, NUMBER_OF_TRAINING_SAMPLES) &&
read_data_from_csv(argv[2], testing_data, testing_classifications, NUMBER_OF_TESTING_SAMPLES))
{
/********************************步骤1:定义初始化Random Trees的参数******************************/
float priors[] = {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}; // weights of each classification for classes
CvRTParams params = CvRTParams(25, // max depth
5, // min sample count
0, // regression accuracy: N/A here
false, // compute surrogate split, no missing data
15, // max number of categories (use sub-optimal algorithm for larger numbers)
priors, // the array of priors
false, // calculate variable importance
4, // number of variables randomly selected at node and used to find the best split(s).
100, // max number of trees in the forest
0.01f, // forrest accuracy
CV_TERMCRIT_ITER | CV_TERMCRIT_EPS // termination cirteria
);
/****************************步骤2:训练 Random Decision Forest(RDF)分类器*********************/
printf( "\nUsing training database: %s\n\n", argv[1]);
CvRTrees* rtree = new CvRTrees;
rtree->train(training_data, CV_ROW_SAMPLE, training_classifications,
Mat(), Mat(), var_type, Mat(), params);
// perform classifier testing and report results
Mat test_sample;
int correct_class = 0;
int wrong_class = 0;
int false_positives [NUMBER_OF_CLASSES] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
printf( "\nUsing testing database: %s\n\n", argv[2]);
for (int tsample = 0; tsample < NUMBER_OF_TESTING_SAMPLES; tsample++)
{
// extract a row from the testing matrix
test_sample = testing_data.row(tsample);
/********************************步骤3:预测*********************************************/
result = rtree->predict(test_sample, Mat());
printf("Testing Sample %i -> class result (digit %d)\n", tsample, (int) result);
// if the prediction and the (true) testing classification are the same
// (N.B. openCV uses a floating point decision tree implementation!)
if (fabs(result - testing_classifications.at(tsample, 0))
>= FLT_EPSILON)
{
// if they differ more than floating point error => wrong class
wrong_class++;
false_positives[(int) result]++;
}
else
{
// otherwise correct
correct_class++;
}
}
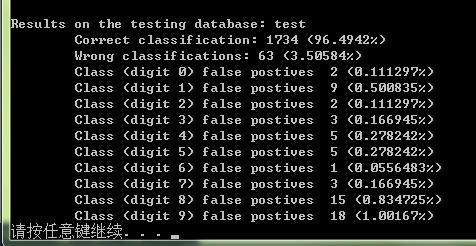
printf( "\nResults on the testing database: %s\n"
"\tCorrect classification: %d (%g%%)\n"
"\tWrong classifications: %d (%g%%)\n",
argv[2],
correct_class, (double) correct_class*100/NUMBER_OF_TESTING_SAMPLES,
wrong_class, (double) wrong_class*100/NUMBER_OF_TESTING_SAMPLES);
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_CLASSES; i++)
{
printf( "\tClass (digit %d) false postives %d (%g%%)\n", i,
false_positives[i],
(double) false_positives[i]*100/NUMBER_OF_TESTING_SAMPLES);
}
// all matrix memory free by destructors
// all OK : main returns 0
return 0;
}
// not OK : main returns -1
return -1;
}
/******************************************************************************/
设置数据集 train test:
在test数据集上的正确率: